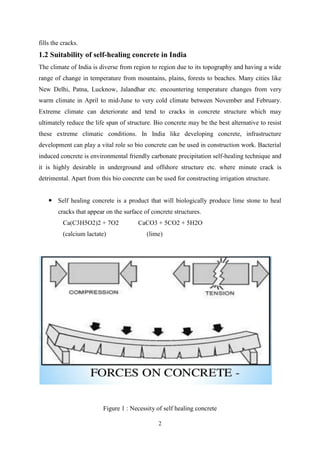
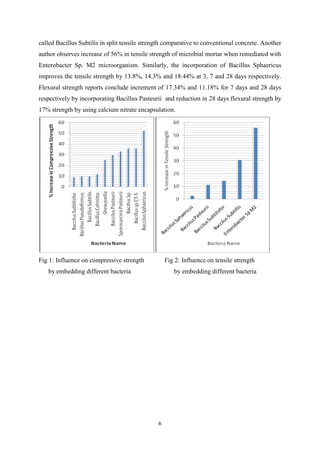
The seminar report by Irshad Ali Ansari presents research on self-healing concrete as part of his B.Tech in Civil Engineering. It discusses various approaches to self-healing, particularly the use of bacteria to enhance concrete durability and repair cracks, while comparing the properties of bio-concrete with conventional concrete. The report highlights significant improvements in the mechanical and durability properties of concrete through microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation.