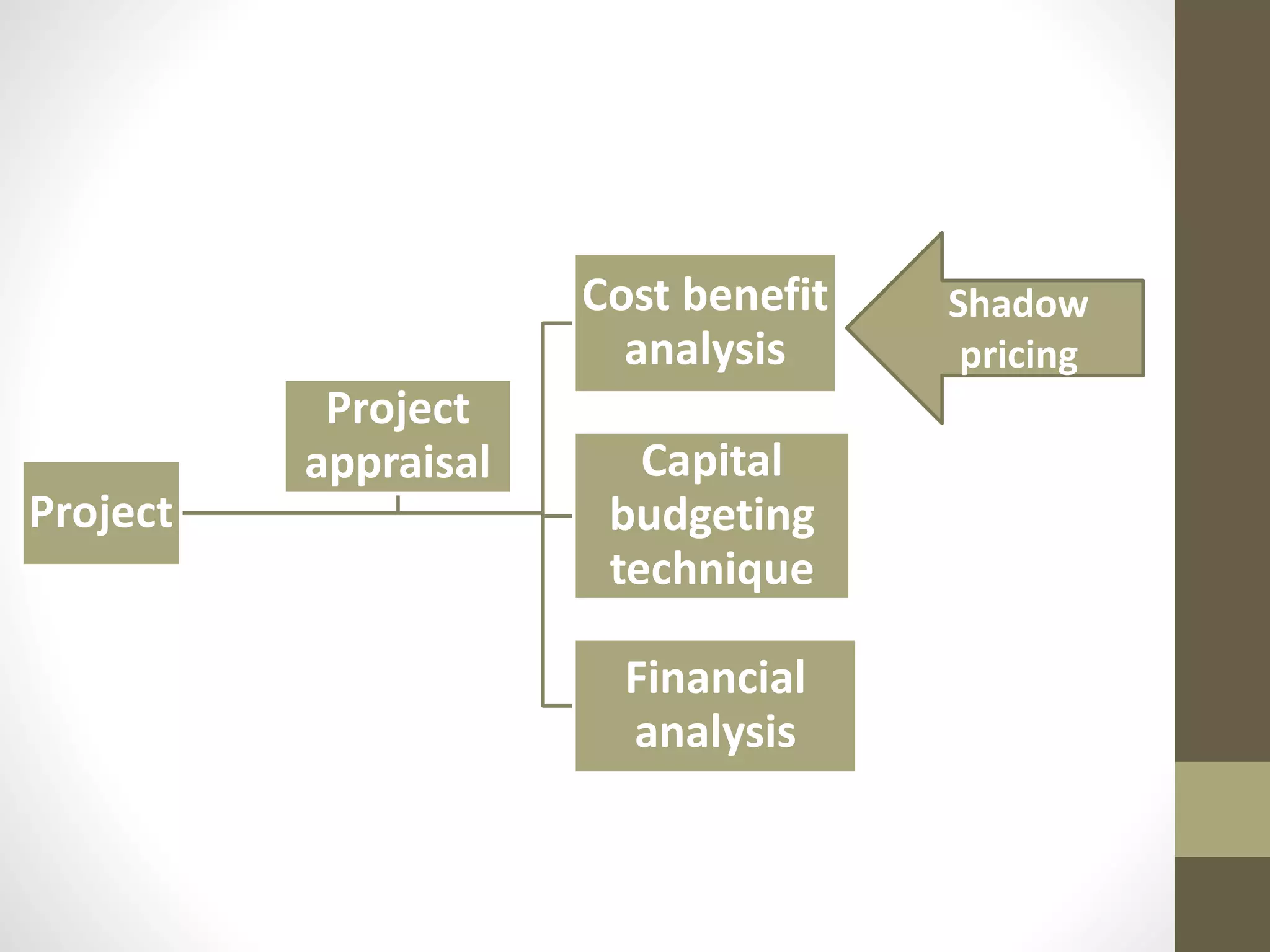
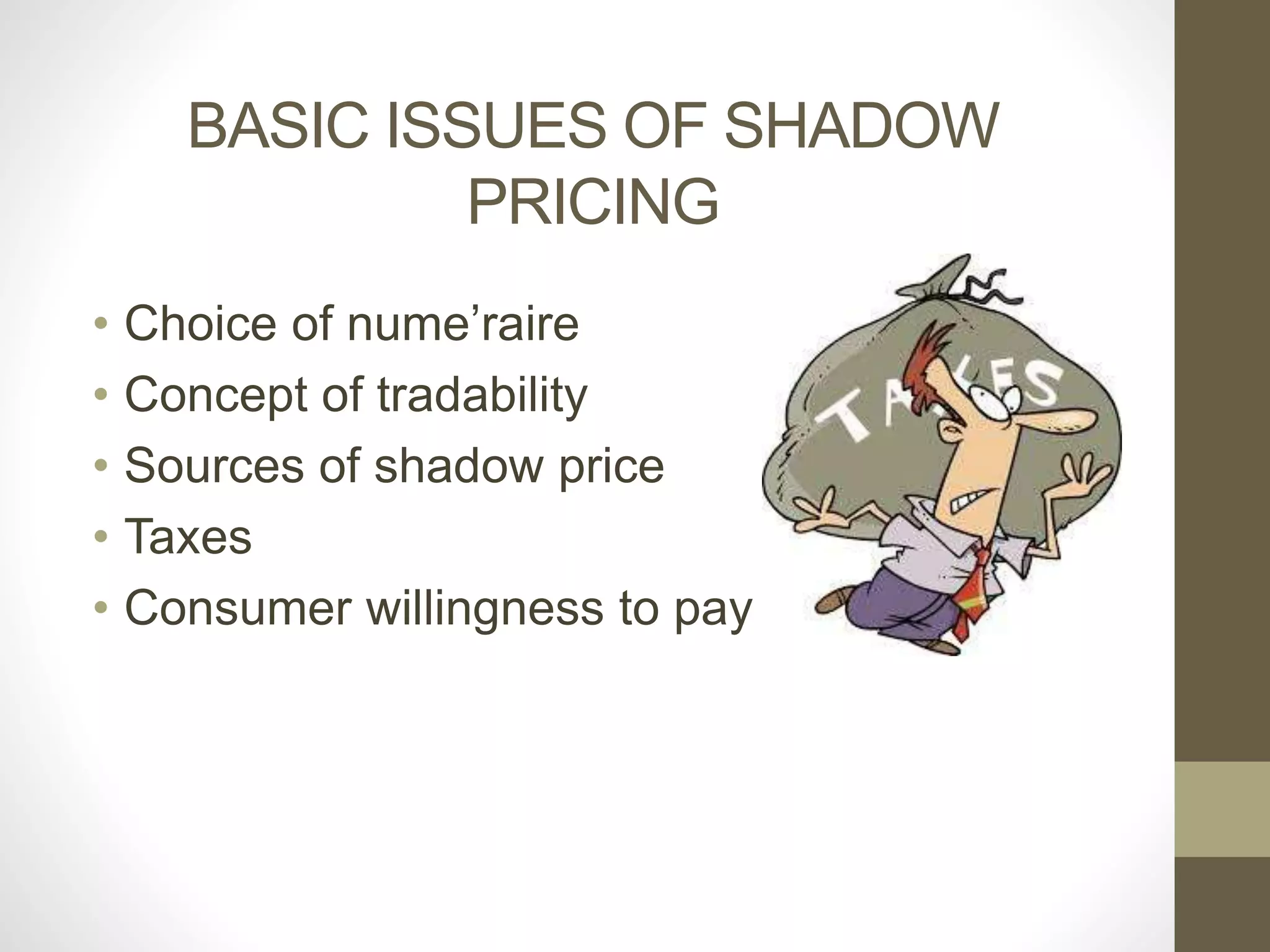
The document discusses shadow pricing, a tool used in project appraisal and capital budgeting techniques, especially in developing countries. Shadow pricing measures social costs and benefits by assigning proxy values to goods and services when market prices are distorted due to imperfect competition, underemployment, and foreign exchange restrictions. While it provides a convenient way to optimally allocate resources and consider economic opportunity costs, shadow pricing also has limitations like being based on assumptions and lacking adequate reliable data.