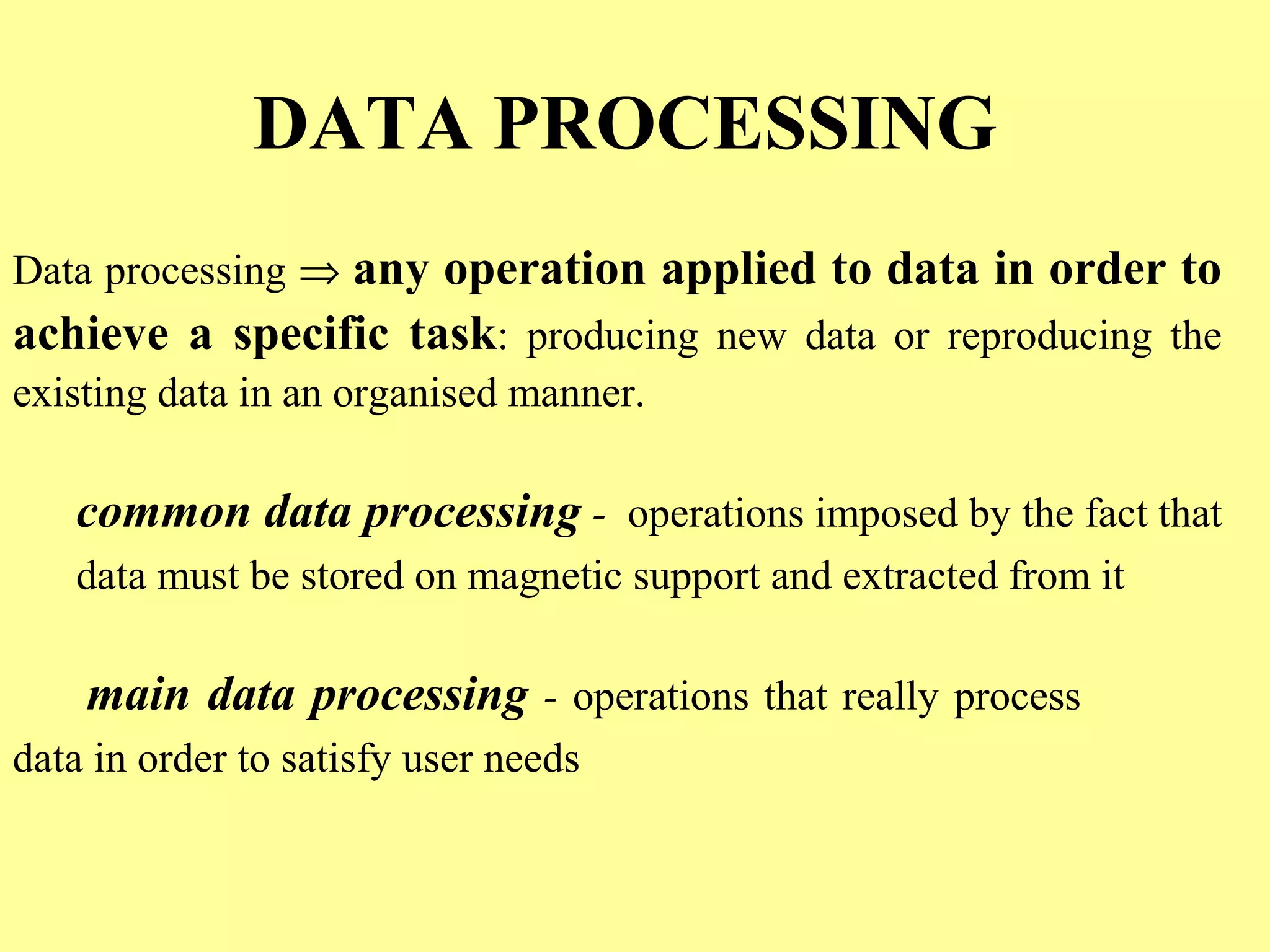
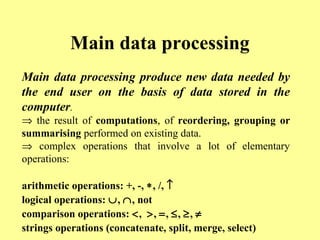
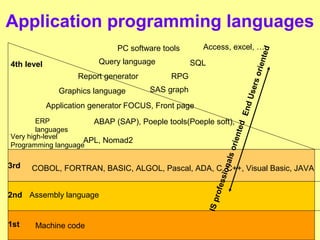
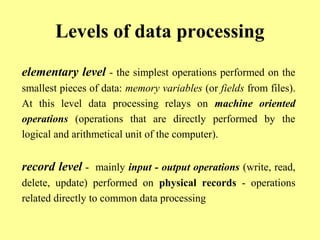
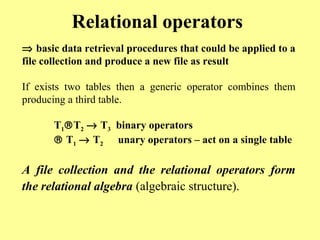
Data processing involves operations applied to data to achieve specific tasks like producing new data or organizing existing data. Common data processing includes storing, retrieving, and encoding/decoding data for magnetic storage. Main data processing uses operations like computations, reordering, grouping, and summarizing to produce new user-needed data from stored data. Programming languages have evolved from machine code through assembly languages to modern high-level languages like C++ and Java. Data processing can occur at the elementary, record, file, and relational levels.