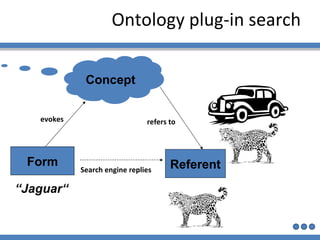
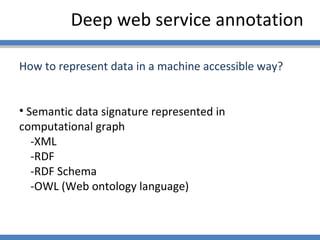
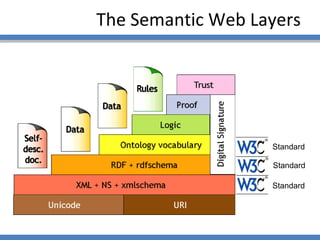
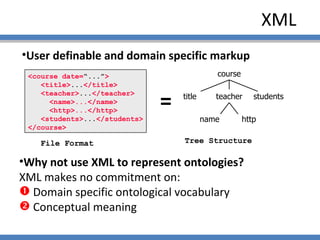
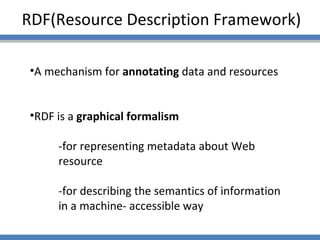
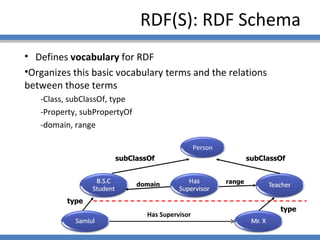
The document discusses using semantic technologies like XML, RDF, and OWL to represent data on the web in a structured format that is accessible to machines. It describes two main approaches for accessing semantic data on the deep web: ontology plug-in search and deep web service annotation. Both approaches require a semantic web crawler or bot to harvest concepts from deep web forms and iteratively link them to build enriched ontologies that define domain terms and relationships to provide machine-interpretable meaning.


![The Semantic Web The Semantic Web is an extension of the current web in which information is given well-defined meaning , better enabling computers and people to work in co-operation . [Tim Berners-Lee , 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/towardthesemanticdeepweb-091028145635-phpapp01/85/Toward-The-Semantic-Deep-Web-4-320.jpg)