The Semantic Web is an extension of the World Wide Web, envisioned by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. Its core goal is to enable machines to understand the meaning (semantics) of information on the web, rather than just processing it as linked documents.
Machine-Readability:
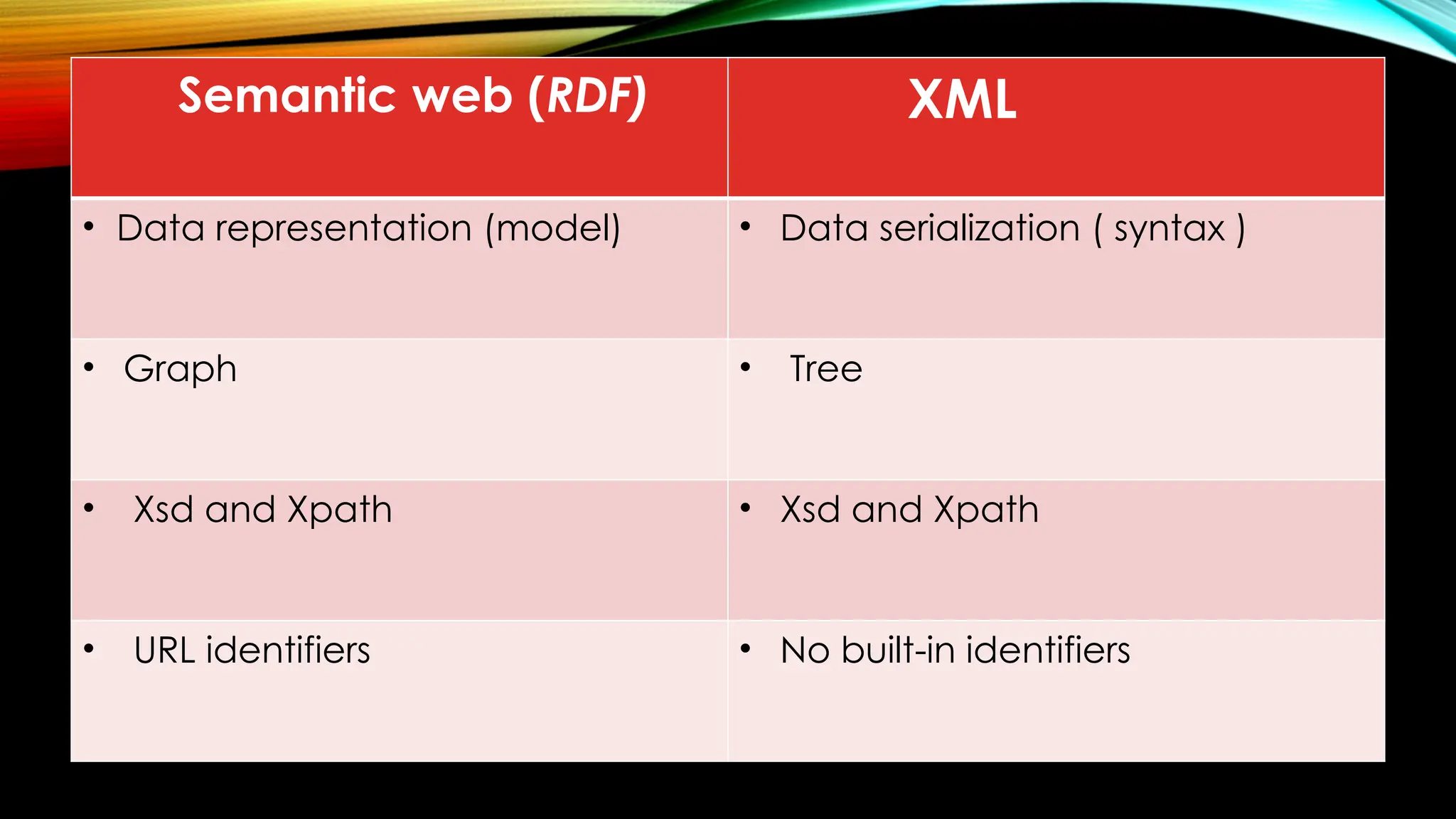
It aims to transform the web into a "web of data" where information is structured and annotated in a way that allows machines to interpret its meaning and relationships.
Standards and Technologies:
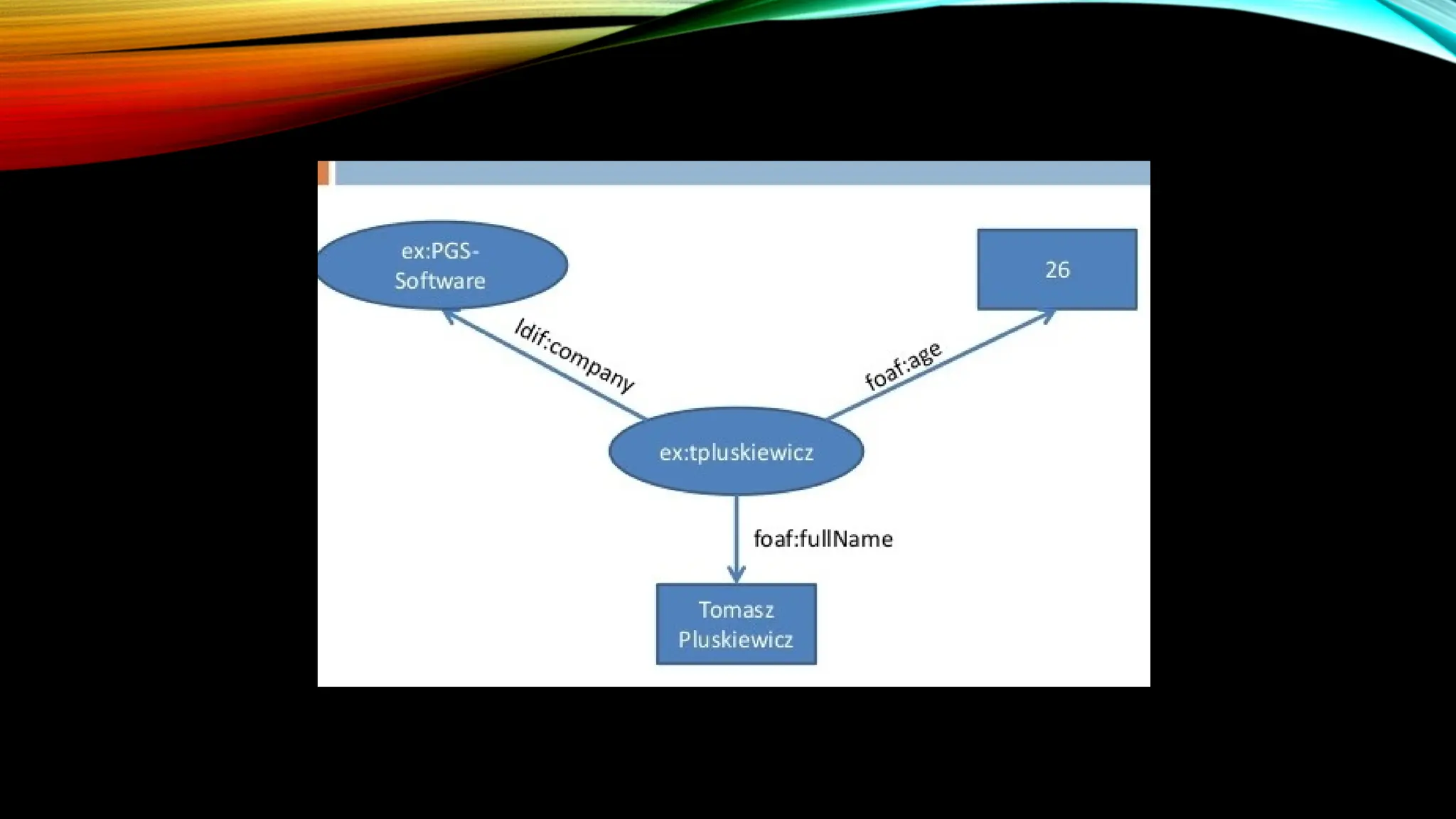
It relies on standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), such as the Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL). RDF provides a framework for defining metadata, while OWL is used to formally represent ontologies, which describe concepts, relationships, and categories within a domain.
Data Interoperability:
By providing common data formats and exchange protocols, the Semantic Web facilitates the integration and combination of data from diverse sources, enabling seamless sharing and reuse of information across applications and systems.
Enhanced Information Retrieval and Reasoning:
The embedded semantics allow for more intelligent information retrieval, enabling systems to understand user queries in context and provide more relevant results. It also supports reasoning over data, allowing machines to infer new information based on existing relationships.
Applications:
Semantic Web technologies underpin various applications, including knowledge graphs, recommendation systems, and semantic search engines, leading to more intelligent and context-aware AI systems.
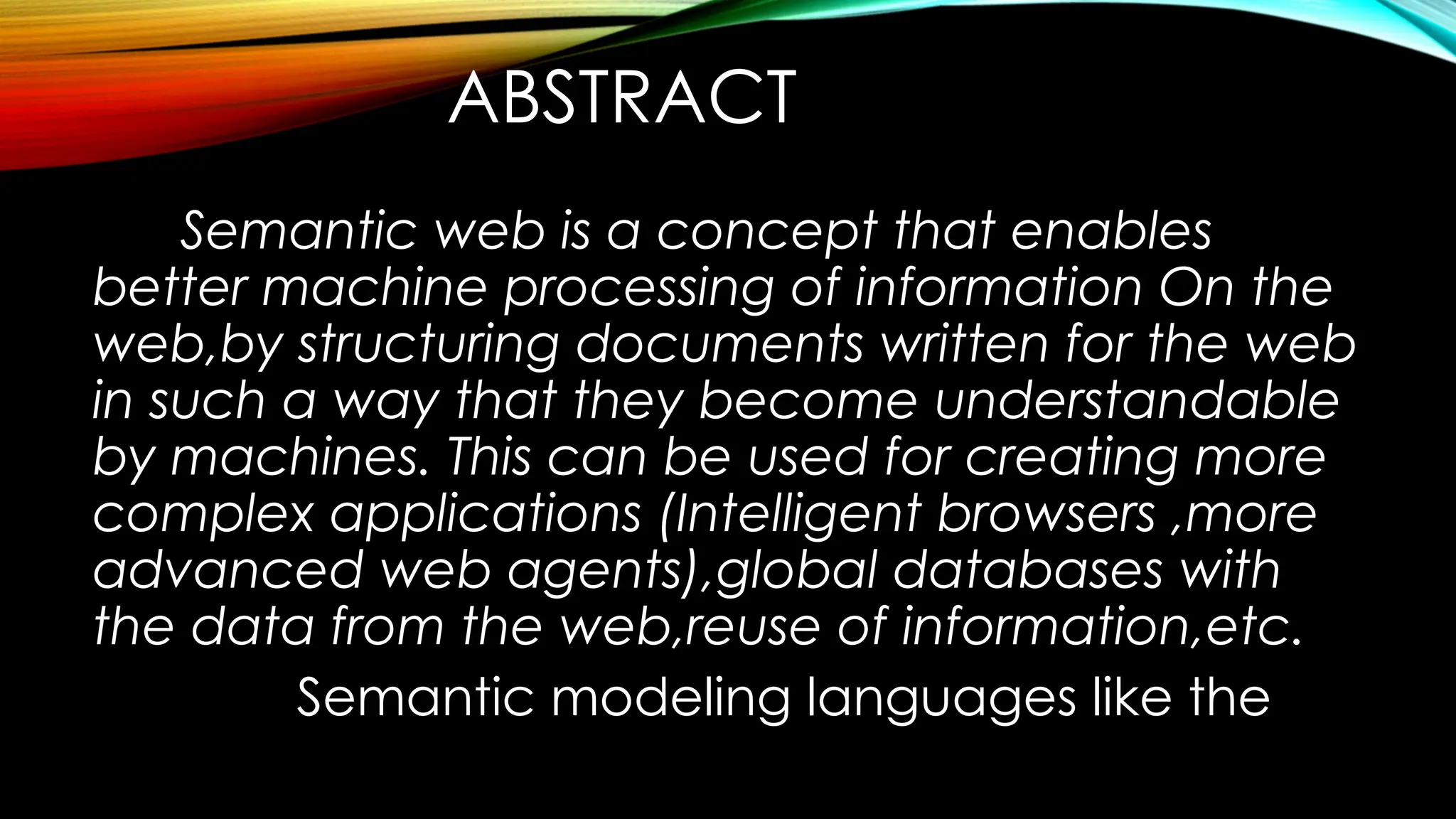
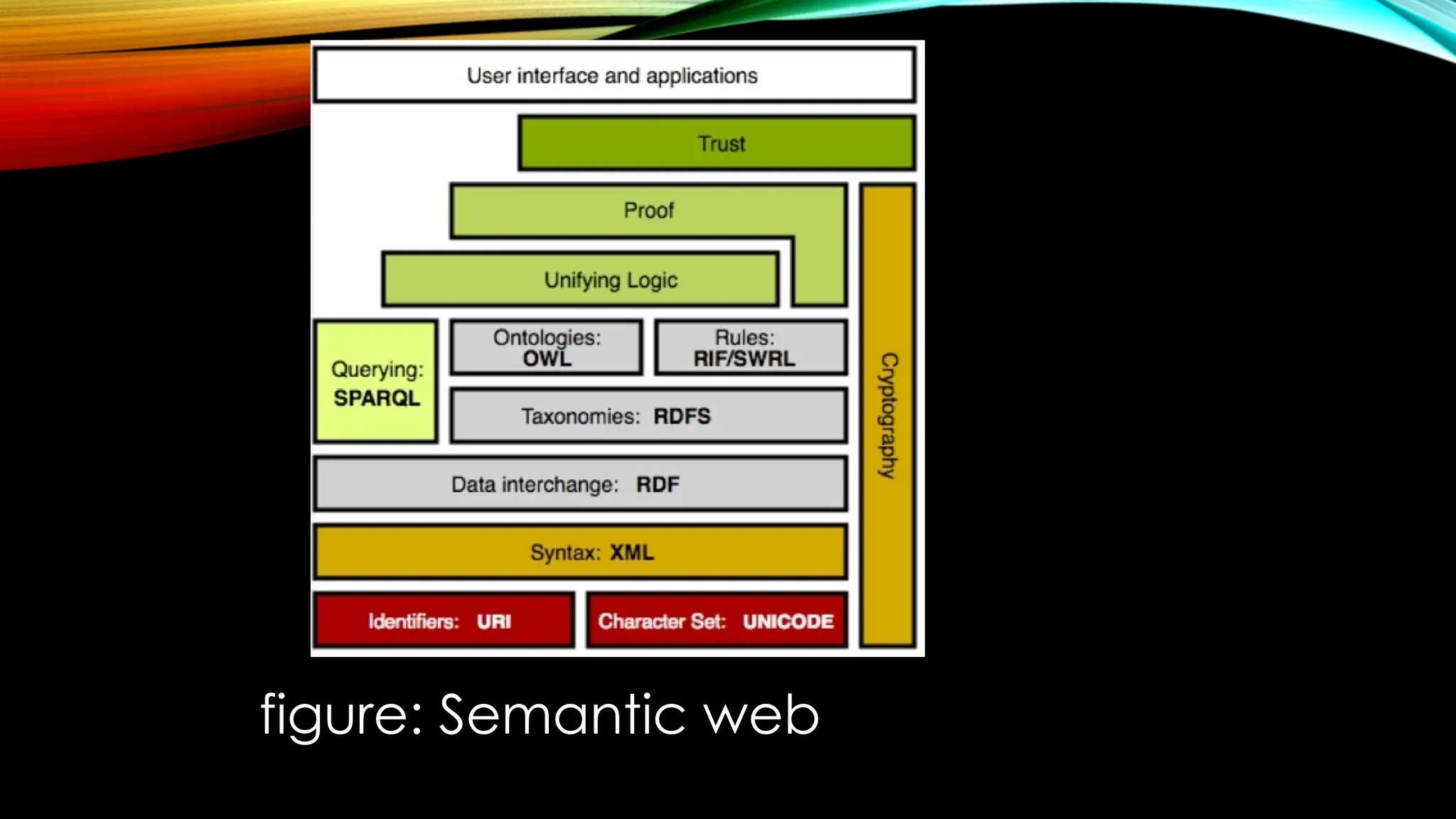
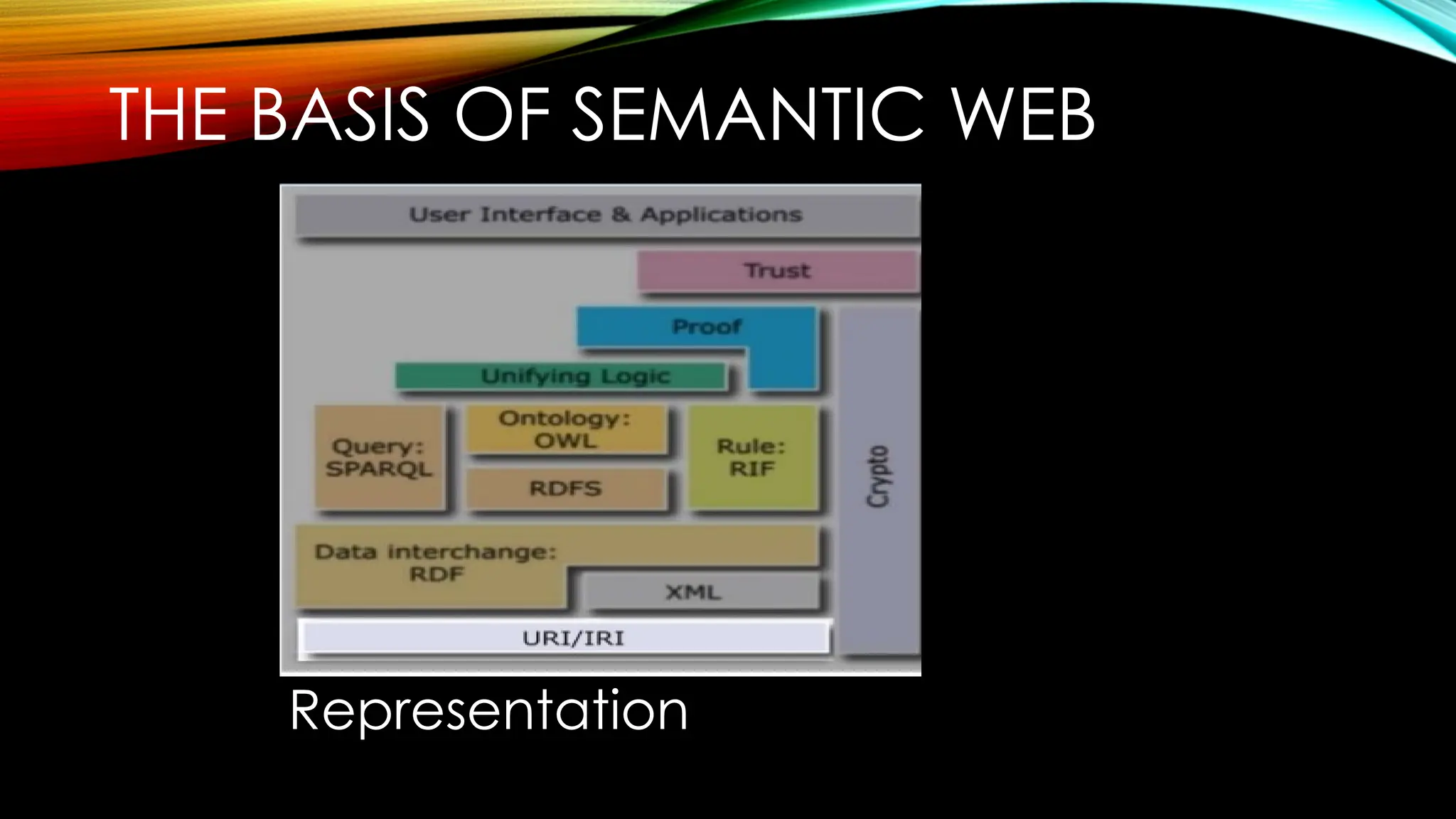
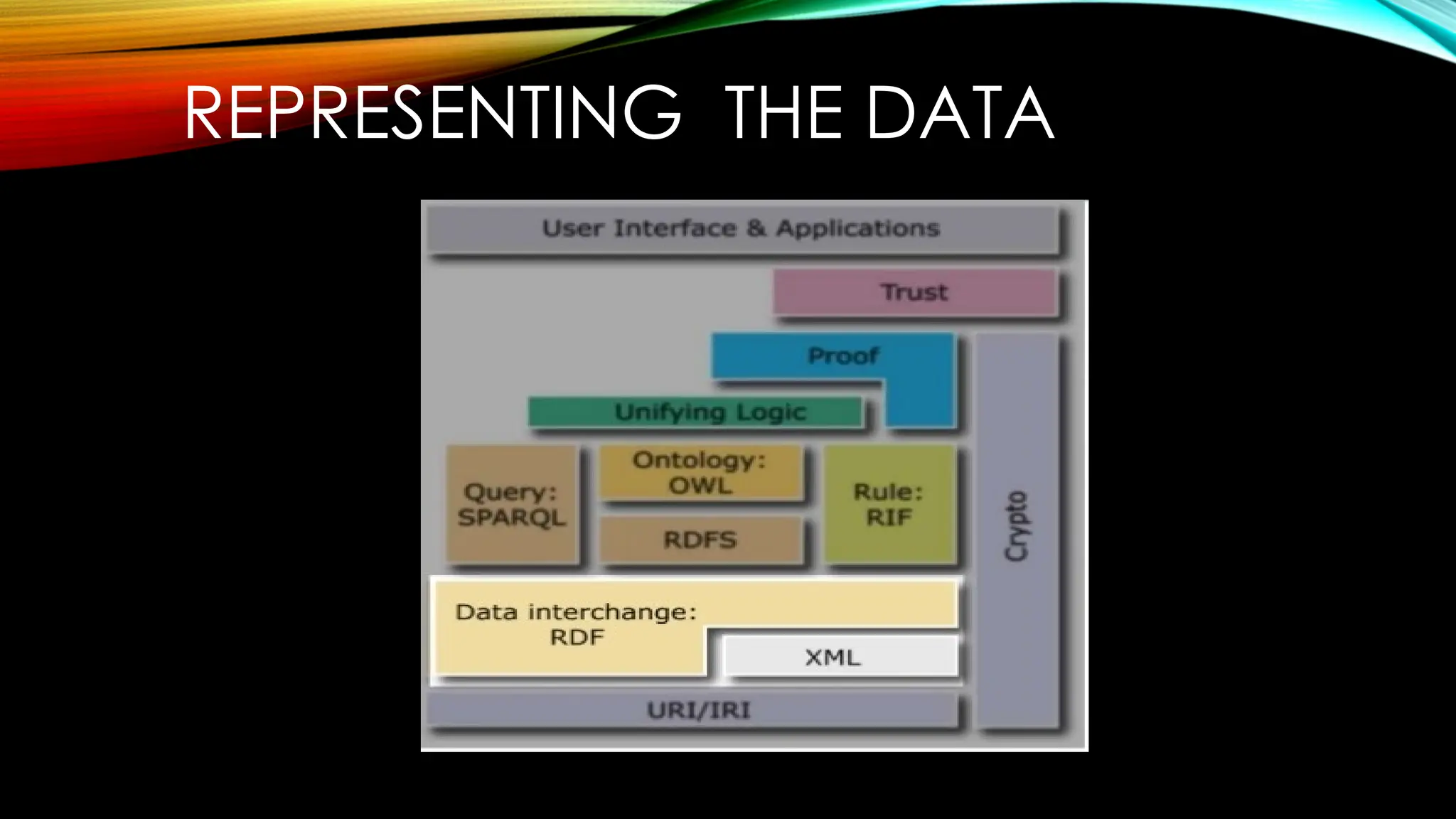
Semantic Web is an extension to the World Wide Web. The purpose of the semantic web is to provide structure to the web and data in general. It emphasizes on representing a web of data instead of web of documents. It allows computers to intelligently search, combine and process the web content based on the meaning that the content has. Three main models of the semantic web are:
Building models
Computing with Knowledge
Exchanging Information
Building Models: Model is a simplified version or description of certain aspects of the real-time entities. Model gathers information which is useful for the understanding of the particular domain.
Computing Knowledge: Conclusions can be obtained from the knowledge present. Example: If two sentences are given as 'John is the son of Harry' and another sentence given is- 'Hary's father is Joey', then the knowledge that can be computed from it is - 'John is the grandson of Joey' Similarly, another example useful in the understanding of computing knowledge is- 'All A is B' and 'All B is C', then the conclusion that can be drawn from it is - 'All A are C' respectively.
Exchanging Information: It is an important aspect. Various communication protocols have been implemented for the exchange of information like the TCP/IP, HTML, WWW. Web Services have also been used for the exchange of the data.
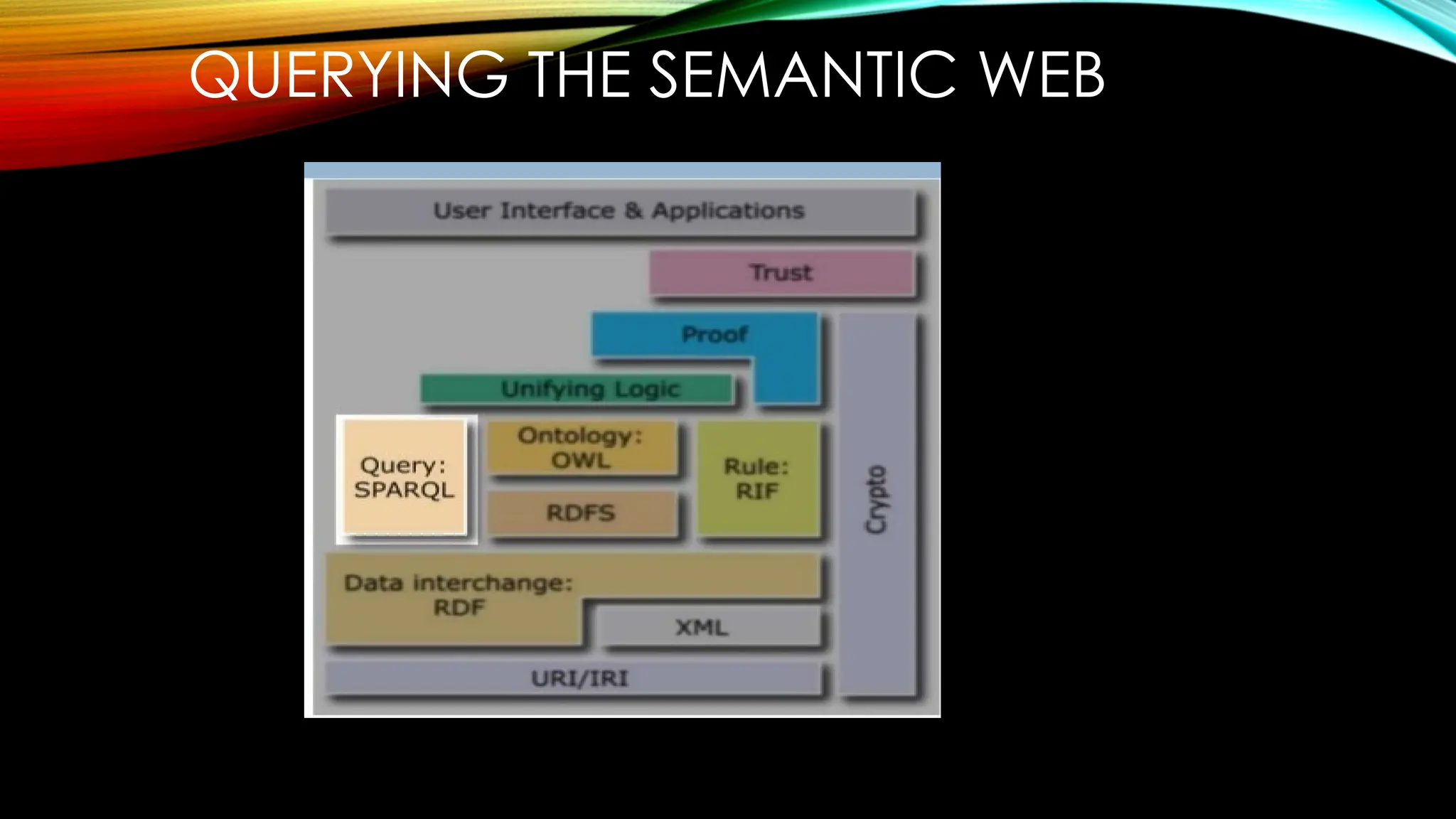
The technologies associated with the semantic web