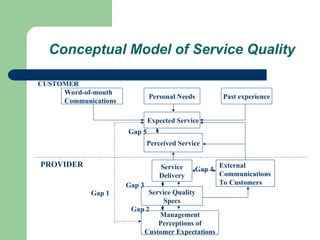
Servqual is a multi-dimensional instrument designed to evaluate consumer expectations and perceptions of service quality across five key dimensions: tangibles, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy. The model includes gaps that identify discrepancies between management perceptions and customer expectations, which assist businesses in diagnosing service quality issues. By measuring service quality through a structured questionnaire, companies can track customer perceptions over time and improve upon service delivery standards.







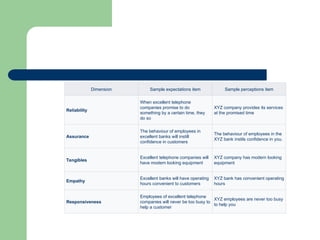

![Businesses use the SERVQUAL instrument (i.e. questionnaire) to
measure potential service quality problems and the model of
service quality to help diagnose possible causes of the problem.
The model of service quality is built on the expectancy-
confirmation paradigm which suggests that consumers perceive
quality in terms of their perceptions of how well a given service
delivery meets their expectations of that delivery.[12]
Thus, service
quality can be conceptualized as a simple equation:
SQ = P- E](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4547servqual-241010025635-d4b5b969/85/4547_servqual-ppt-service-quality-service-10-320.jpg)