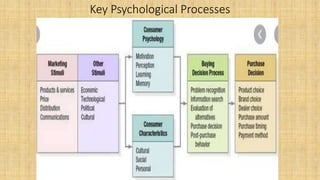
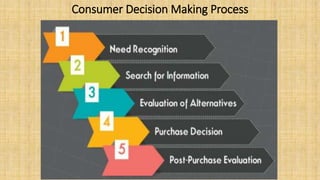
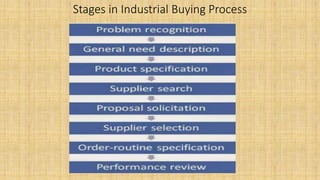
The document discusses consumer behavior and organizational buying. It defines consumer behavior as how individuals make decisions to spend resources on consumption items. Organizational buying refers to the decision-making process formal organizations use to identify, evaluate and select products and suppliers. The document outlines factors that influence consumer behavior such as social, cultural, personal, psychological factors and marketing factors. It also discusses the different types of buying decisions and roles involved in organizational purchases.