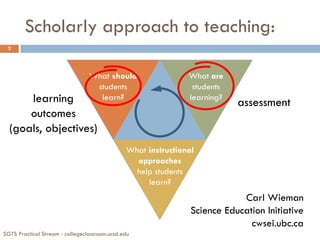
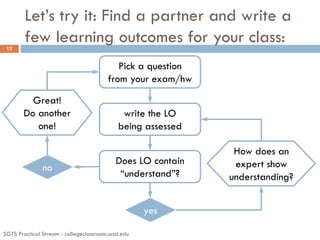
The document discusses the importance of defining clear learning outcomes in education, emphasizing their role in guiding both instructors and students. It outlines strategies for developing course-level and topic-level outcomes, utilizing Bloom's taxonomy to create effective assessments. Additionally, it encourages sharing these outcomes with students to enhance their understanding and engagement in the learning process.








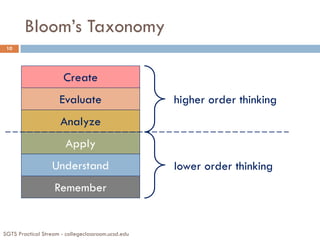


![Bloom’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain
(Levels of Learning) [Wieman, 2007]
14
6. Synthesis: transform and combine ideas to create something new
develop, create, propose, formulate, design, invent
5. Evaluation: think critically about and defend a position
judge, appraise, recommend, justify, defend, criticize, evaluate
4. Analysis: break down concepts into parts
compare, contrast, categorize, distinguish, identify, infer
3. Application: apply comprehension to unfamiliar situations
apply, demonstrate, use, compute, solve, predict, construct, modify
2. Comprehension: demonstrate understanding of ideas, concepts
describe, explain, summarize, interpret, illustrate
1. Factual Knowledge: remember and recall factual knowledge
define, list, state, label, name, describe
SGTS Practical Stream - collegeclassroom.ucsd.edu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practical3learningoutcomes-130517172055-phpapp02/85/SGTS-Practical-3-Learning-Outcomes-14-320.jpg)