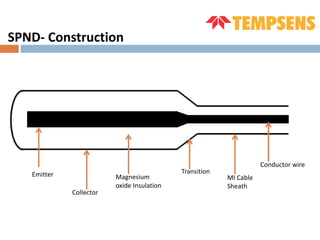
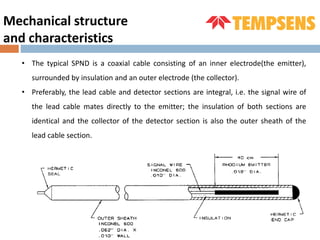
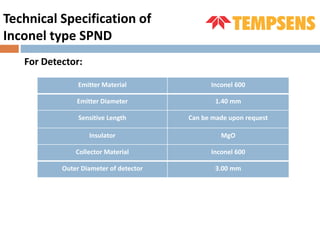
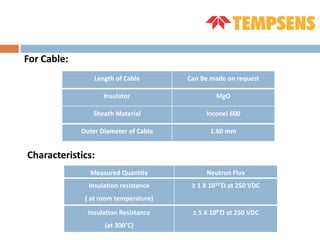
The document discusses self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs), which are used in nuclear reactors for monitoring in-core neutron flux without needing an external power source. It details their construction, characteristics, and materials used, as well as their applications and advantages, such as simplicity and robustness, along with disadvantages like limited operating range. The document emphasizes the importance of emitter material in determining performance and includes technical specifications for inconel type SPNDs.