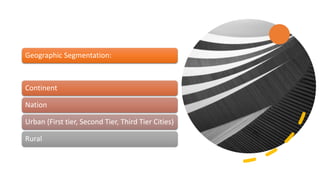
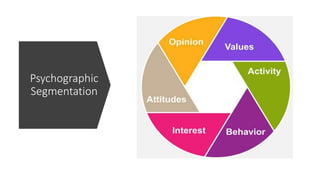
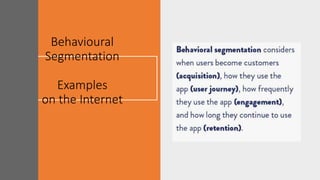
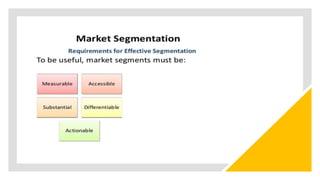
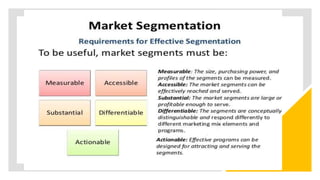
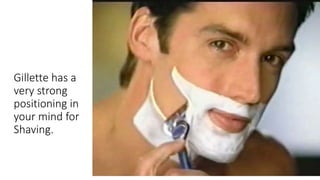
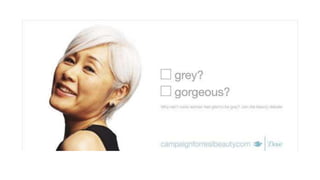
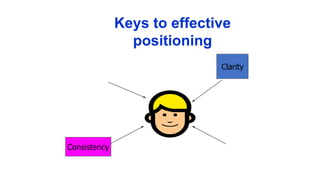
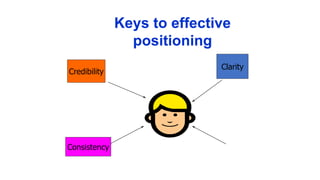
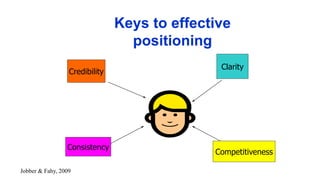
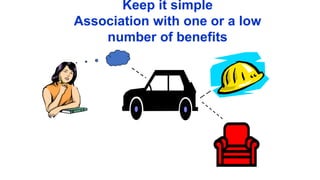
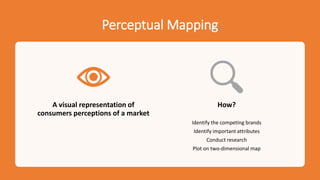
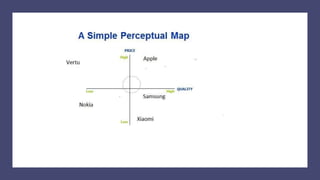
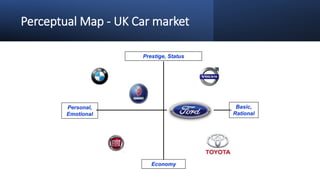
The document discusses key concepts in segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP) for marketing. It defines different types of segmentation criteria including geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral segmentation. It also explains the different targeting strategies of undifferentiated, focused, and differentiated targeting. Finally, it defines positioning as the space a brand occupies in the consumer's mind and provides examples from companies like Gillette, Apple, Dove, and Benetton to illustrate effective positioning strategies.