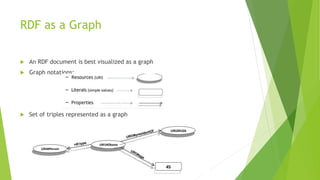
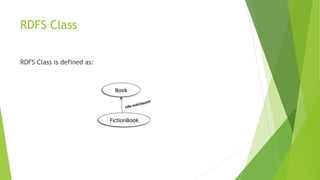
The document discusses the Semantic Web, which aims to make web content machine-readable by adding metadata. It defines semantics as meaning versus syntax as structure. The Semantic Web will allow computers to understand relationships between things like people, places, events and products. An example shows how a Semantic Web browser could act as a personal assistant to efficiently find an action movie showing and Italian restaurant based on a natural language query. RDF and RDFS are introduced as languages to describe resources and define classes, properties, and hierarchies for Semantic Web data.