The document provides an overview of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), its principles, reference architecture, and the evolution towards microservices. It details the components, integration patterns, and types of services involved, including SOAP and RESTful web services. Additionally, it contrasts traditional SOA with microservices in terms of messaging, programming style, and deployment models.








![SOA Principles [1]
▪ Standardized service contract
▫ Services adhere to a communications agreement, as
defined collectively by one or more service-
description documents.
▪ Service loose coupling
▫ Services maintain a relationship that minimizes
dependencies and only requires that they maintain an
awareness of each other.
▪ Service abstraction:
▫ Beyond descriptions in the service contract, services
hide logic from the outside world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-12-320.jpg)
![SOA Principles [2]
▪ Service reusability
▫ Logic is divided into services with the intention of
promoting reuse.
▪ Service autonomy (govern itself)
▫ Services have control over the logic they encapsulate,
from a Design-time and a Run-time perspective.
▪ Service statelessness
▫ Services minimize resource consumption by
deferring the management of state information when
necessary.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-13-320.jpg)
![SOA Principles [3]
▪ Service discoverability
▫ Services are supplemented with communicative meta
data by which they can be effectively discovered and
interpreted.
▪ Service composability
▫ Services are effective composition participants,
regardless of the size and complexity of the
composition.
▪ Service granularity
▫ A design consideration to provide optimal scope and
right granular level of the business functionality in a
service operation.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-14-320.jpg)
![SOA Principles [4]
▪ Service normalization
▫ Services are decomposed or consolidated to a level of
normal form to minimize redundancy (performance
optimization, access, and aggregation).
▪ Service Location transparency
▫ This refers to the ability of a service consumer to
invoke a service regardless of its actual location in
the network.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-15-320.jpg)

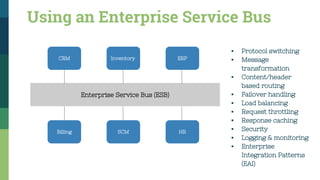
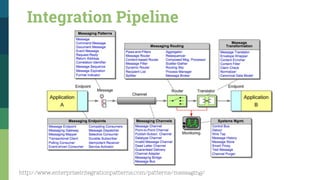
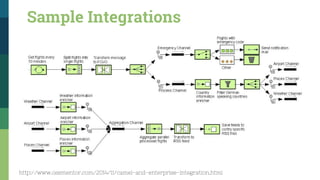
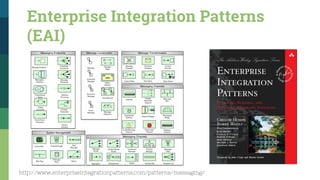





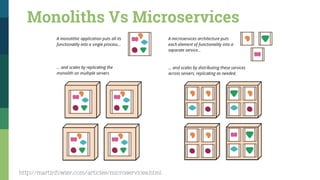
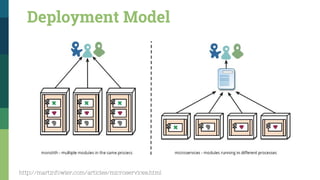
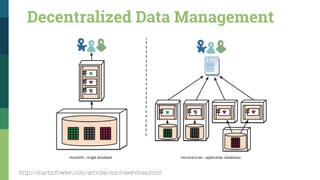
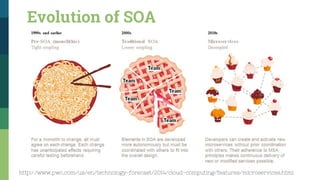
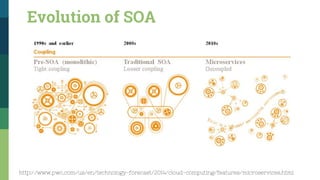
![Traditional SOA Vs Microservices [1]
http://www.pwc.com/us/en/technology-forecast/2014/cloud-computing/features/microservices.html
Traditional SOA Microservices
Messaging Type Synchronous: wait to
connect
Asynchronous: publish
and subscribe
Programming Style Imperative model Reactive programming
(event/callback driven)
Lines of Code per
Service
Hundreds/Thousands Hundreds or fewer
State Stateful Stateless
Databases Large RDBMS NoSQL + RDBMS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-32-320.jpg)
![Traditional SOA Vs Microservices [2]
Traditional SOA Microservices
Code Type Procedural Functional
Means of Evolution Each service evolves and
becomes larger
Each small service is
immutable and can be
abandoned or ignored
Means of systemic
change
Modify the monolith Create a new service
Means of scaling Optimize the monolith Scale individual services
System-level awareness Less aware and event
driven
More aware and event
driven
http://www.pwc.com/us/en/technology-forecast/2014/cloud-computing/features/microservices.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceorientedarchitecturebeyond1-160312174515/85/Service-Oriented-Architecture-Beyond-33-320.jpg)
