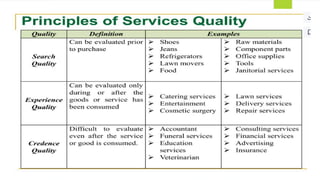
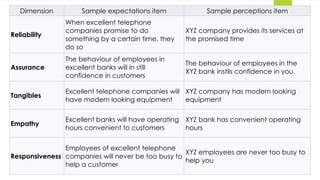
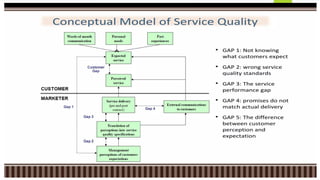
The document discusses the Servqual tool, which is a multi-dimensional instrument for measuring service quality based on consumer expectations and perceptions across five key dimensions: tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. It elaborates on the gaps model that identifies discrepancies between customer expectations and actual service delivery, detailing five specific gaps that can arise in service quality. Additionally, the document outlines potential reasons for these gaps, emphasizing the importance of understanding customer expectations and aligning service standards.