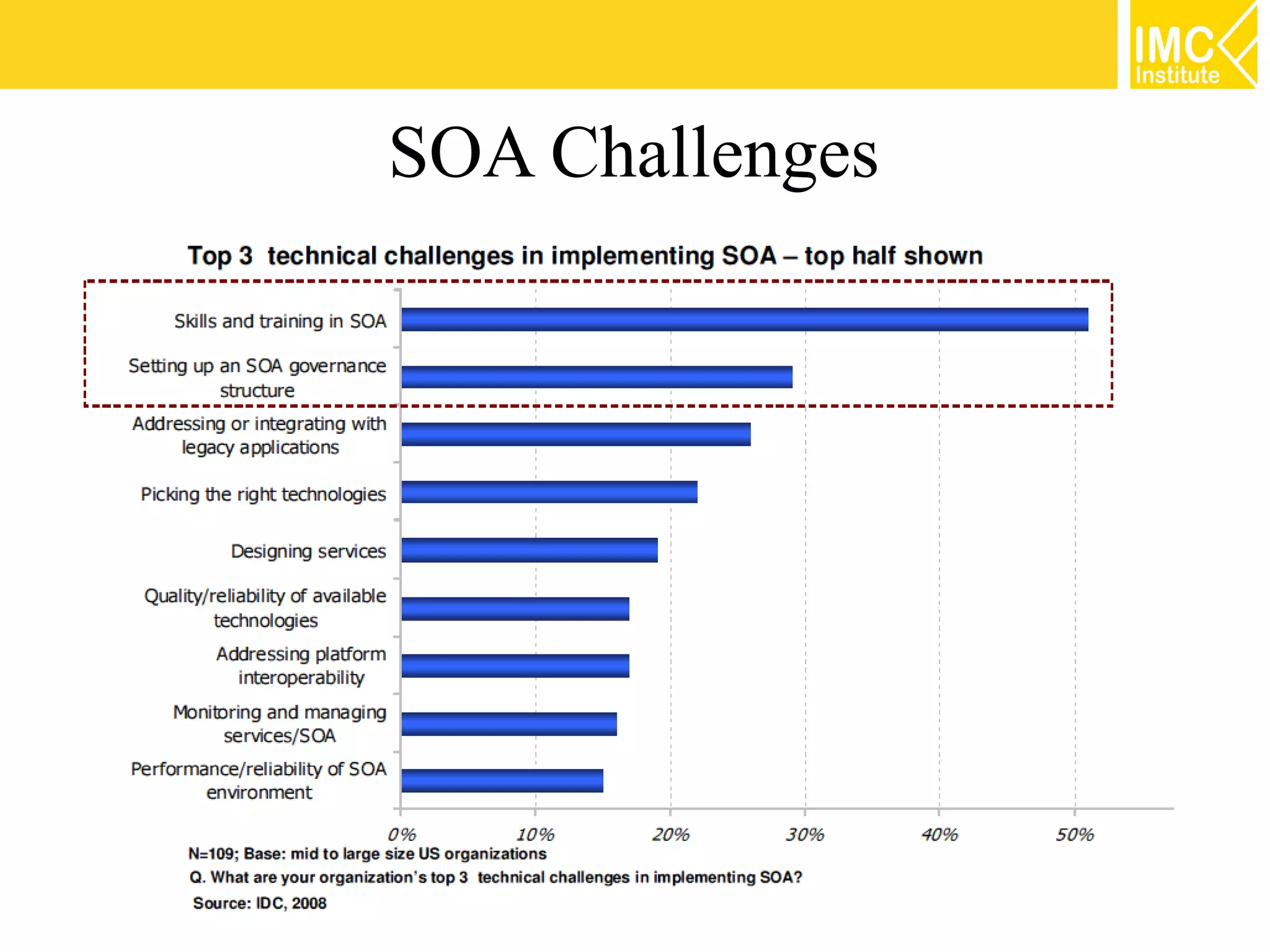
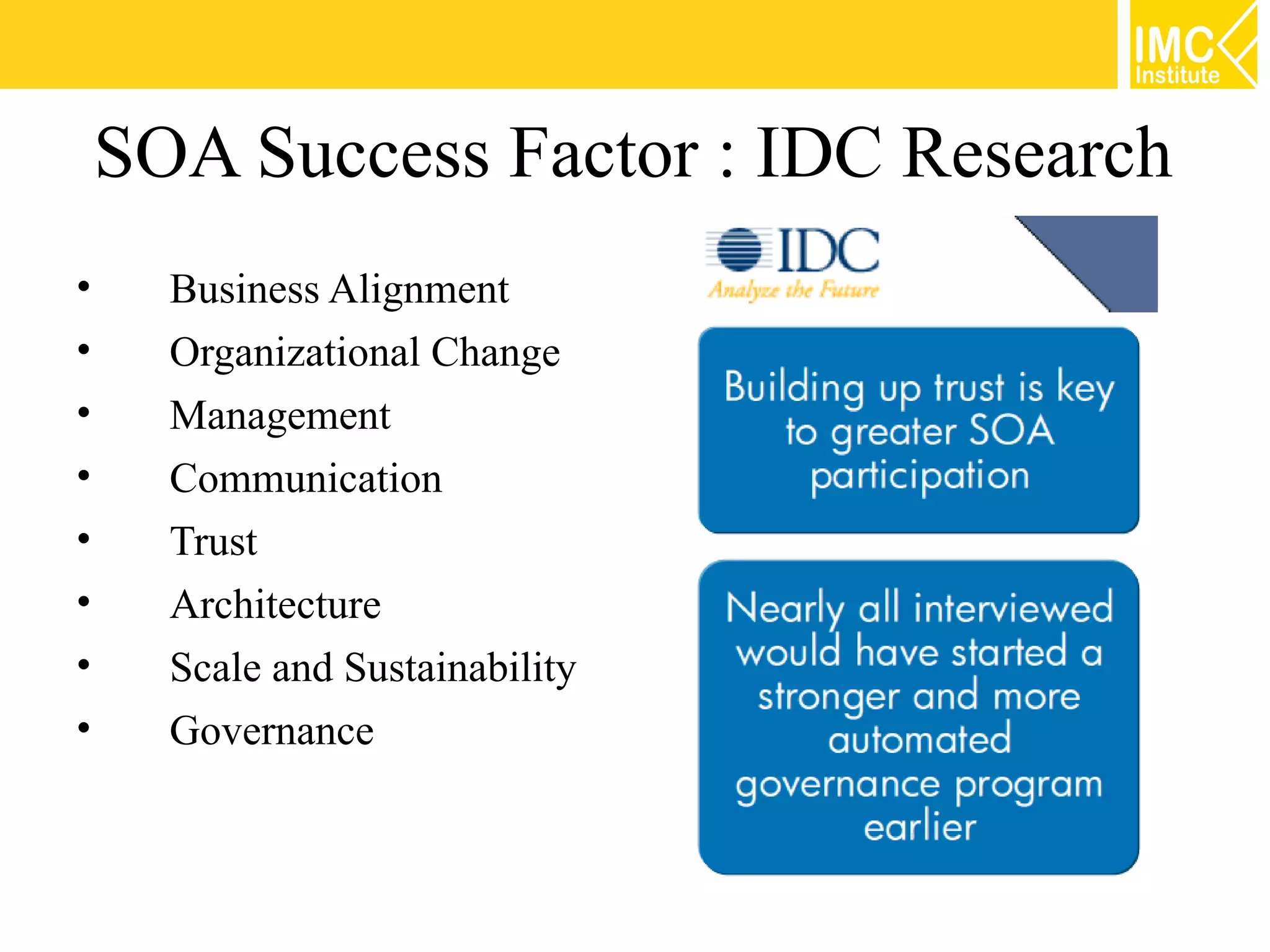
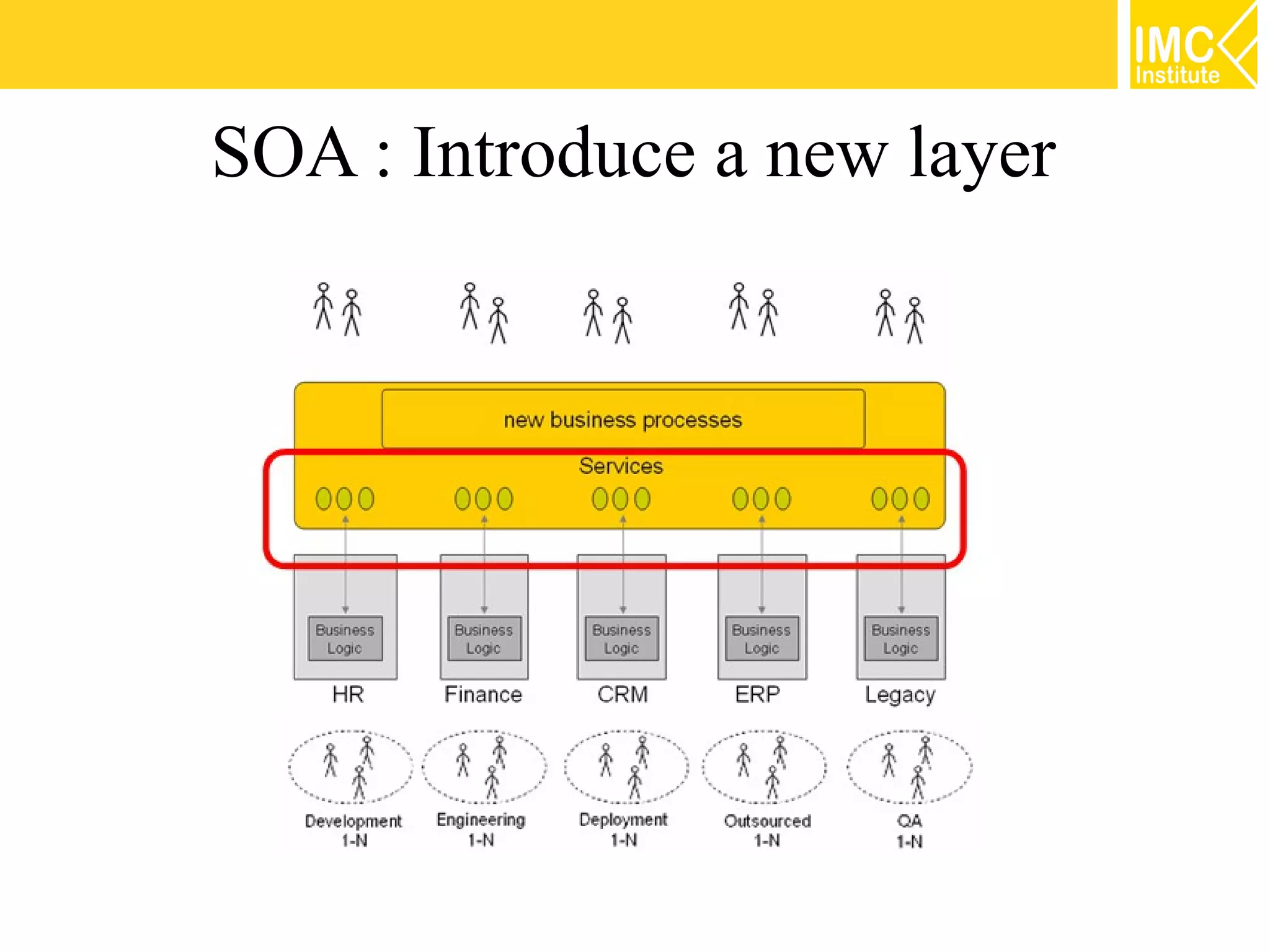
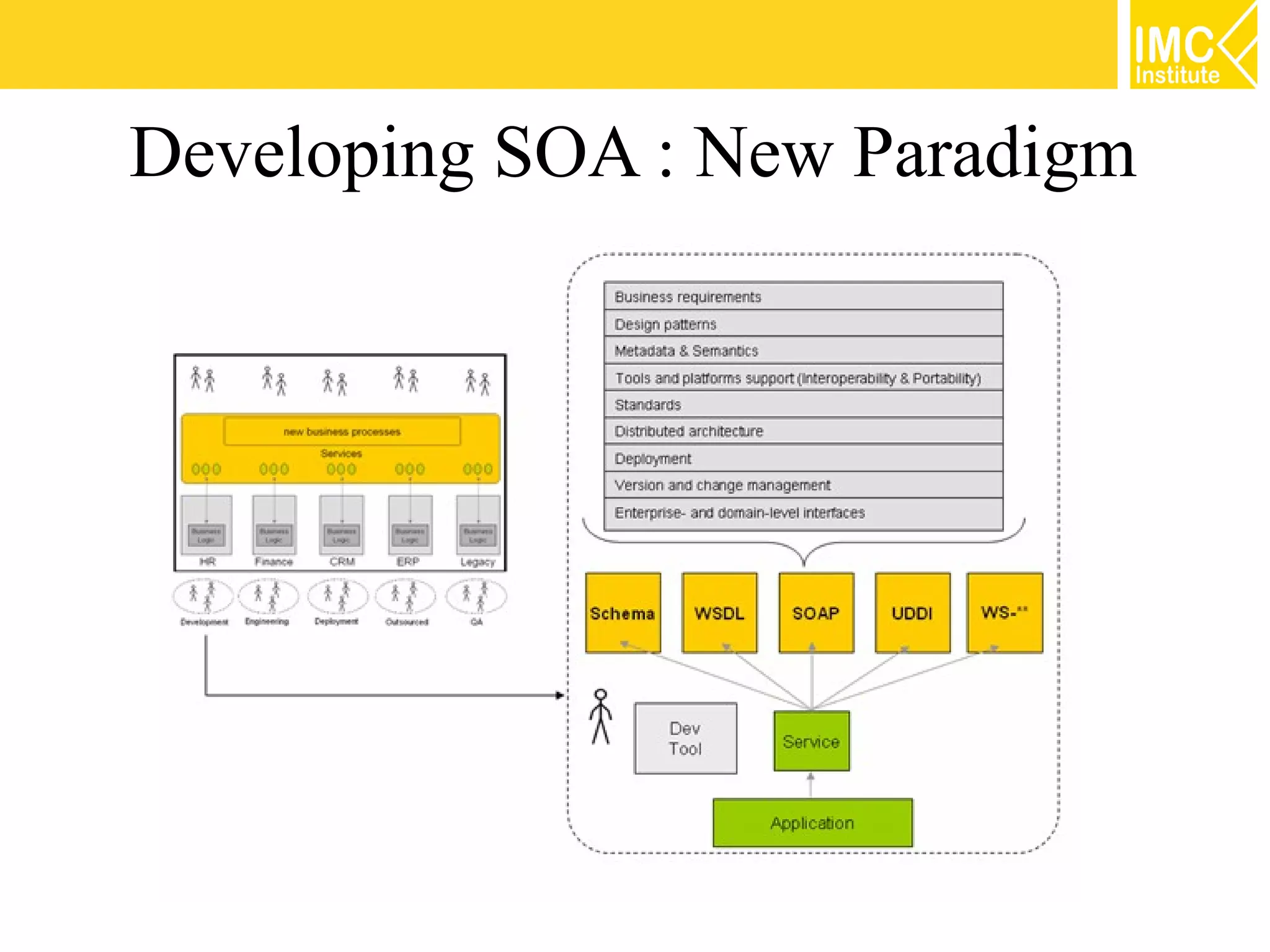
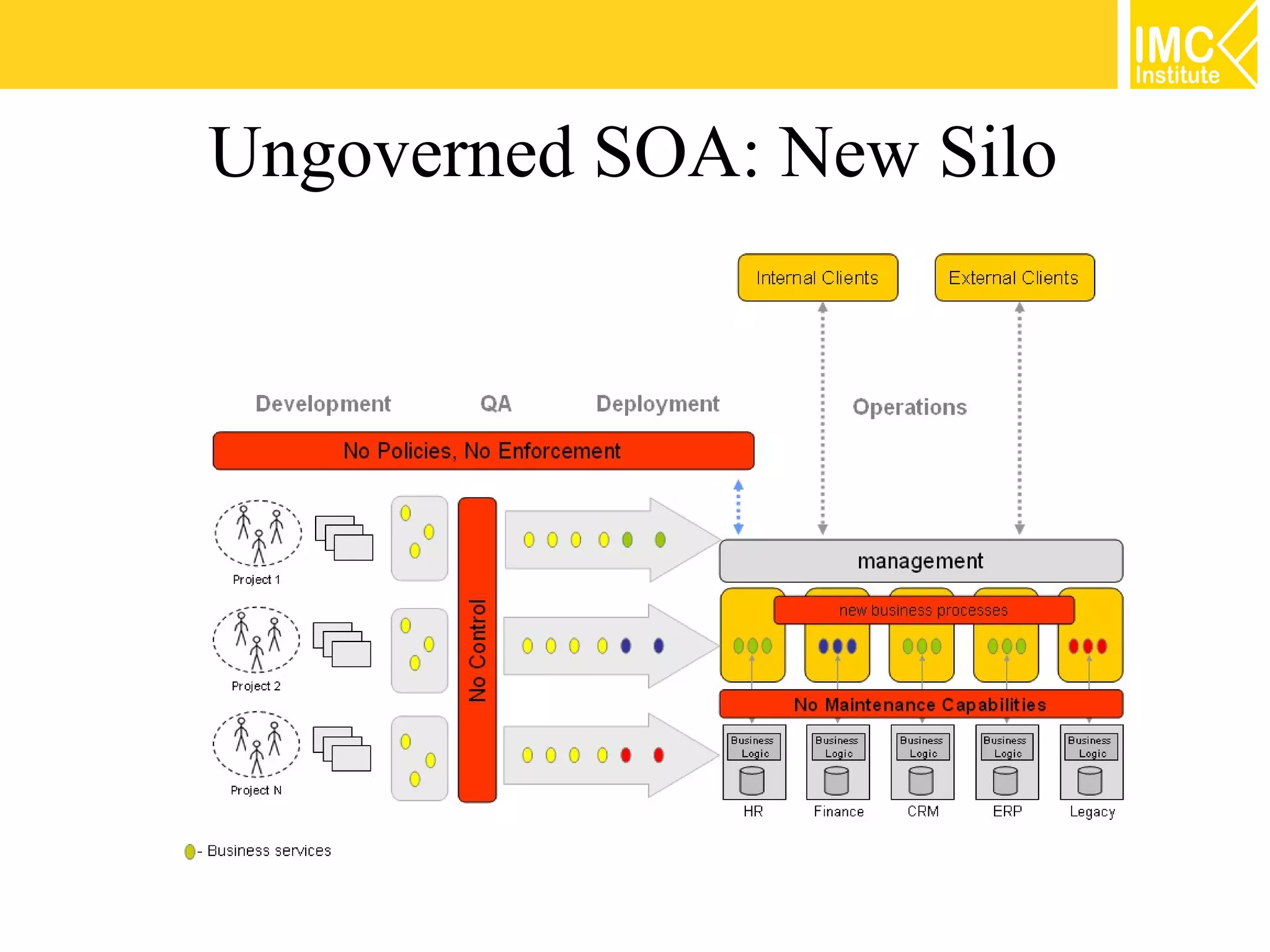
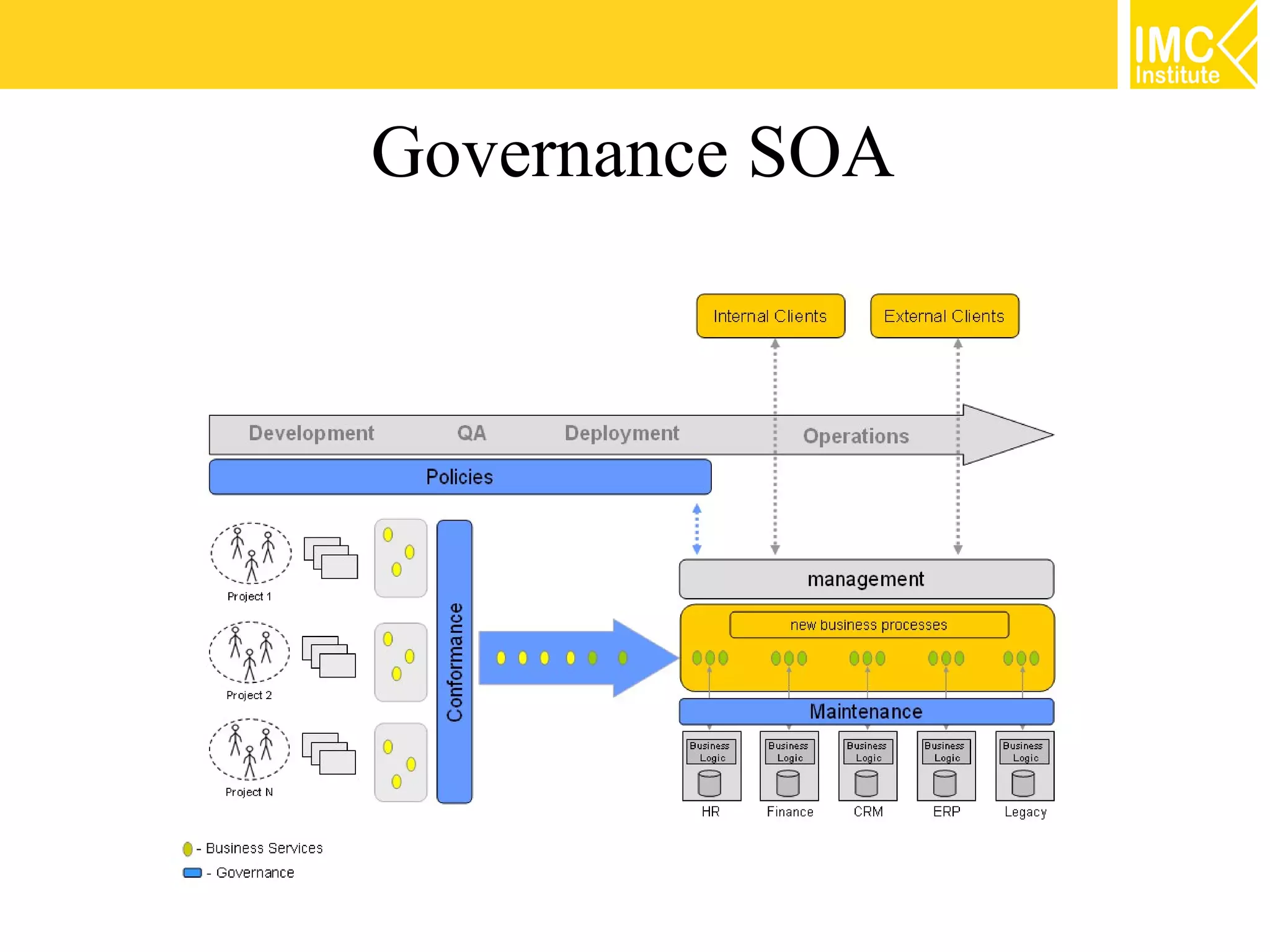
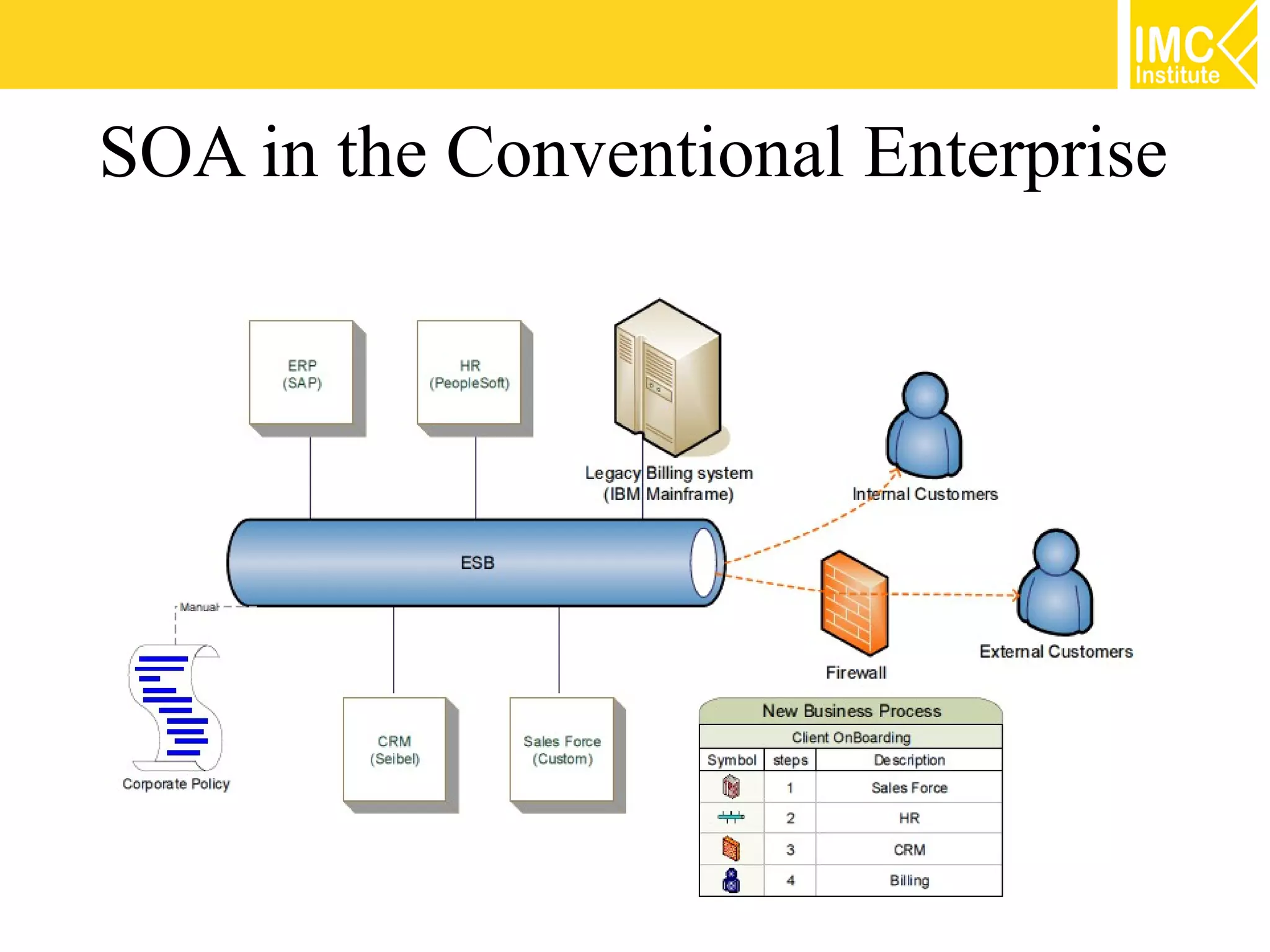
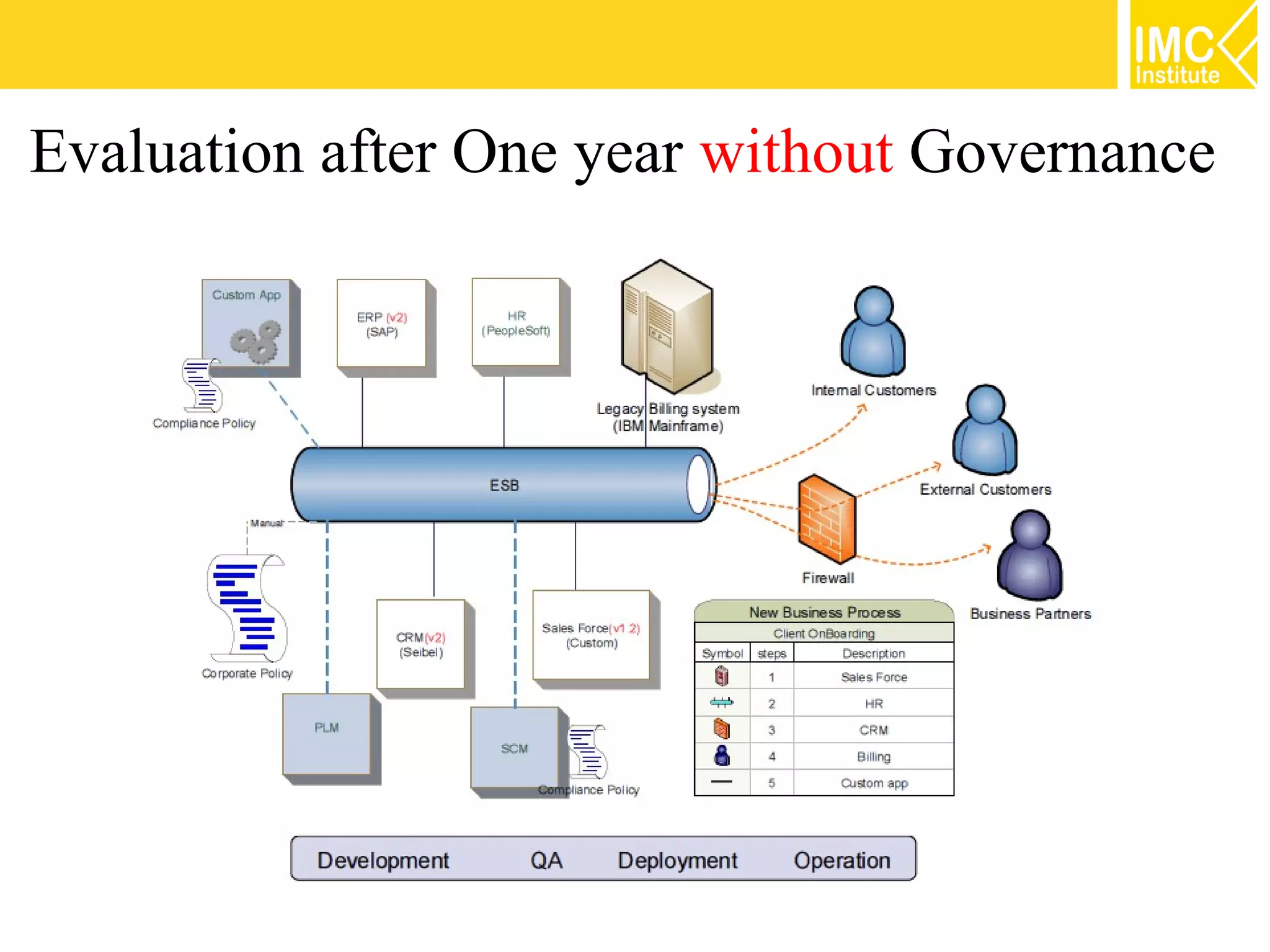
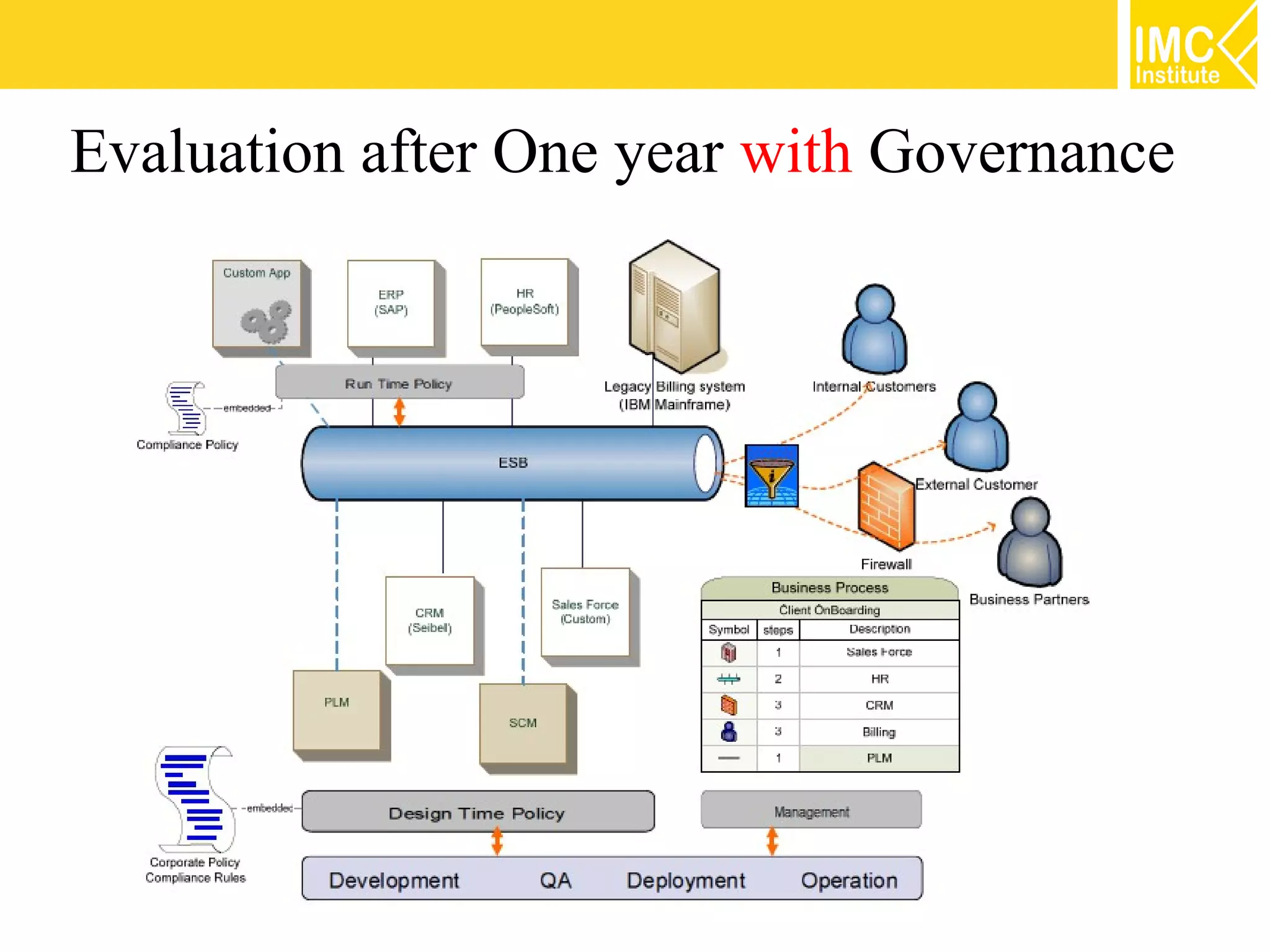
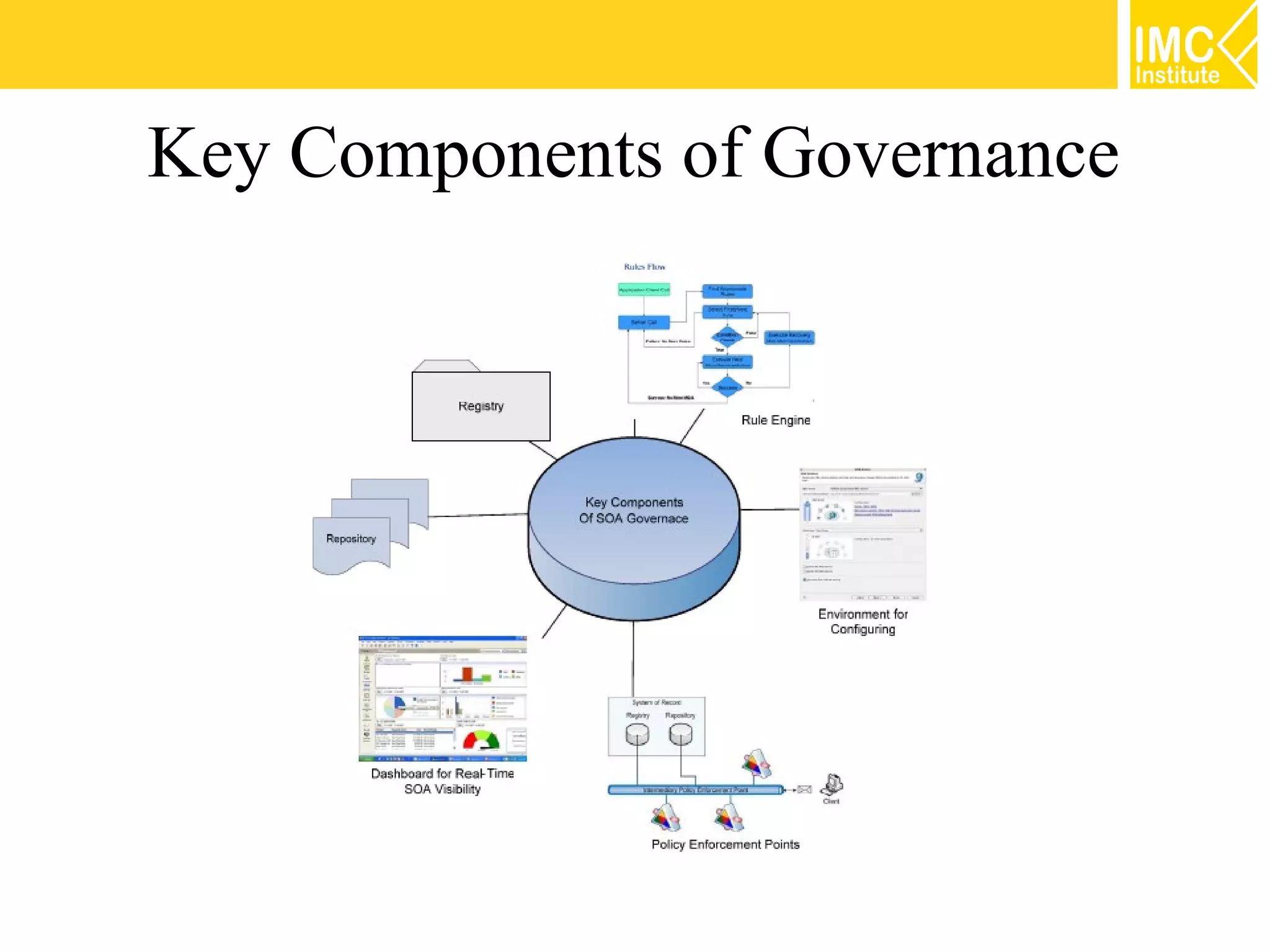
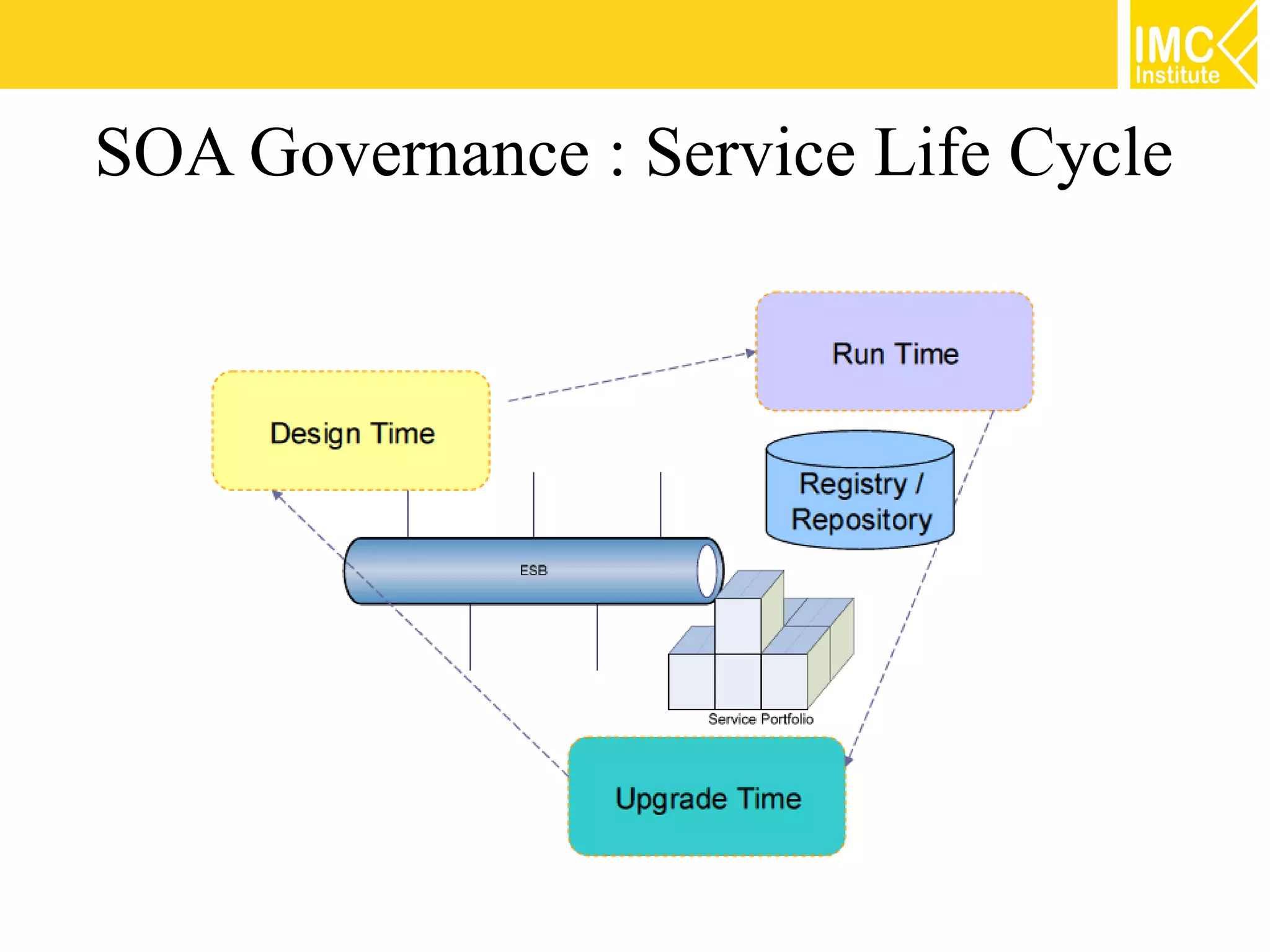
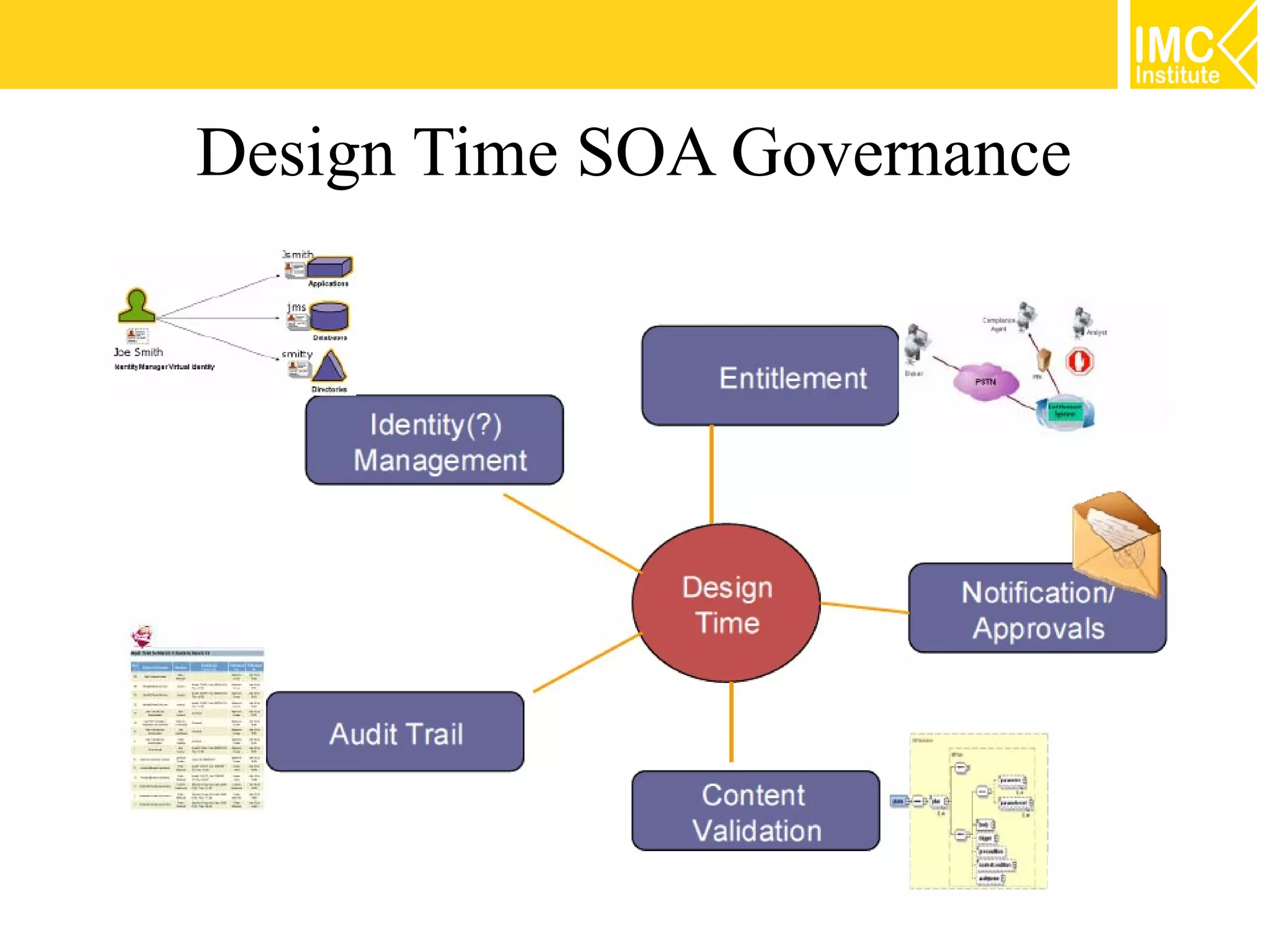
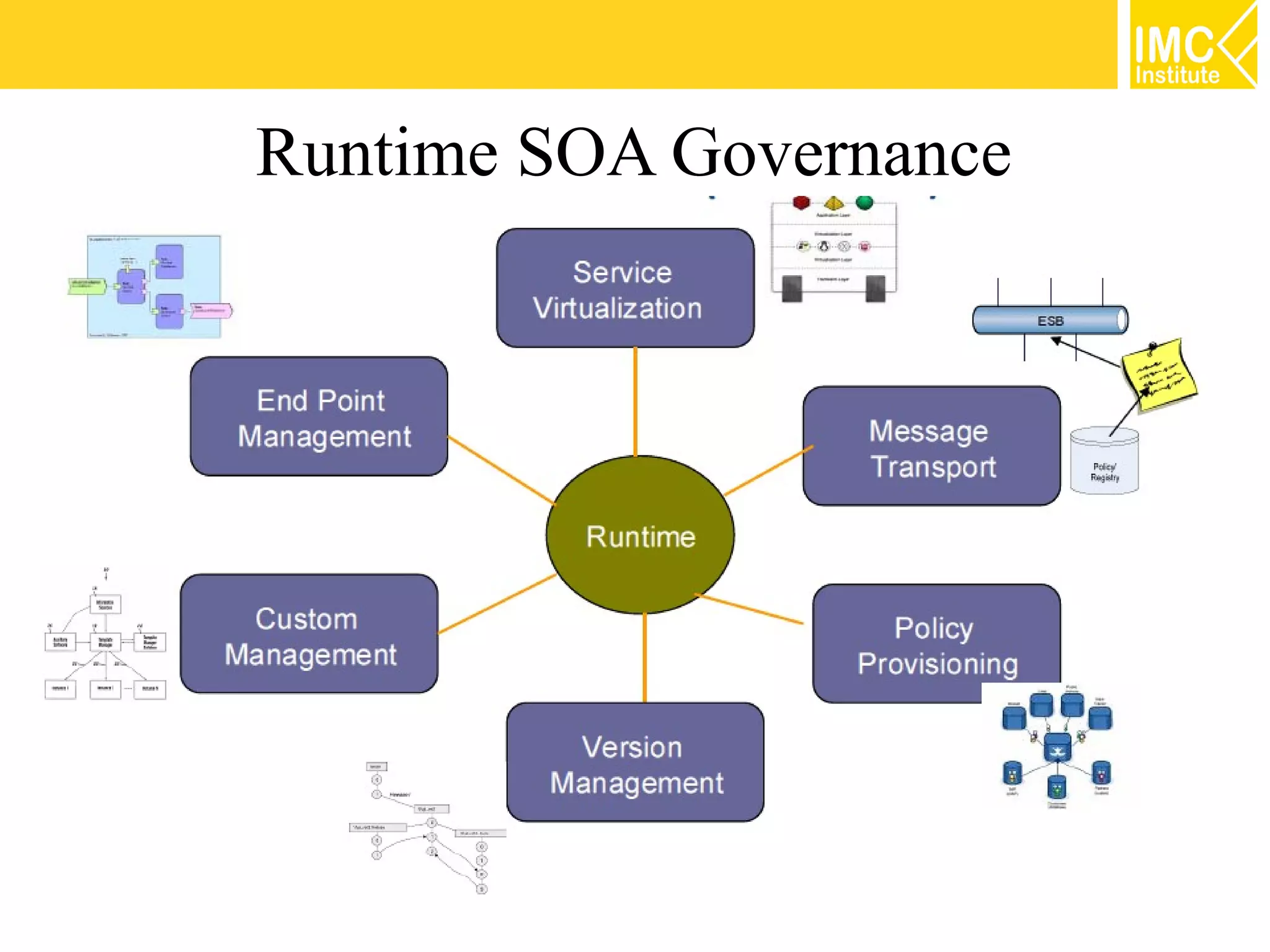
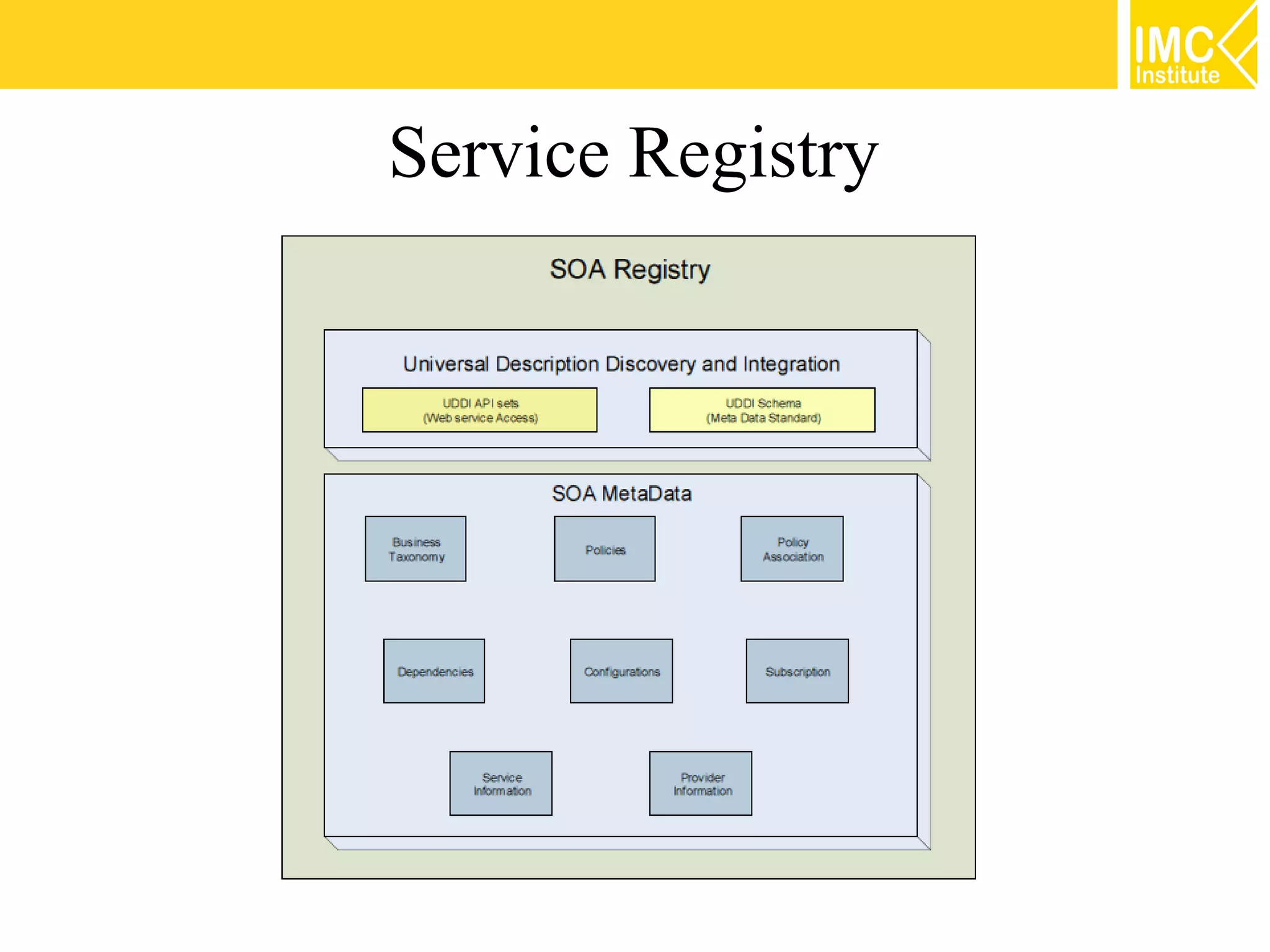
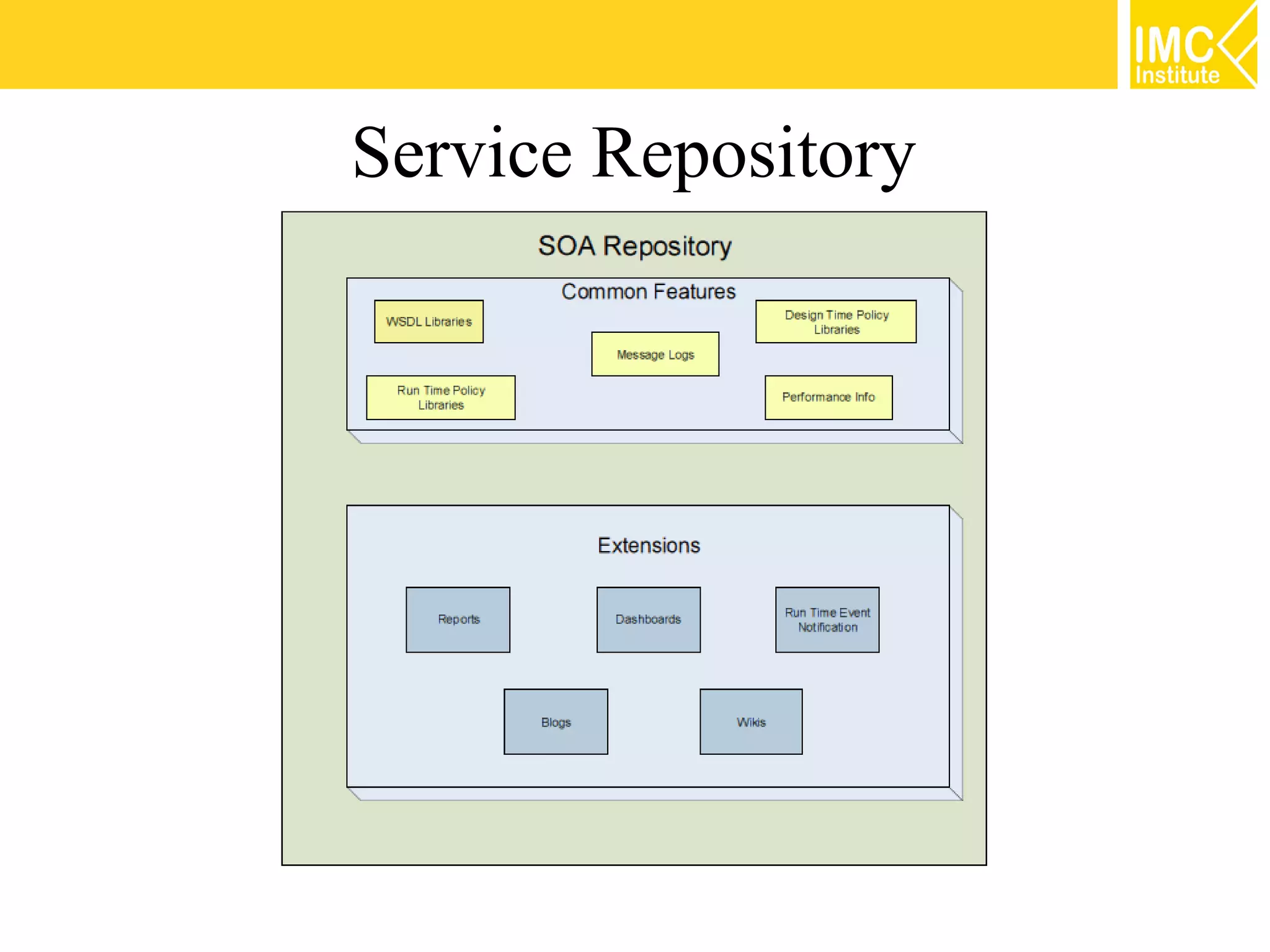
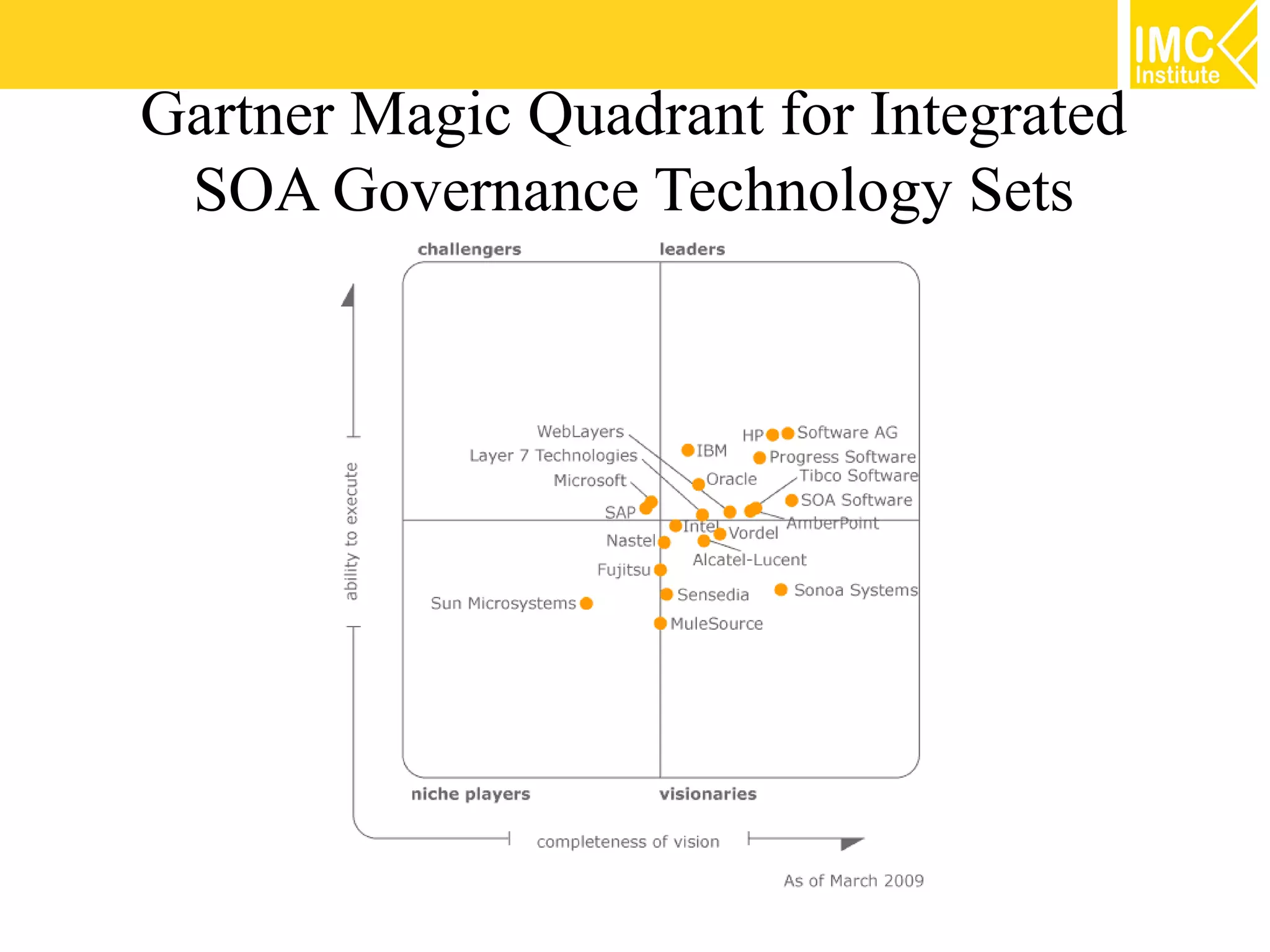
This document discusses SOA governance. It begins by outlining some of the challenges of SOA adoption, including lack of standards and organizational change. It then defines SOA governance as the processes used to oversee and control SOA implementation according to recognized practices. Key components of governance include a registry, policies, and testing. The document also discusses design time and runtime governance, as well as technologies that support governance like ESBs, repositories, and governance products. It concludes with checklists and best practices for implementing SOA governance.