Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX
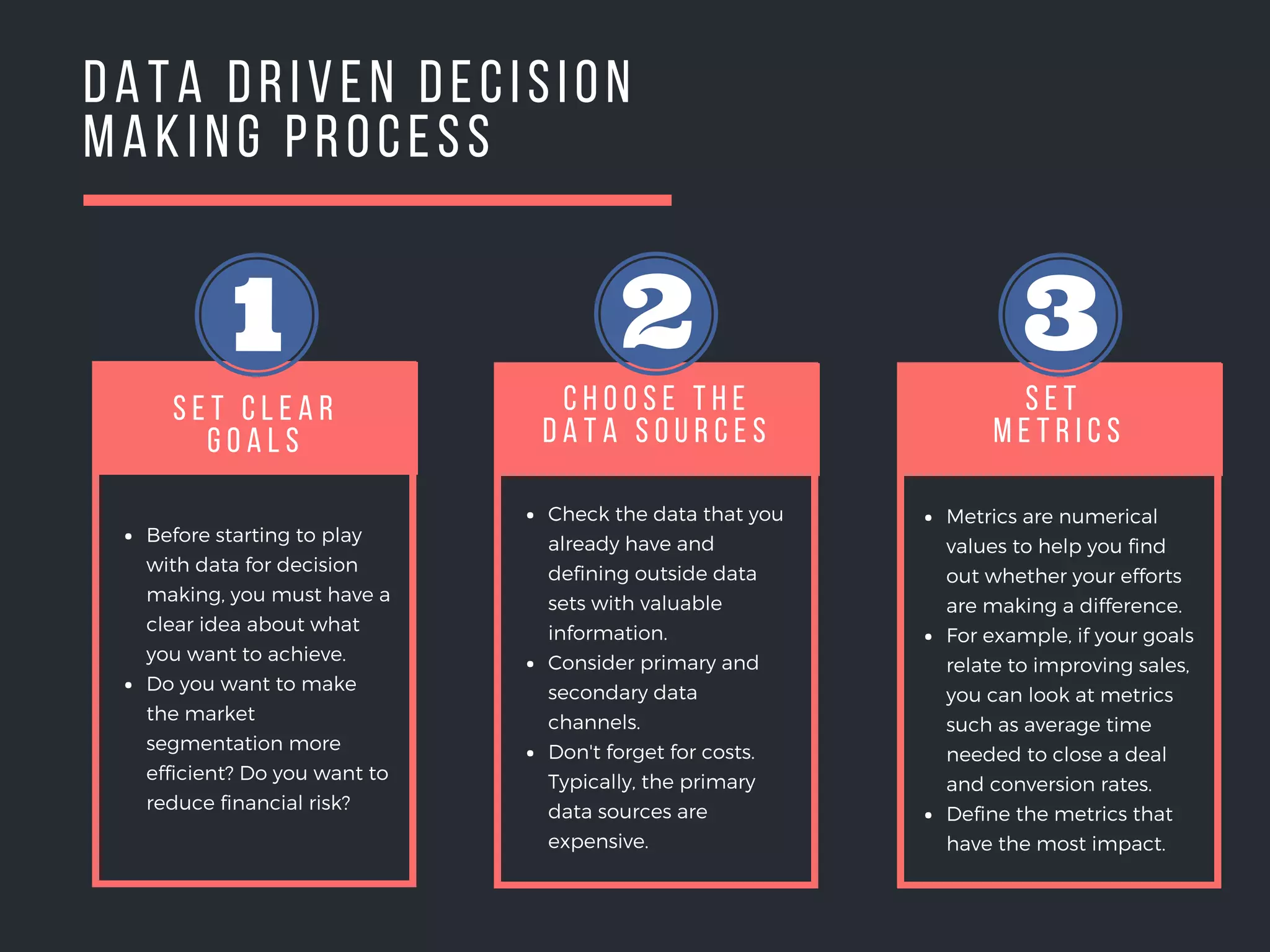
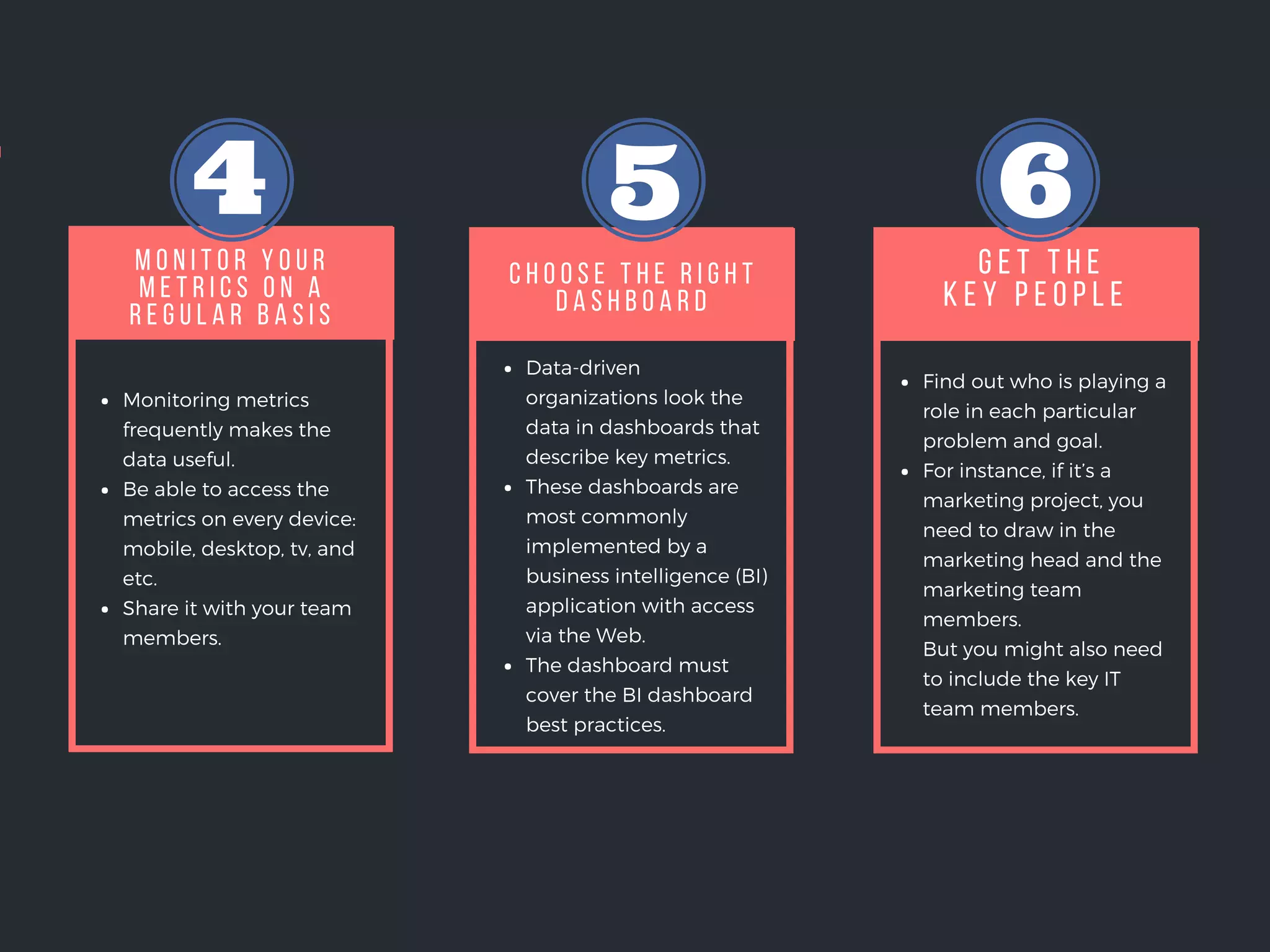

This document outlines the key steps in a data driven decision making process: 1. Set metrics to measure the impact of efforts towards goals like sales improvements. Define the most impactful metrics. 2. Choose appropriate data sources by checking available internal data and defining valuable external data. Consider costs of primary versus secondary sources. 3. Get the right people involved by including heads of relevant departments and key team members from areas like marketing and IT.


