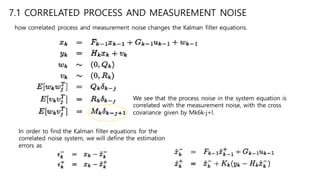
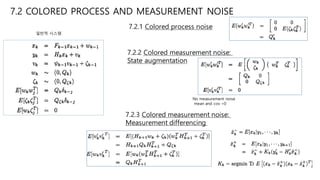
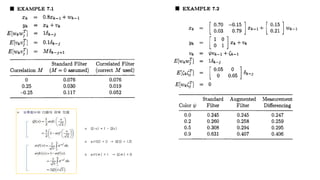
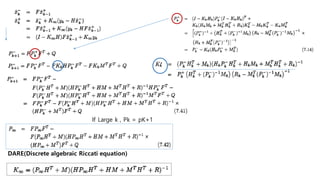
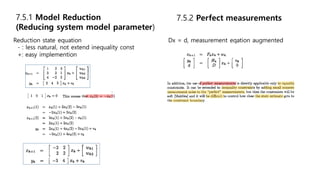
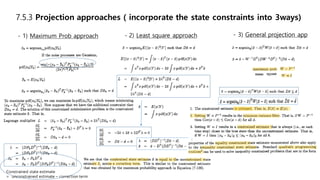
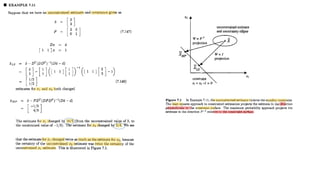
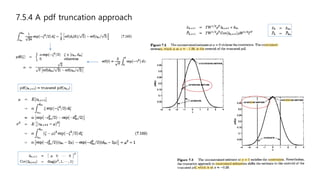
This document discusses several generalizations and modifications that can be made to the standard Kalman filter. Section 7.3 describes how a steady-state Kalman filter can be used instead of a time-varying filter when system dynamics are time-invariant. Section 7.4 discusses a fading memory filter that discounts older measurements to address cases when system dynamics are imperfectly known. Section 7.5 presents several approaches to incorporate state equality and inequality constraints into the Kalman filter formulation, including model reduction, projection approaches, and probability density function truncation.


















![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-28-320.jpg)
![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-29-320.jpg)
![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-30-320.jpg)
![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-31-320.jpg)
![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-32-320.jpg)
![Sensor Fusion Study - Ch7. Kalman Filter Generalizations [김영범]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch7kalmanfiltergeneralizations-200715034919/85/Sensor-Fusion-Study-Ch7-Kalman-Filter-Generalizations-33-320.jpg)