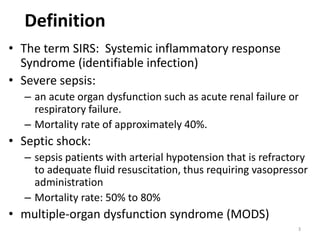
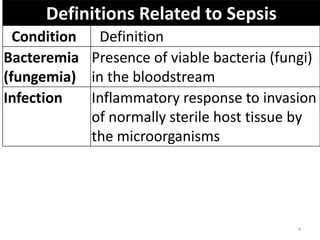
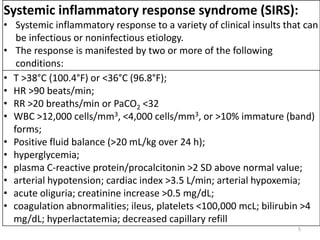
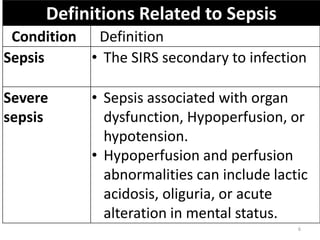
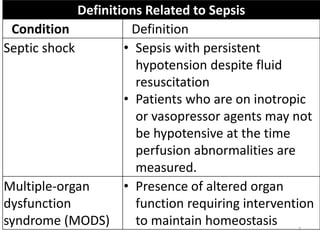
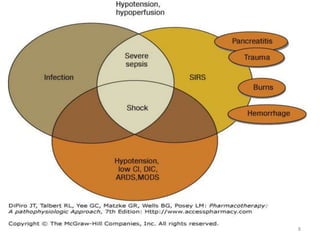
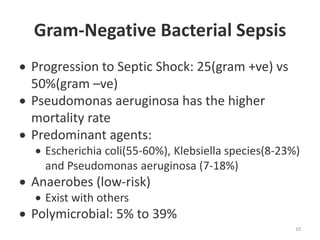
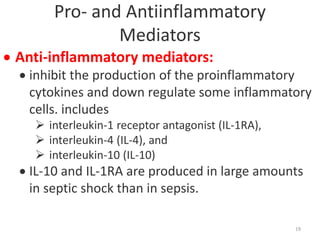
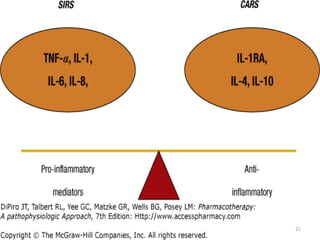
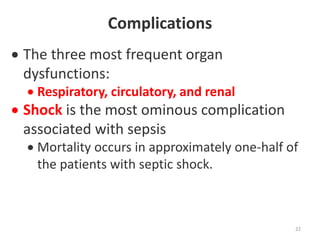
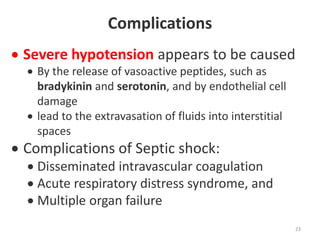
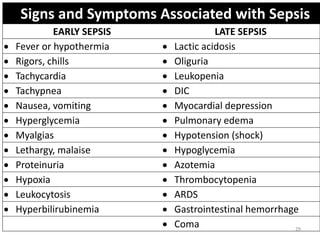
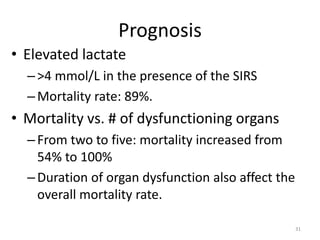
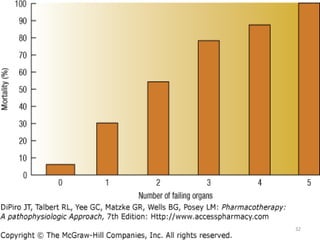
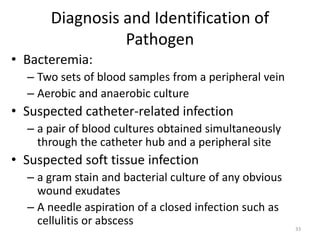
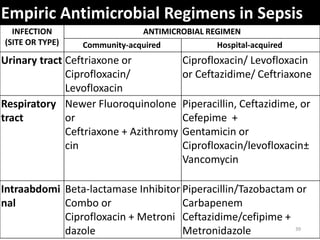
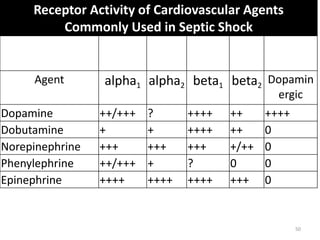
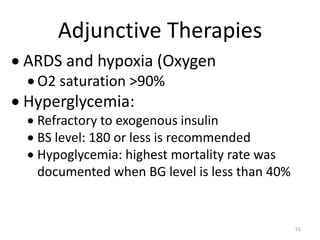
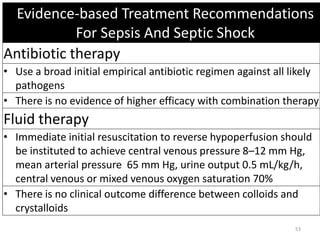
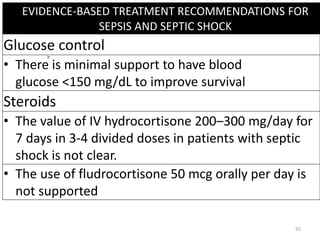
Sepsis is a clinical syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response to infection that can lead to organ dysfunction and death. It ranges from systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) to sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). The leading causes are respiratory, intra-abdominal, and urinary infections from gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. Treatment involves early diagnosis, source control, broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, vasopressors like norepinephrine for hypotension, and organ support. Despite aggressive treatment, sepsis mortality remains high and is associated with the number and duration of organ dysfunctions.