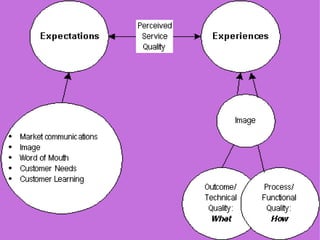
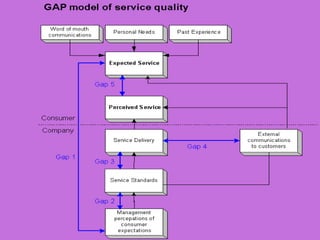
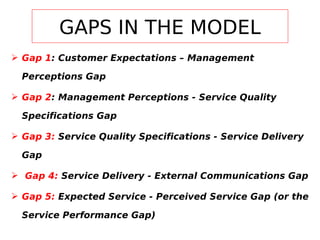
This document discusses the service quality gaps model, which identifies five key gaps that can lead to poor service quality perceptions. The five gaps are: 1) between customer expectations and management perceptions, 2) between management perceptions and service quality specifications, 3) between service quality specifications and service delivery, 4) between service delivery and external communications, and 5) between expected service and perceived service. The model provides an integrated view of the customer-company relationship and identifies factors that can contribute to each gap.