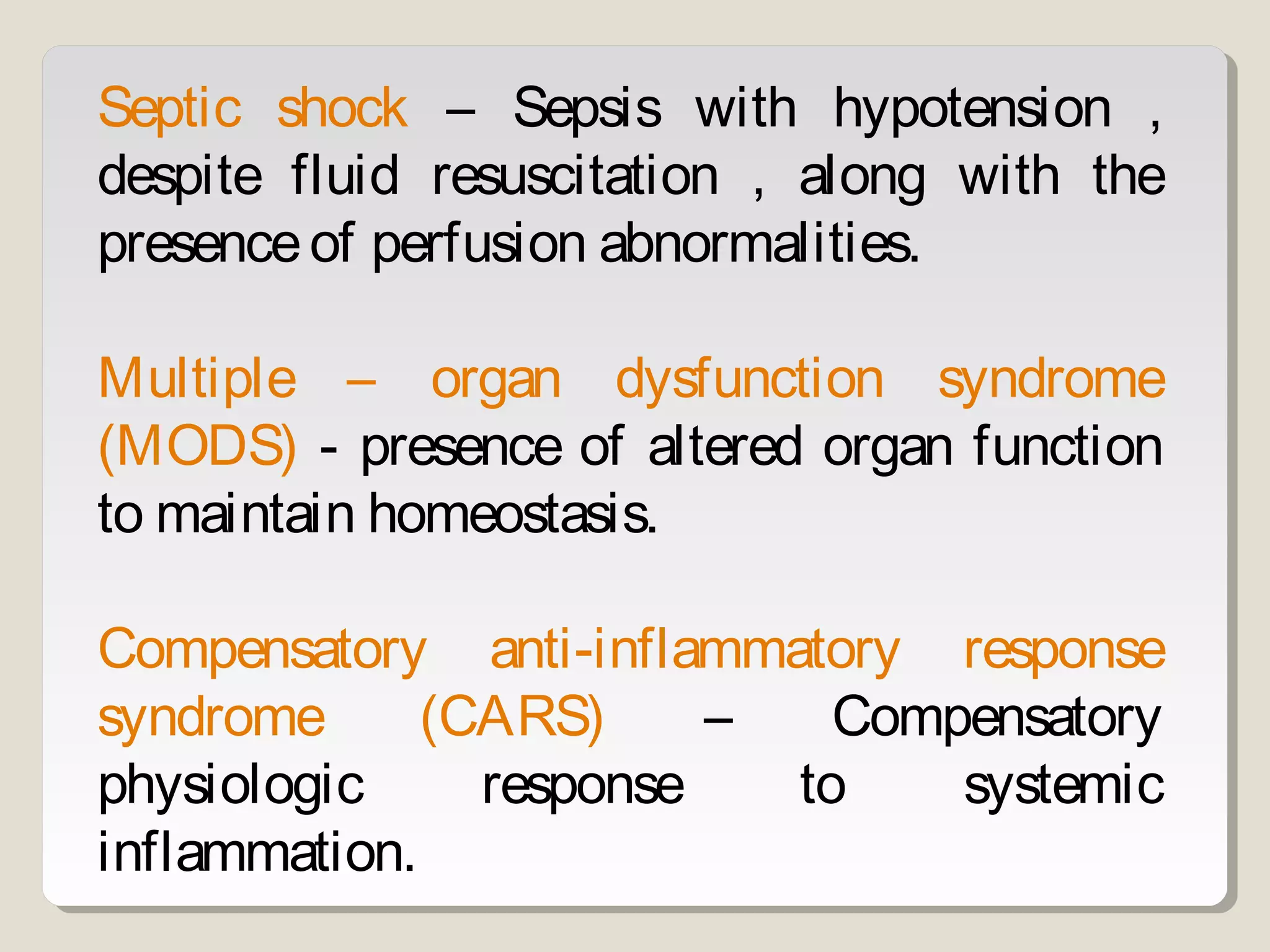
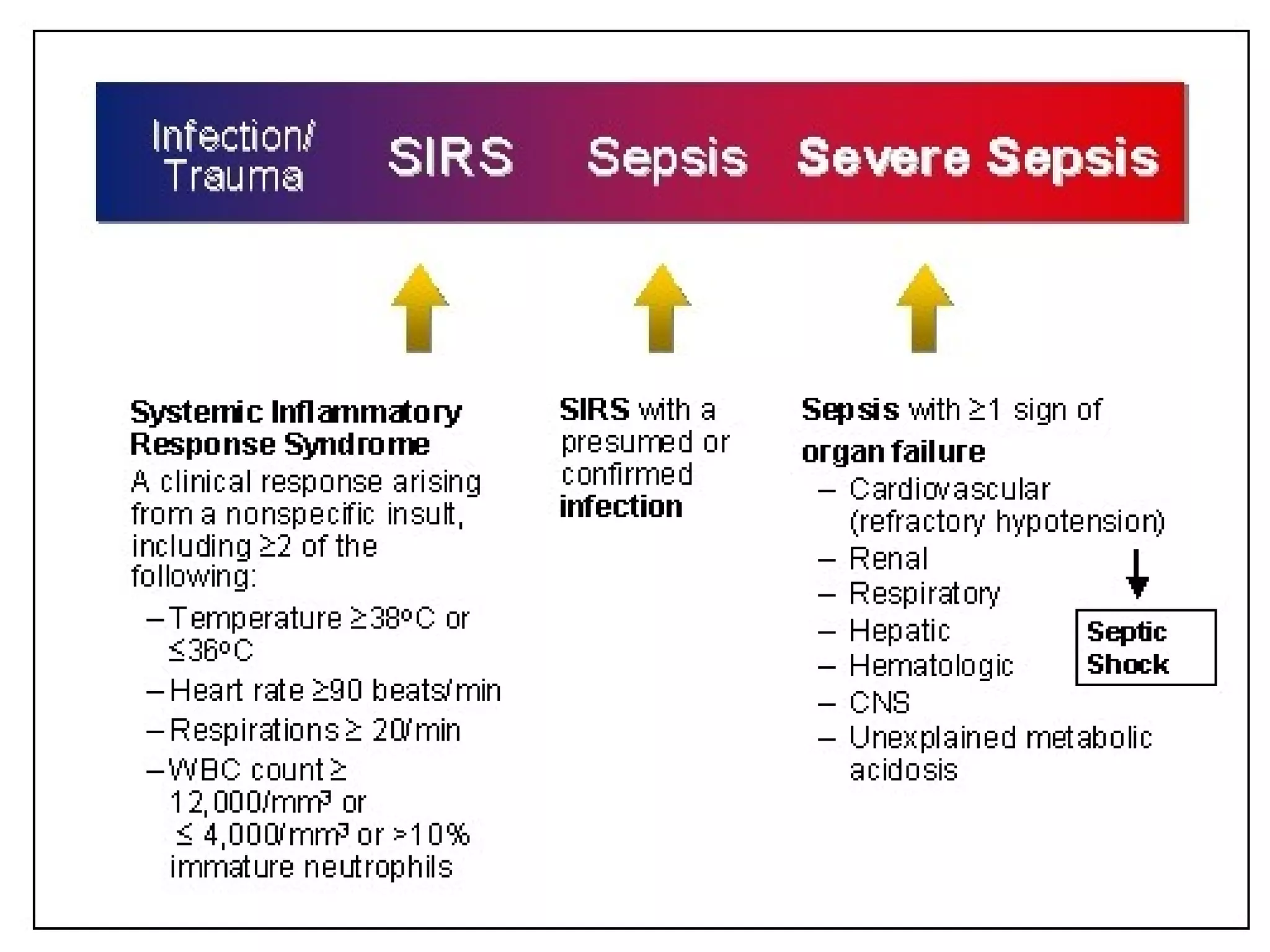
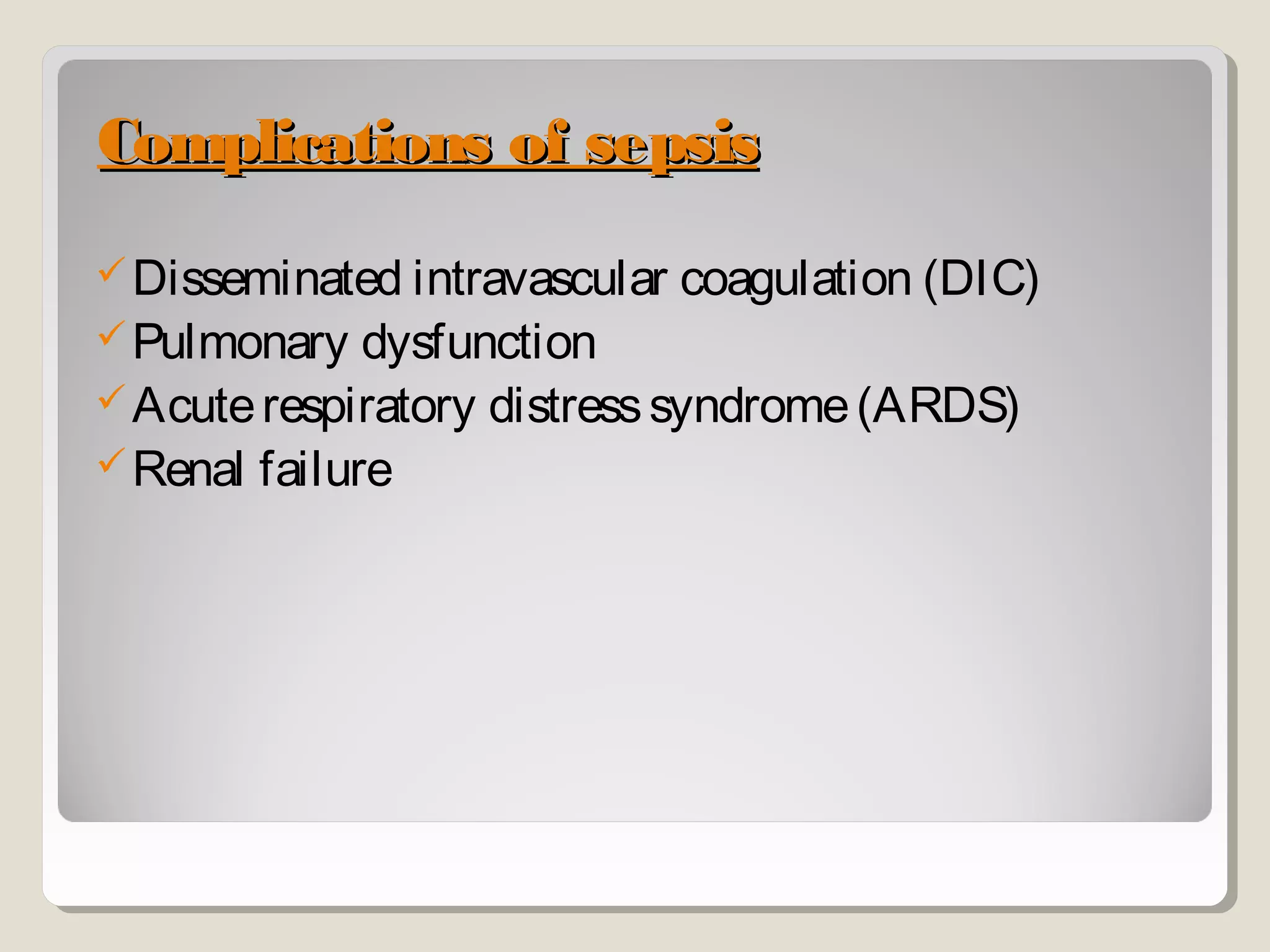
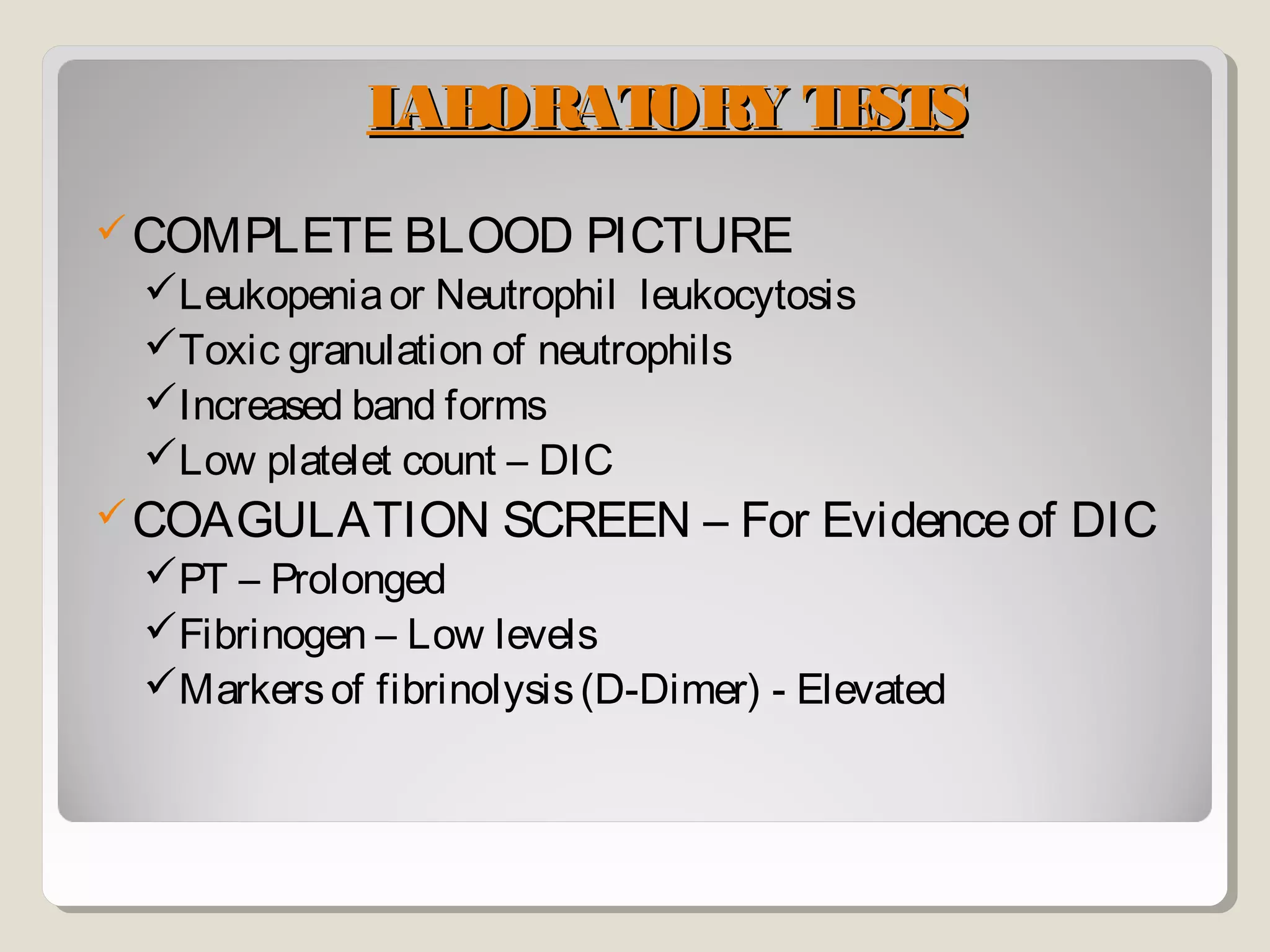
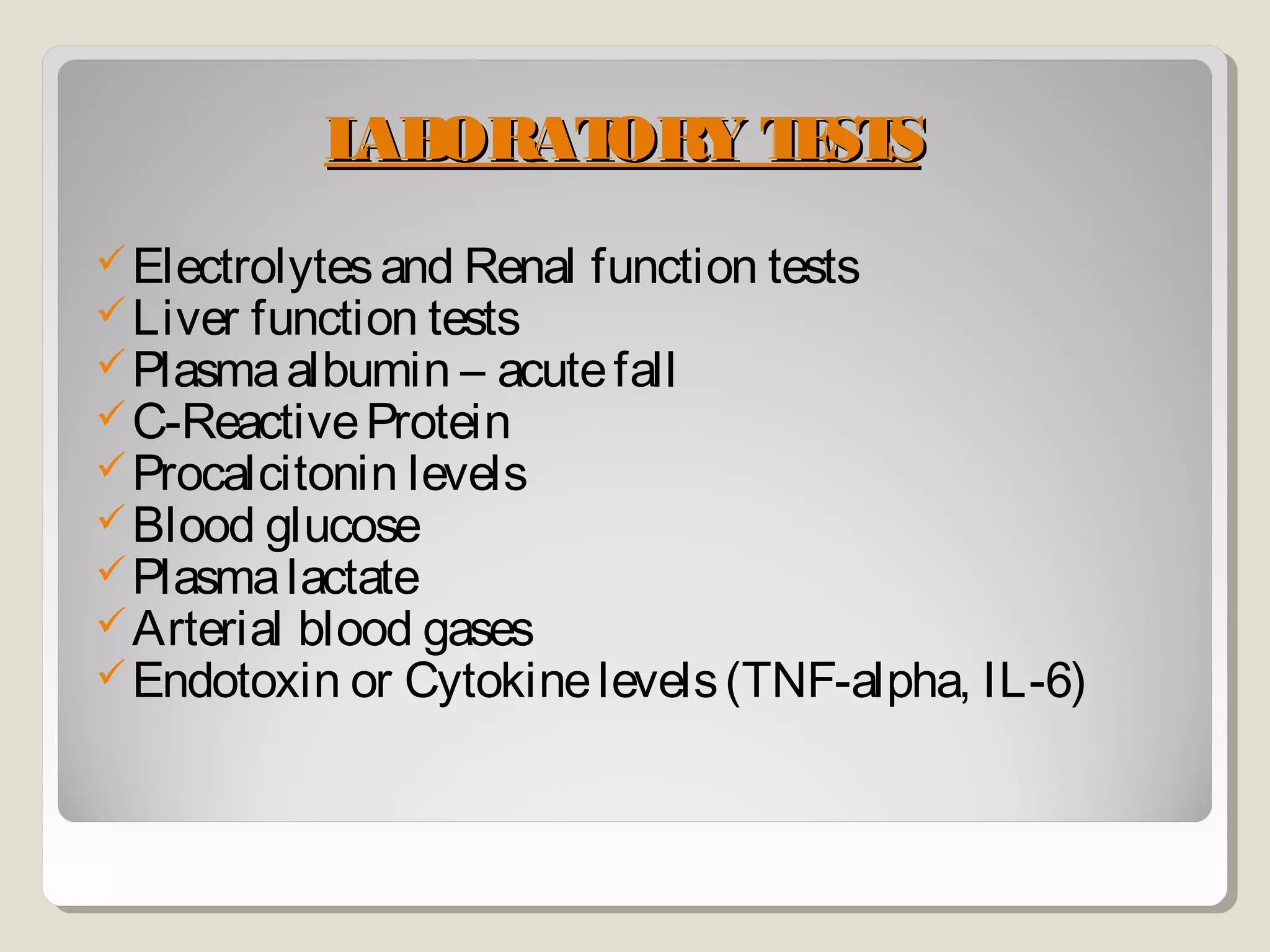
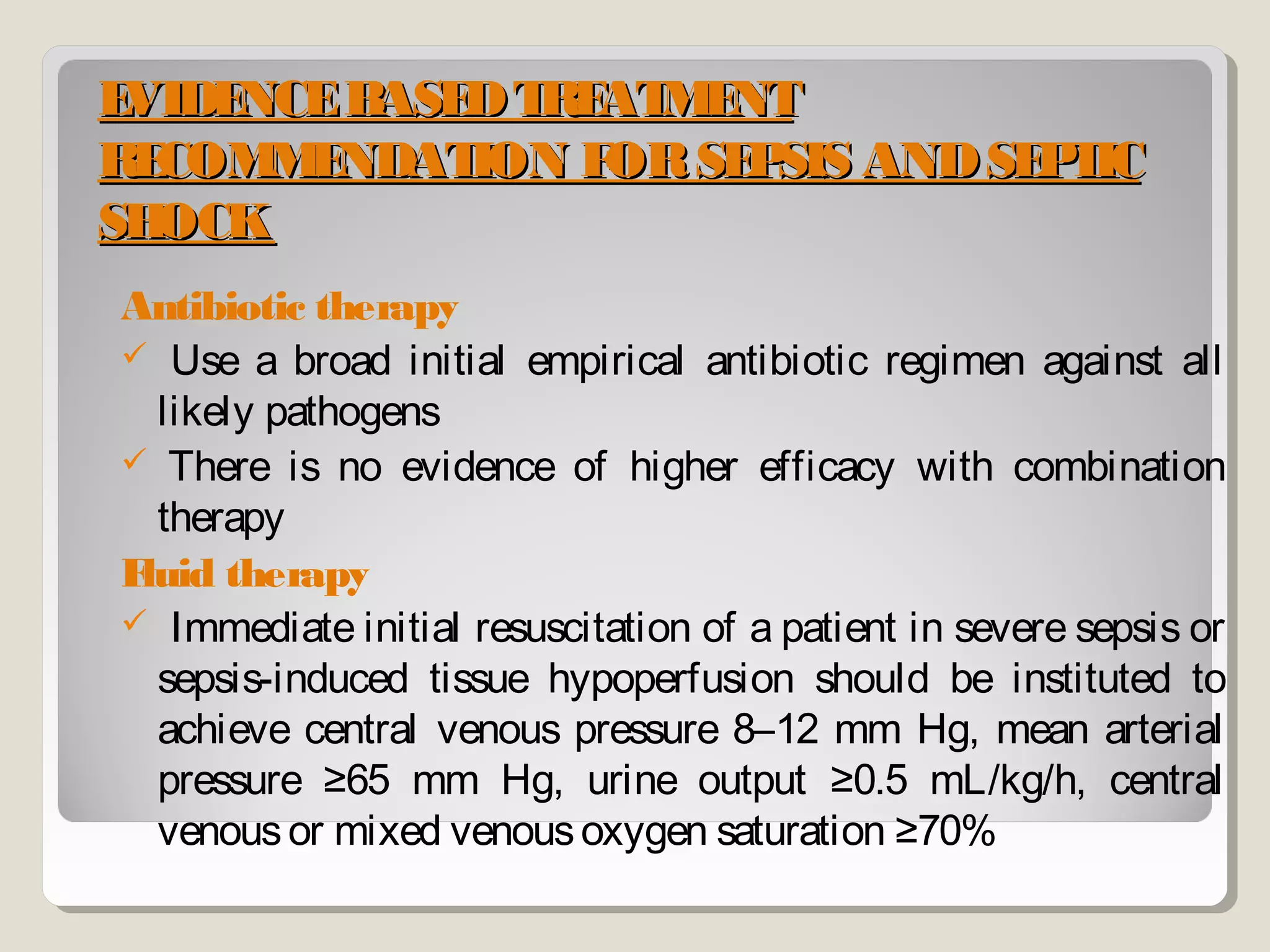
Sepsis and septic shock refer to systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by infection. In 1992, terminology was standardized to classify patients based on severity from systemic inflammatory response syndrome to septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Bacteria are the most common cause, and symptoms may include fever, changes in mental status, and hypotension. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing signs of infection as well as identifying the pathogen through blood and other cultures. Treatment goals are timely diagnosis, eliminating the infection source, and early broad-spectrum antibiotics while preventing organ failure through other supportive measures.