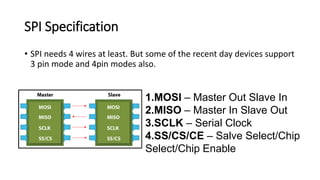
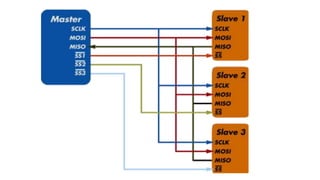
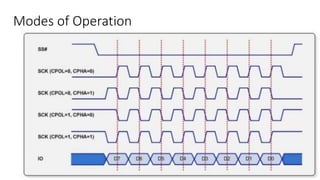
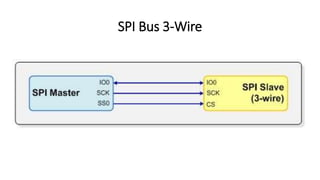
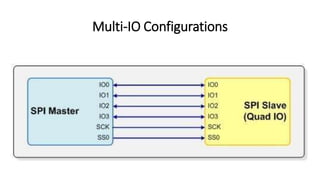
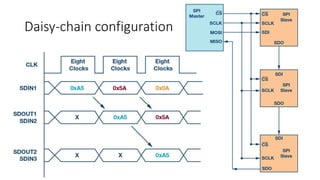
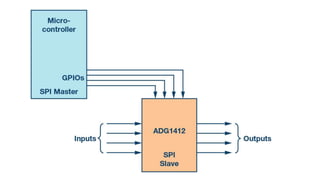
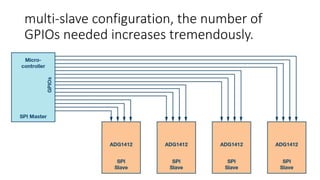
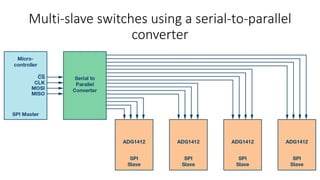
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a widely-used bus for transmitting data between microcontrollers and peripherals like sensors and memory devices, requiring at least four wires. While SPI offers advantages such as higher speed and full duplex communication, it has disadvantages including increased wiring complexity and no built-in error detection. Common applications of SPI include interfacing with sensors, audio devices, cameras, and memory storage.