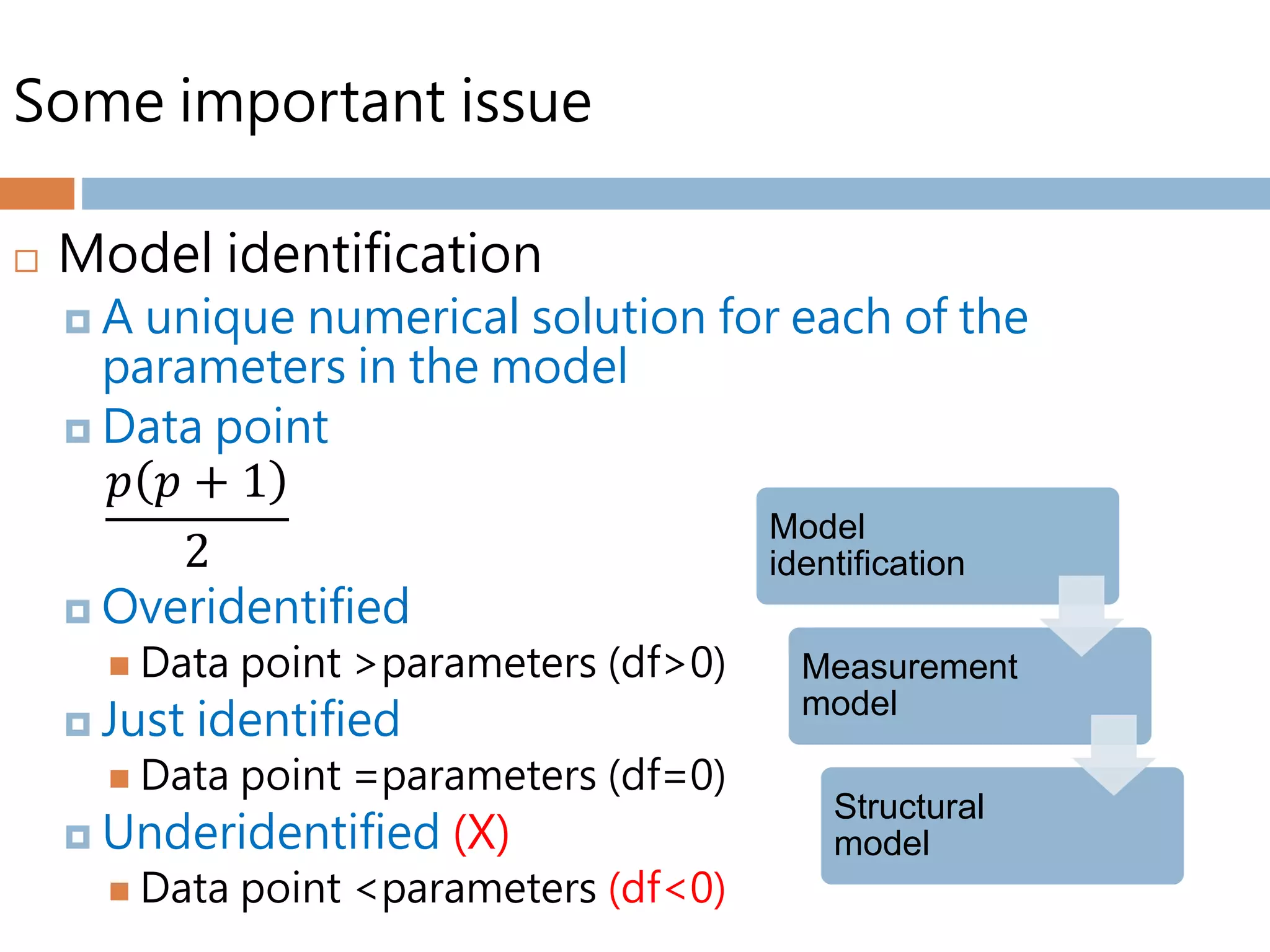
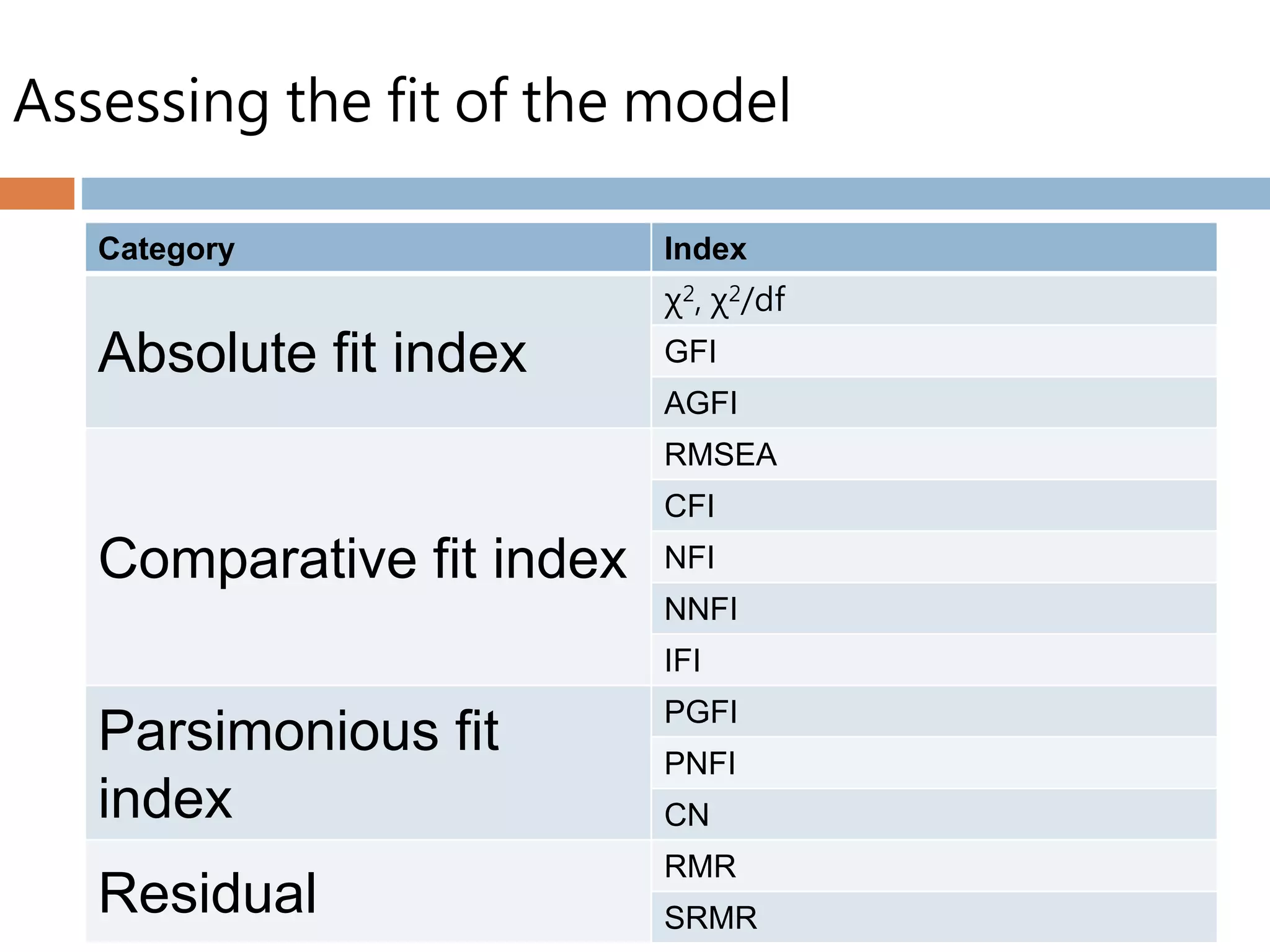
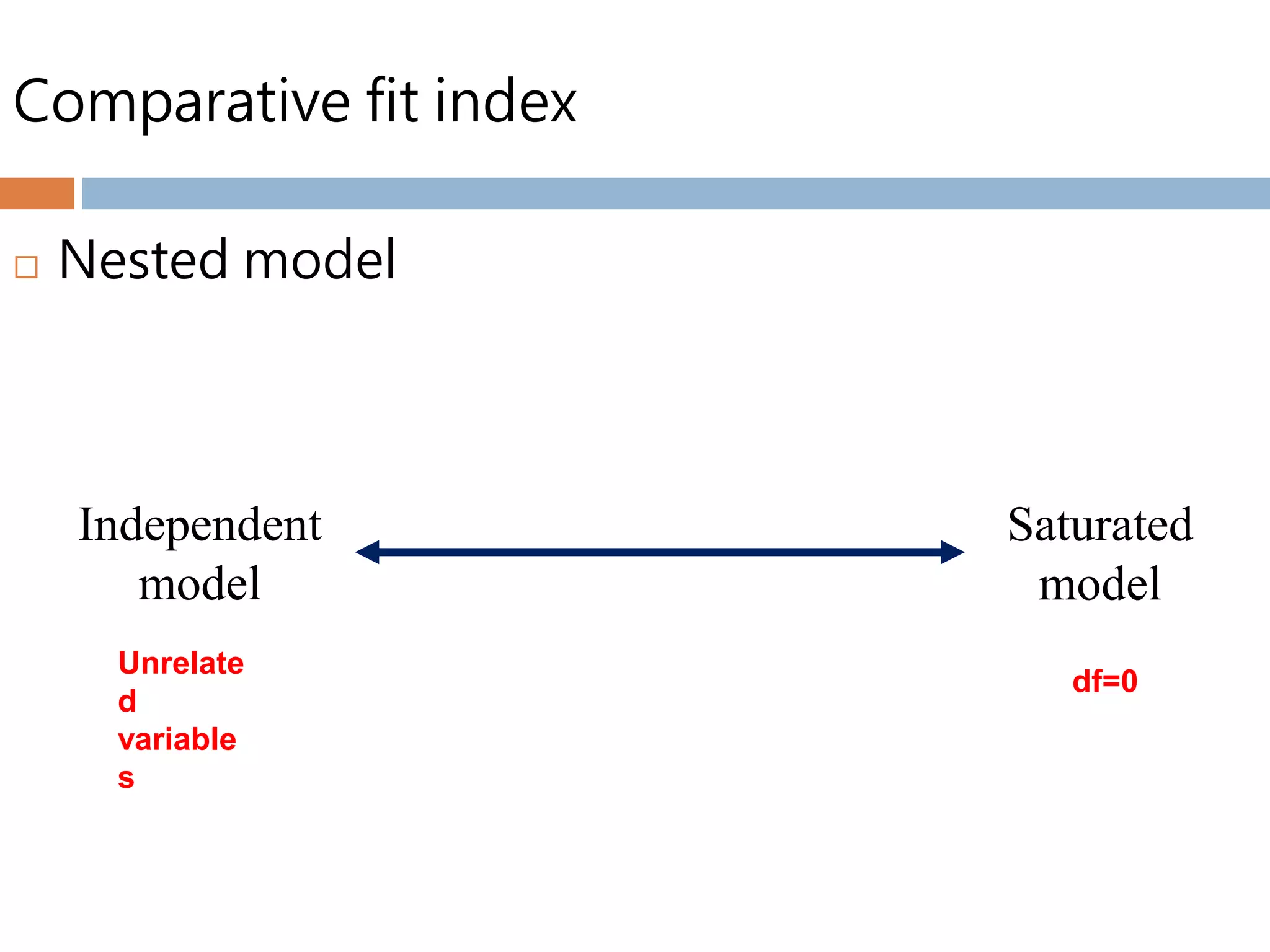
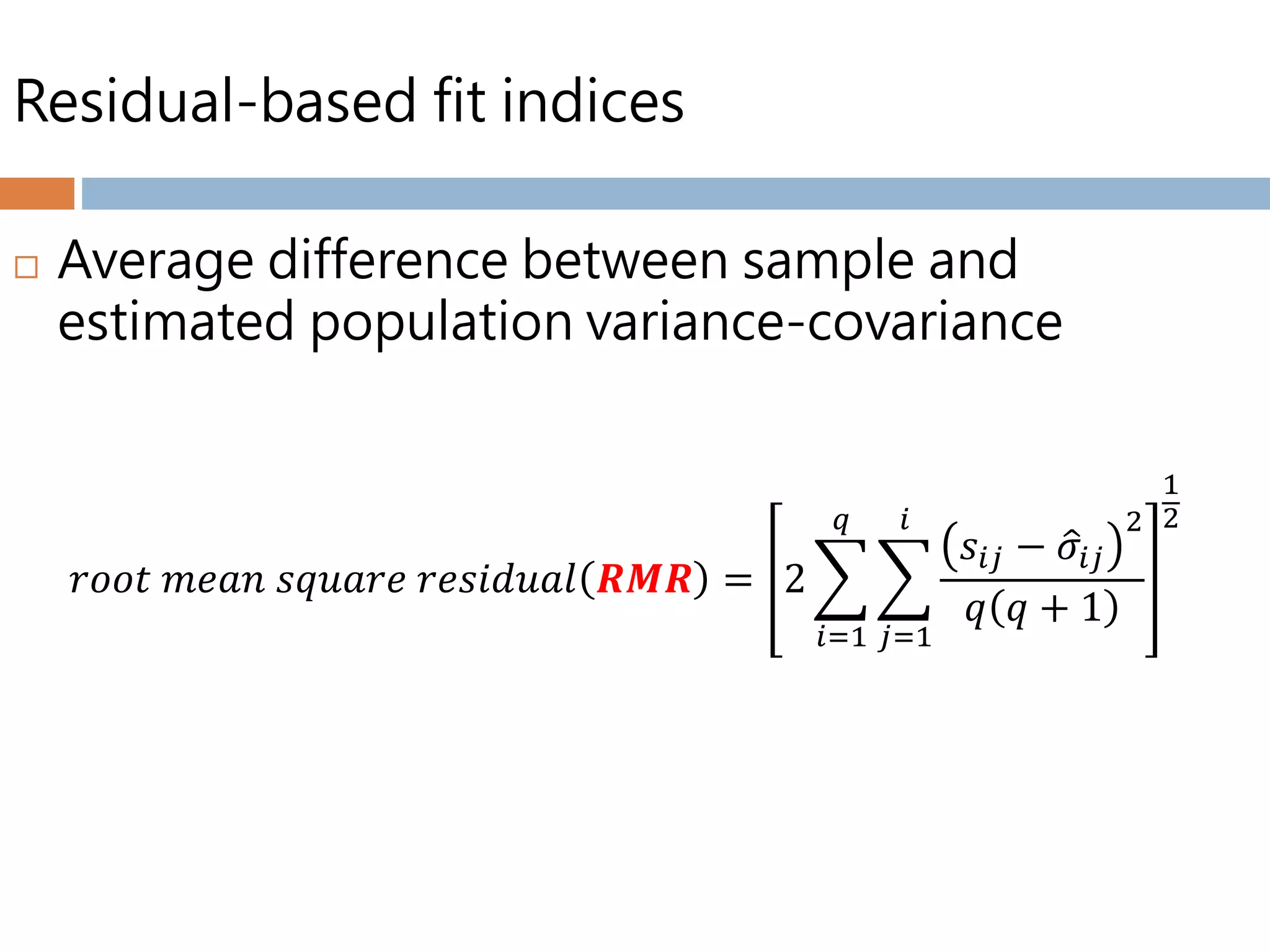
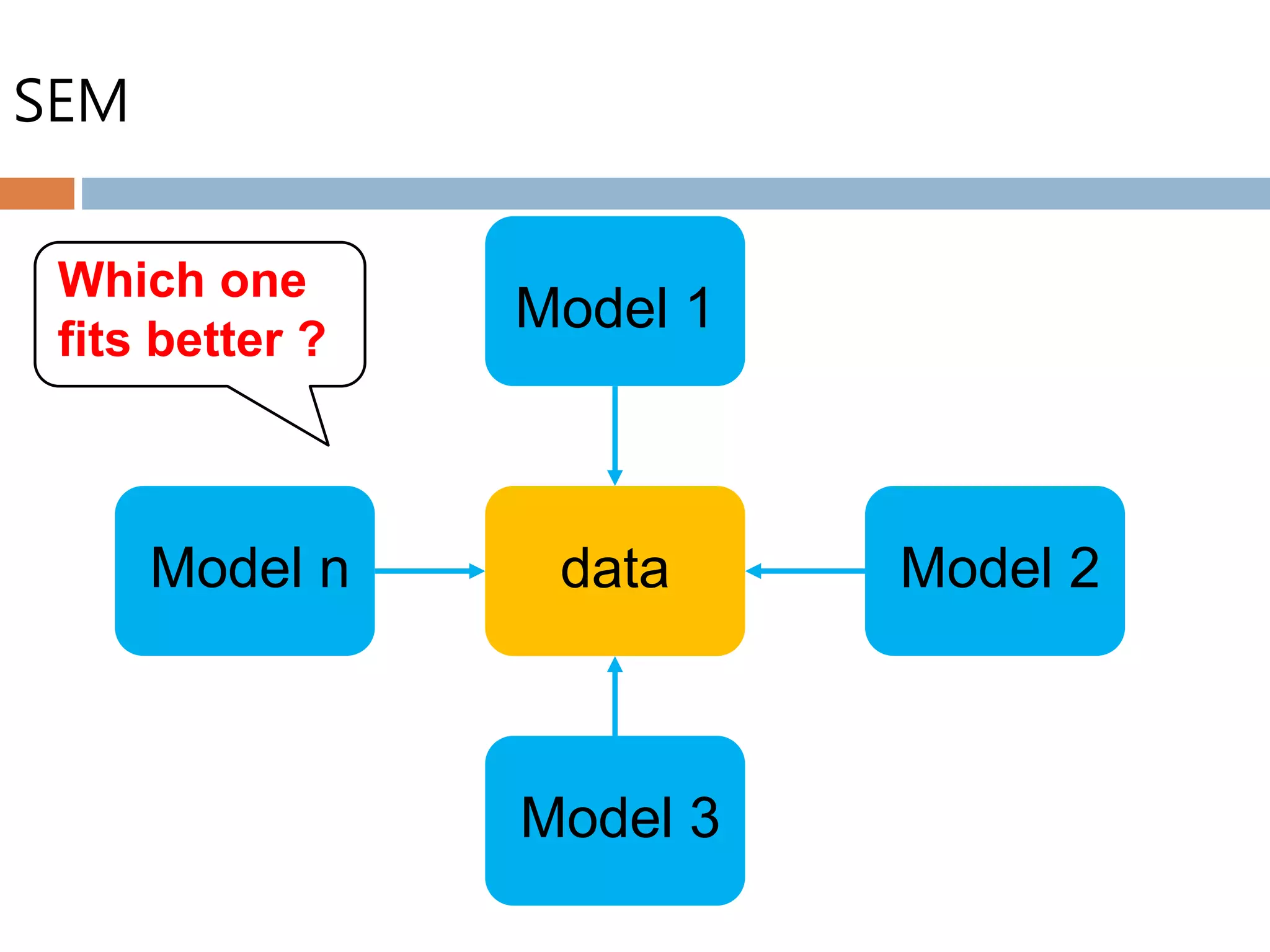
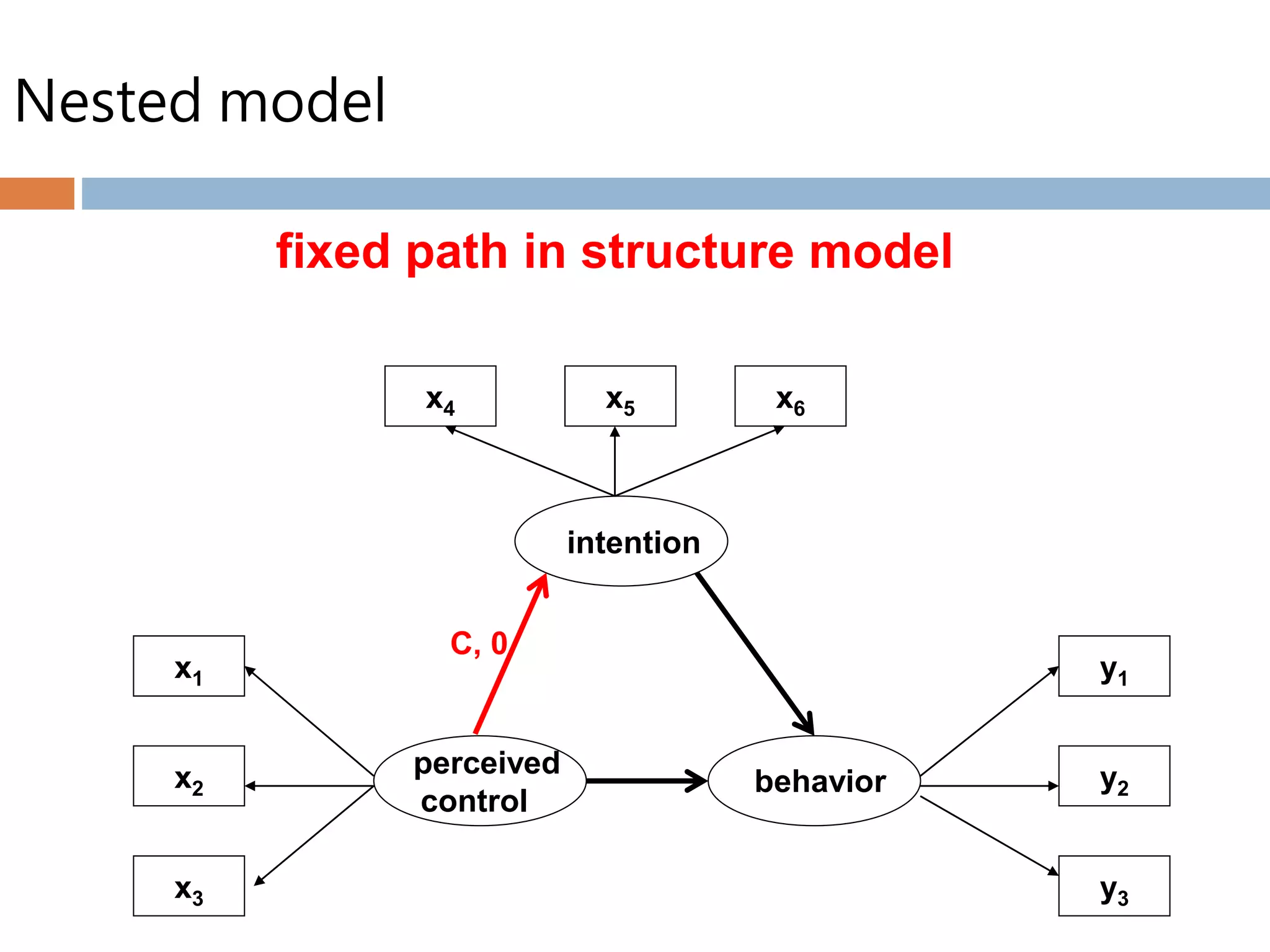
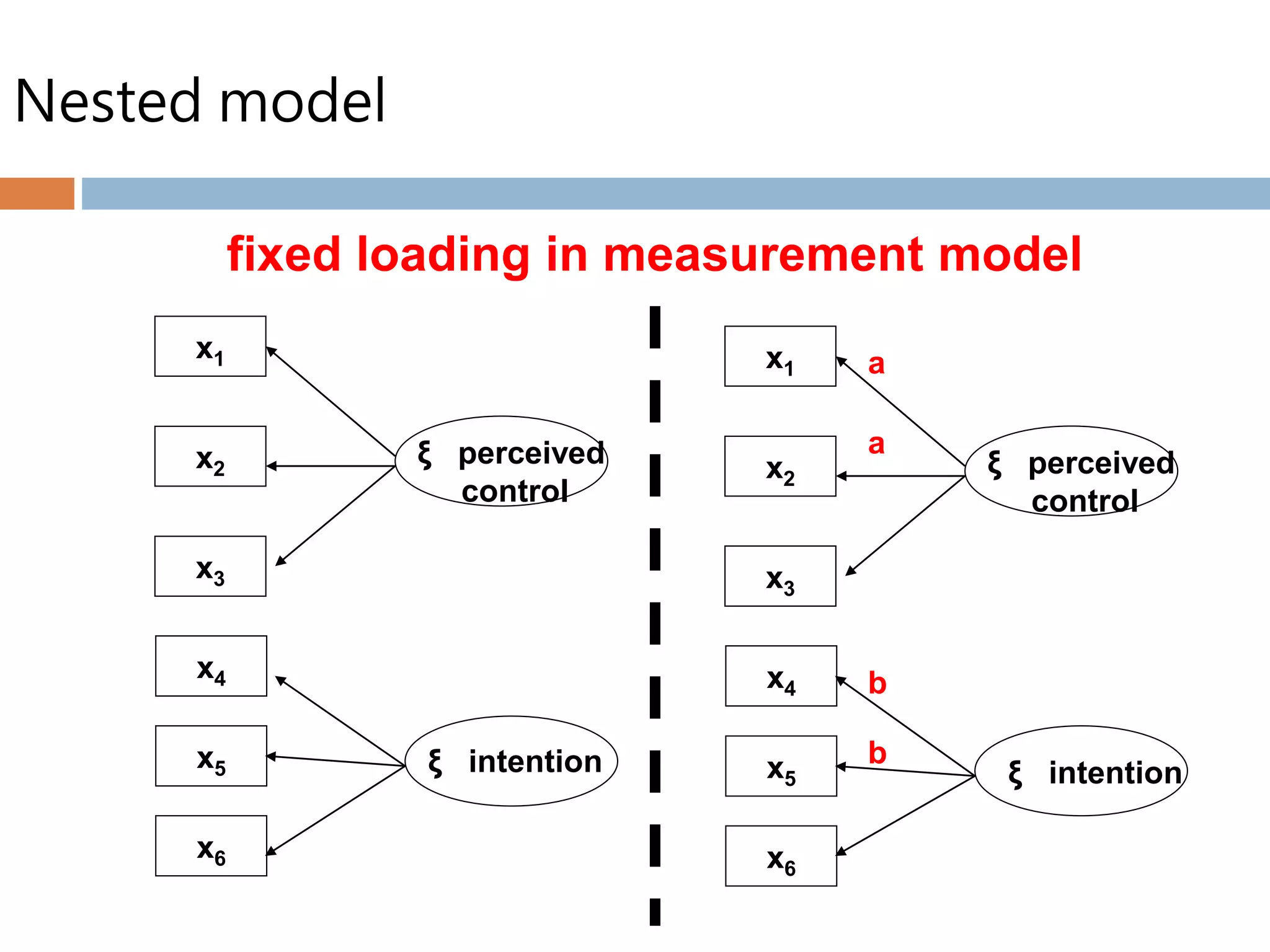
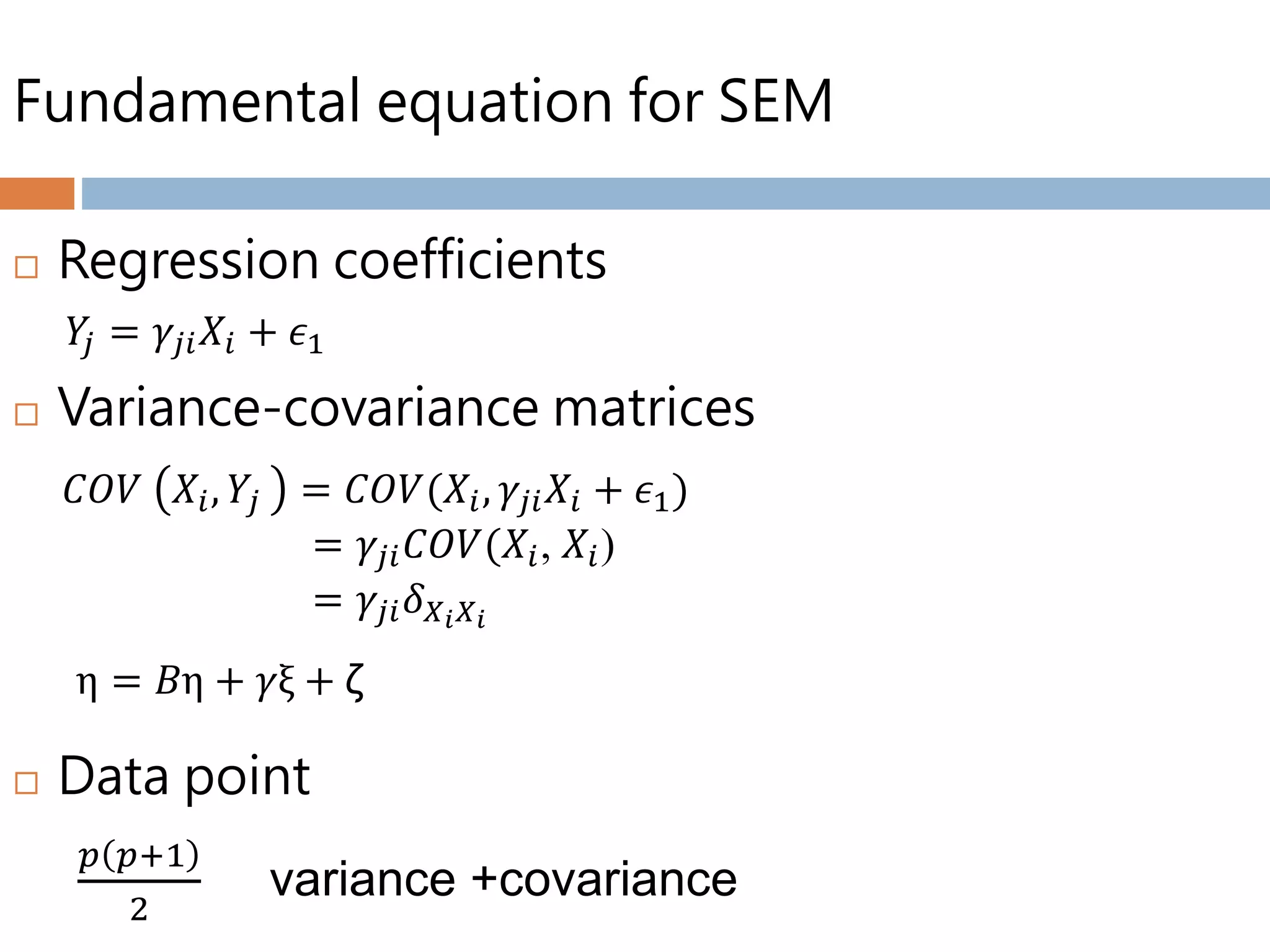
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is used to analyze relationships between multiple independent and dependent variables. It allows for simultaneous testing of these relationships while accounting for measurement error. The goal of SEM is to determine if the estimated population covariance matrix from the model fits the sample covariance matrix. It can be used to test theories, account for variance, and assess reliability and parameter estimates. Key considerations include sample size, normality, linearity, and identification of the model. Model fit is assessed using absolute, comparative, and parsimonious fit indices. Modification indices can also indicate how to improve model fit.




![Graphical representation for SEM
Measurement model
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA)
x1
x3
x2
δ1
δ 2
δ 3
ξ1
λ11
λ21
λ31
δ[delta] ; λ[lambda]; ξ[xi]
x1= λ11 ξ1+ δ1
x2= λ21 ξ1+ δ2
x3= λ31 ξ1+ δ3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sem-170118101257/75/SEM-7-2048.jpg)