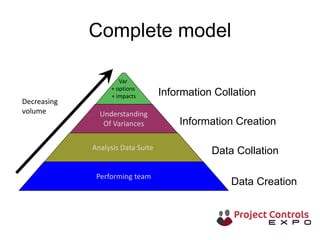
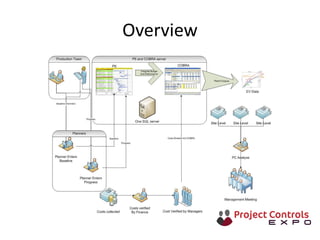
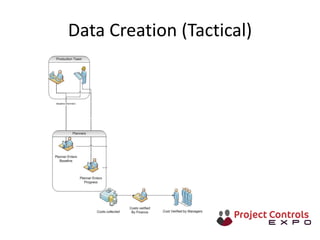
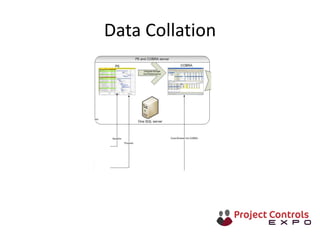
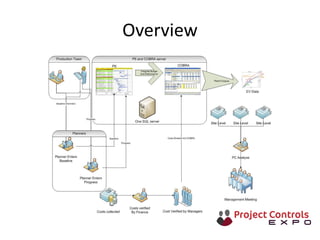
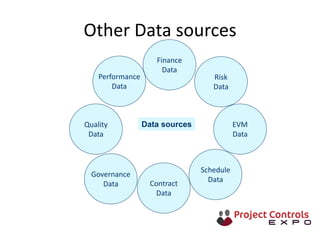
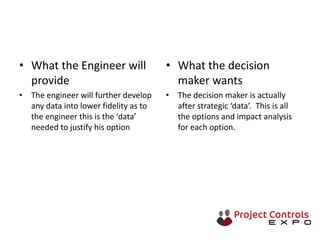
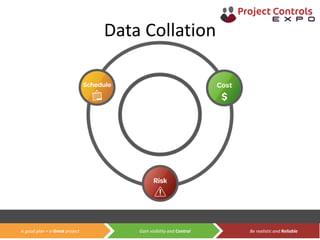
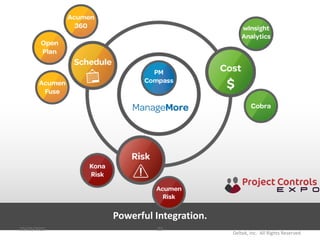
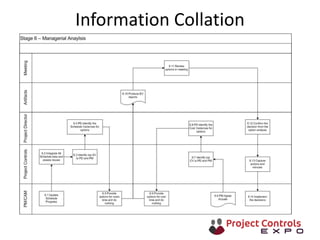
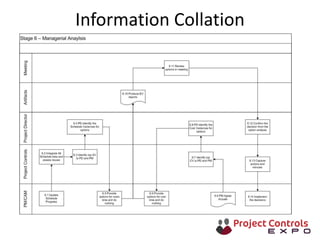
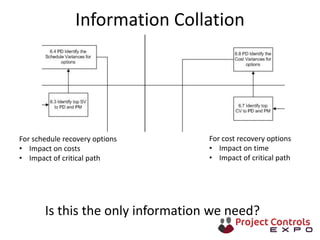
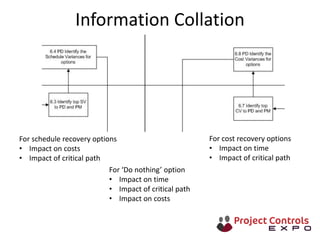
This document discusses data-driven decision making and the role of emotions in decisions. It begins by introducing the topics to be covered: data creation, collation, information creation, collation, and decision making. It then discusses how data is created tactically but decisions require strategic data on options and impacts. Information technology helps integrate and filter data. Decisions inherently involve emotions as rewards and punishments shape choices even when data and options remain constant. Presenting options with emotional impacts, like consequences of inaction, can facilitate decisions. Understanding decision-makers' emotions allows effectively framing information to guide choices. Overall, the document argues decisions stem from both objective information and subjective emotions, so both must be considered to enable well-informed