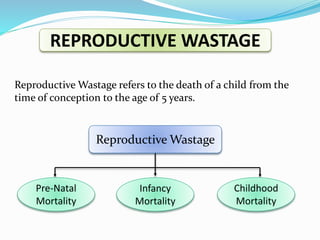
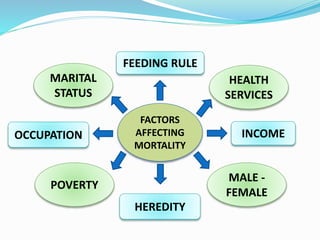
This document discusses the concept of mortality. It defines mortality as death after birth from infancy. Some key causes of mortality discussed include diseases, communicable diseases, violence, and child diseases. It also examines types of child mortality such as neonatal mortality and post-neonatal mortality. Factors affecting mortality include income, occupation, heredity, health services, and gender. The document outlines several ways to measure mortality rates such as crude death rate, infant mortality rate, age-specific death rate, and maternal mortality rate.