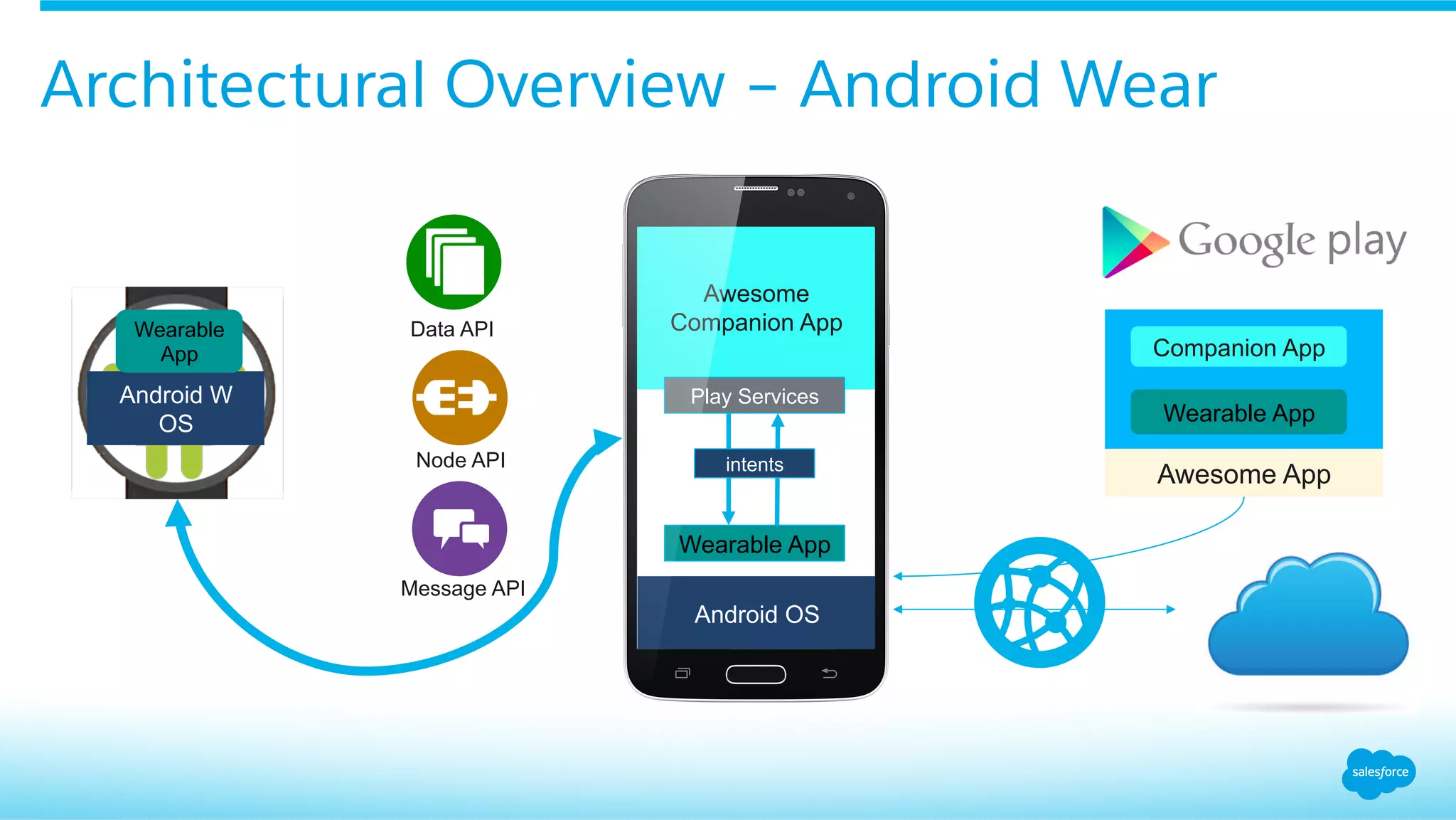
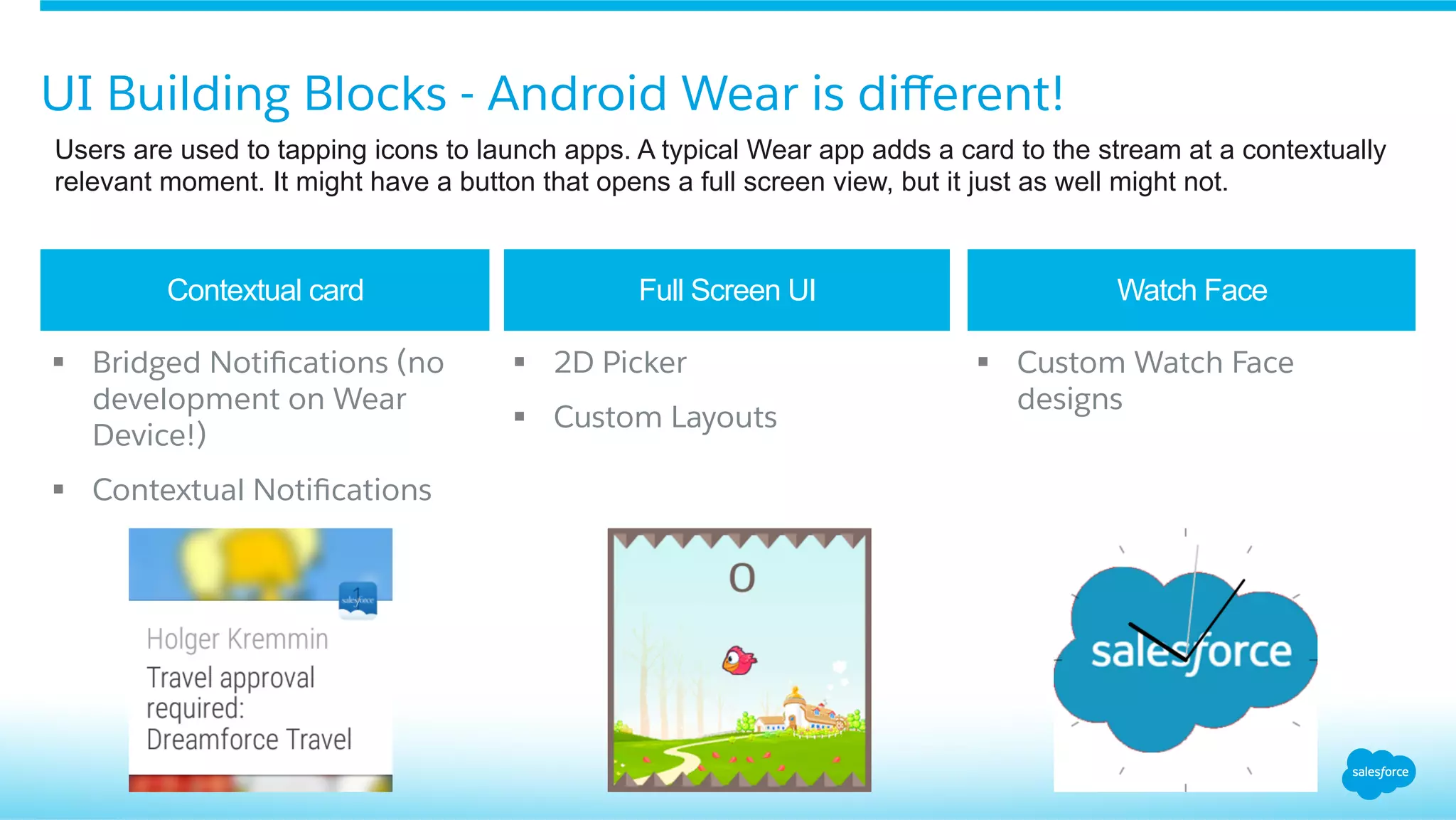
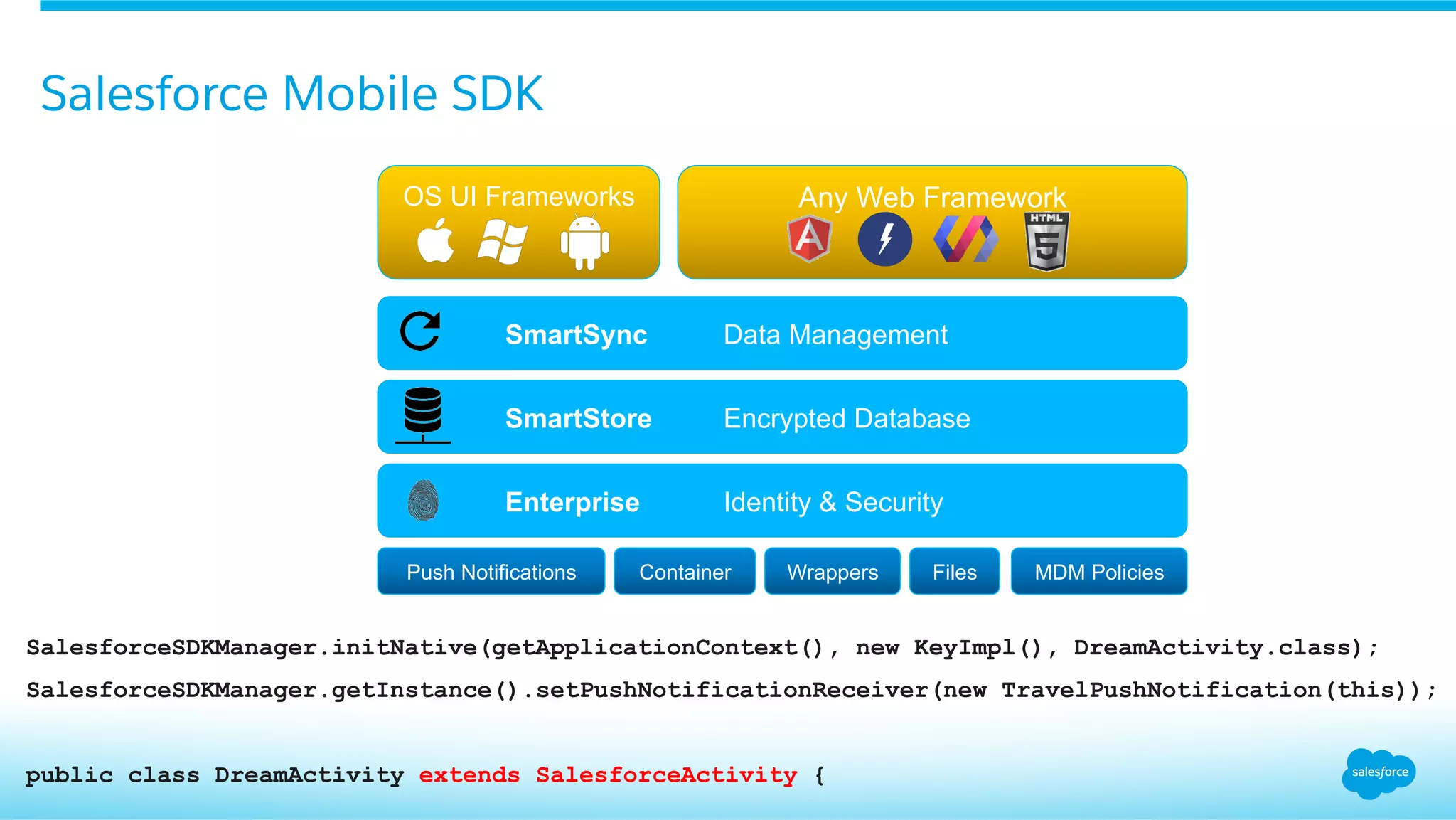
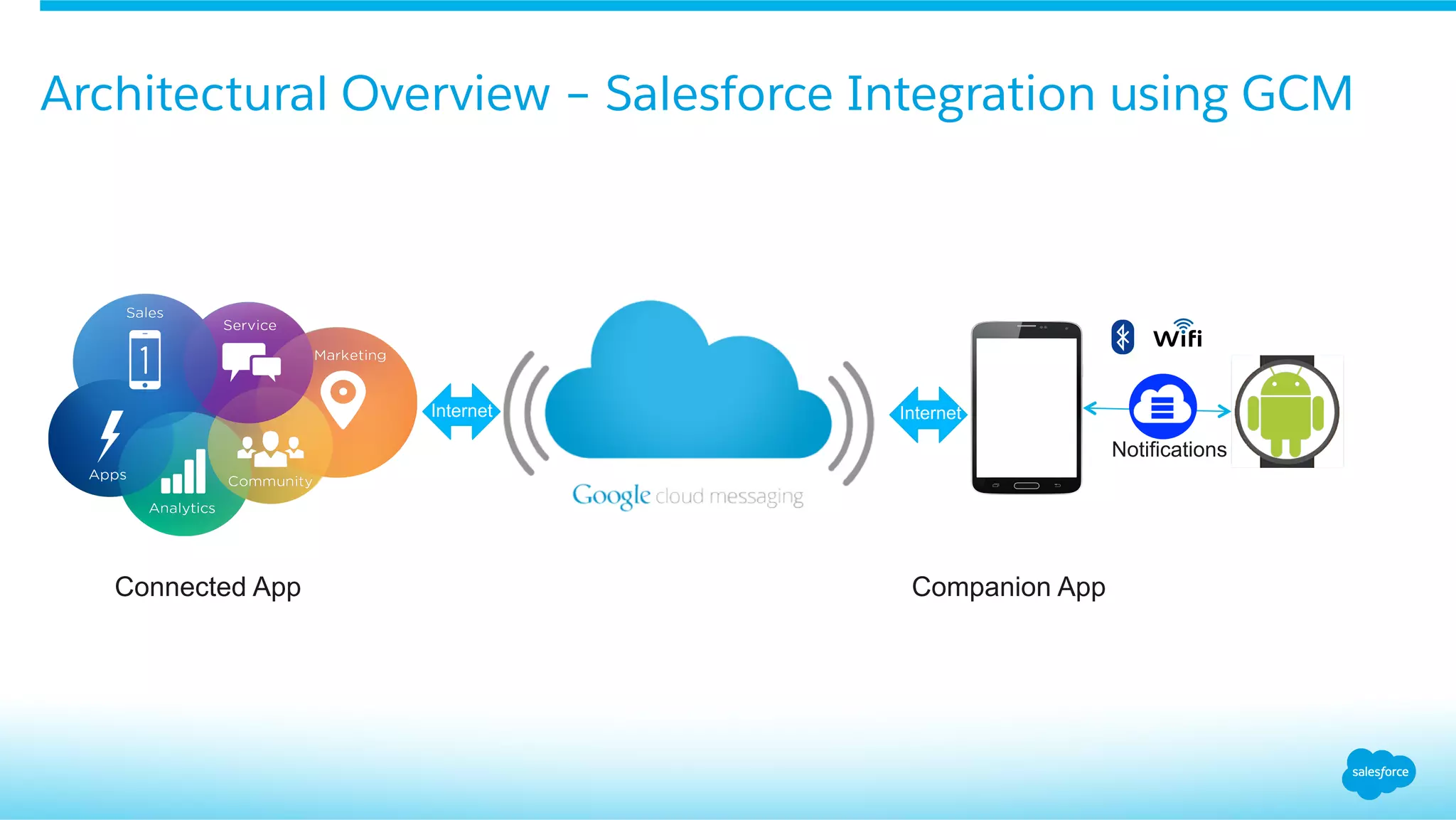
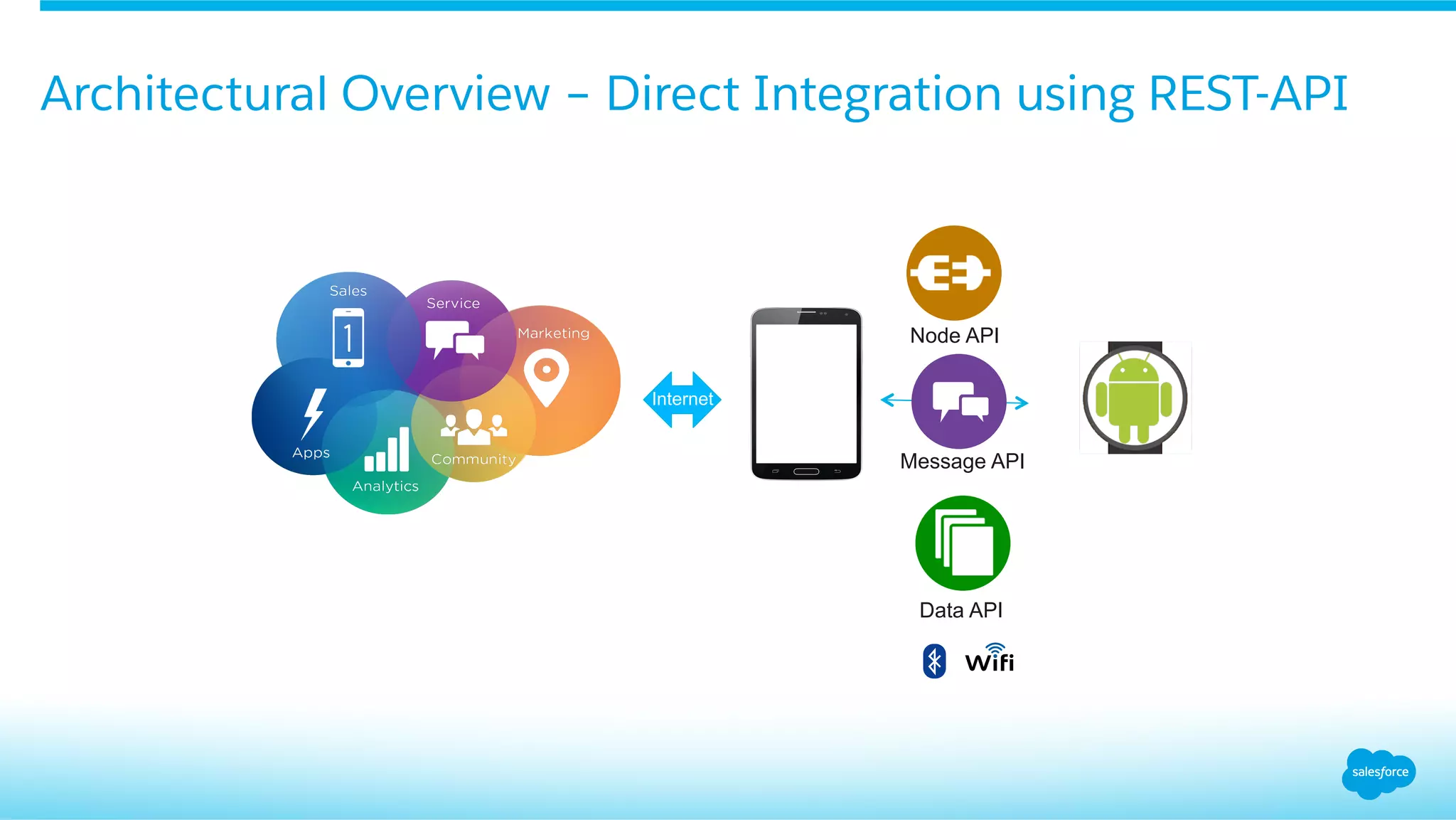
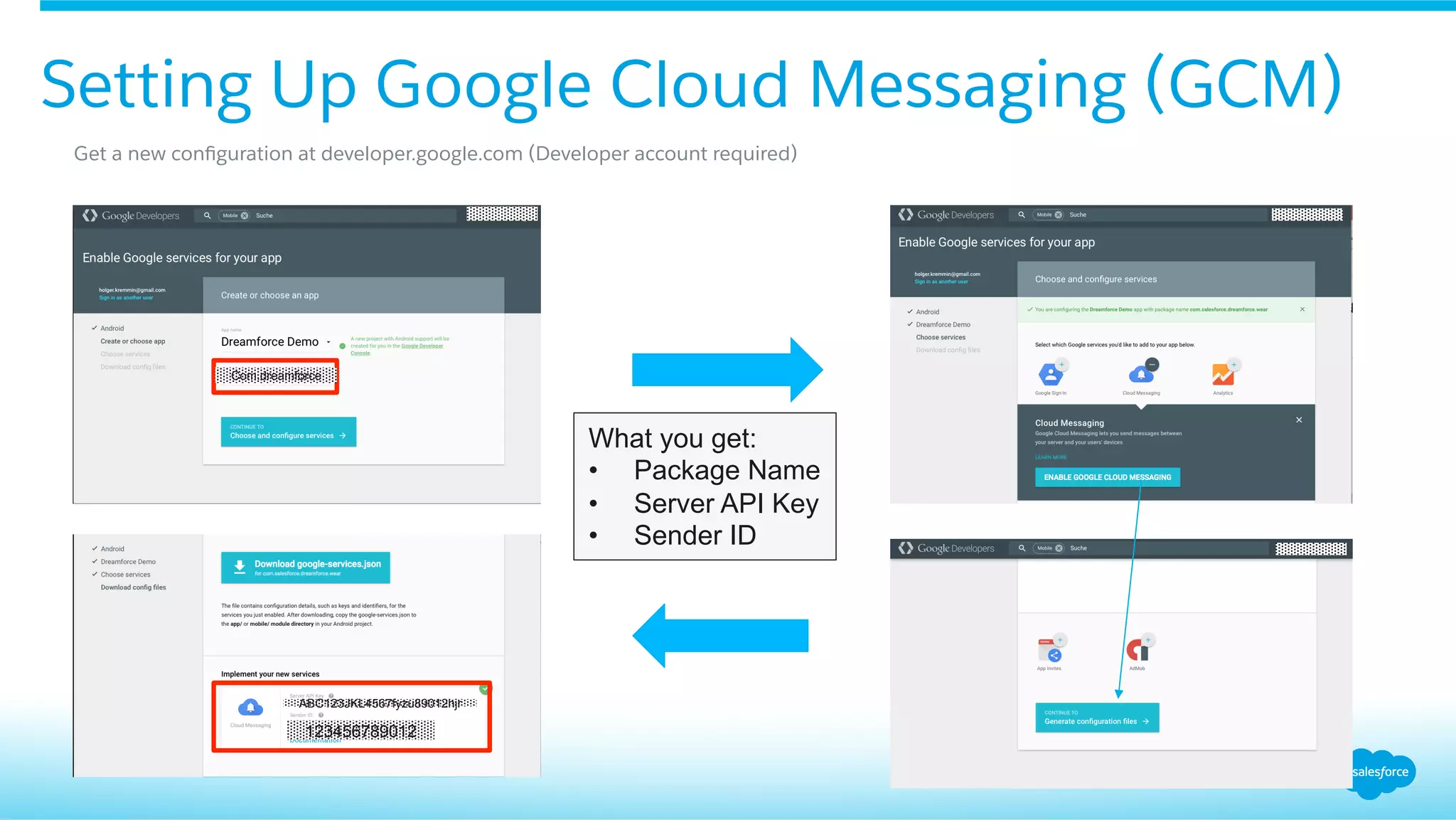
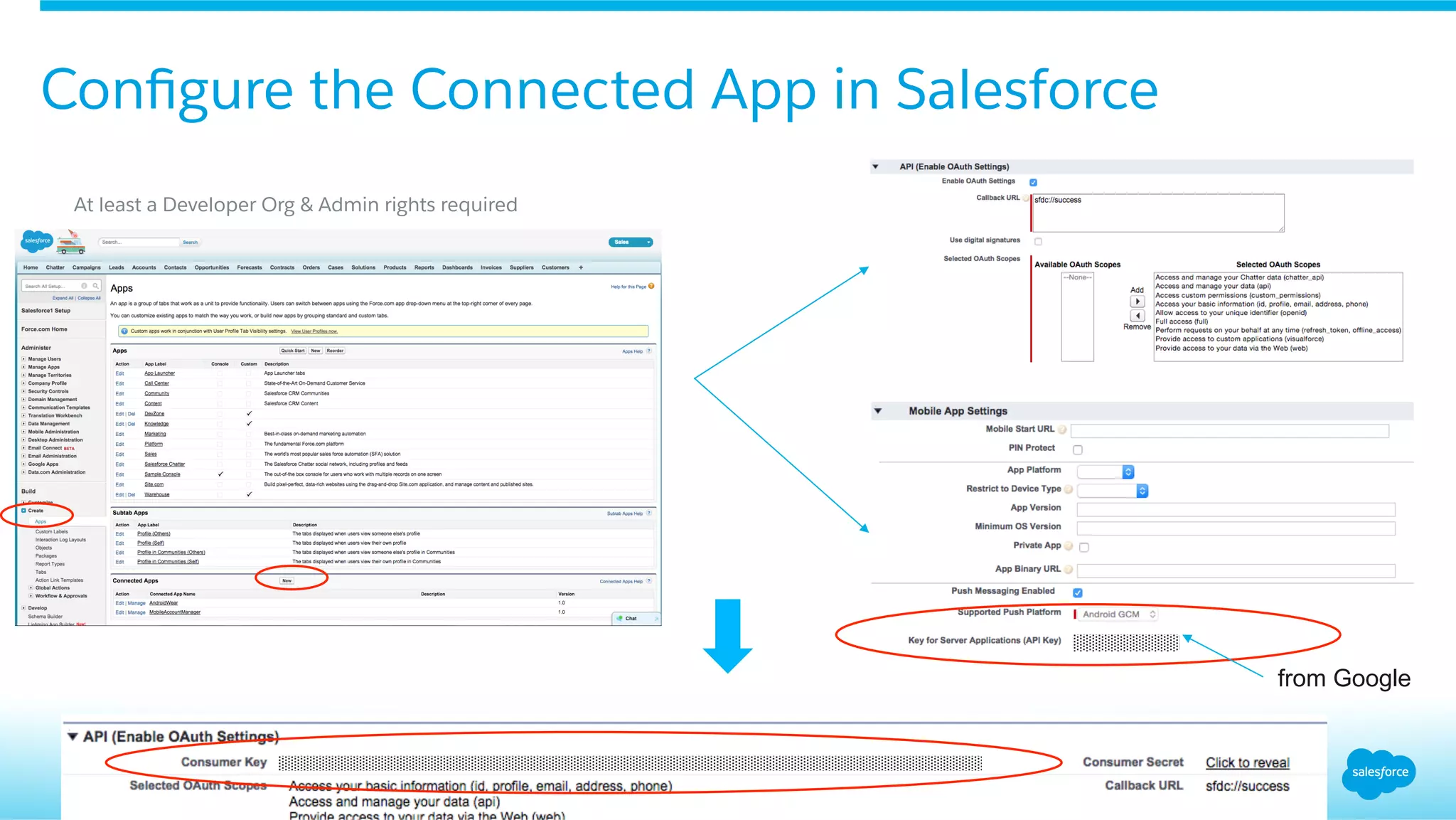
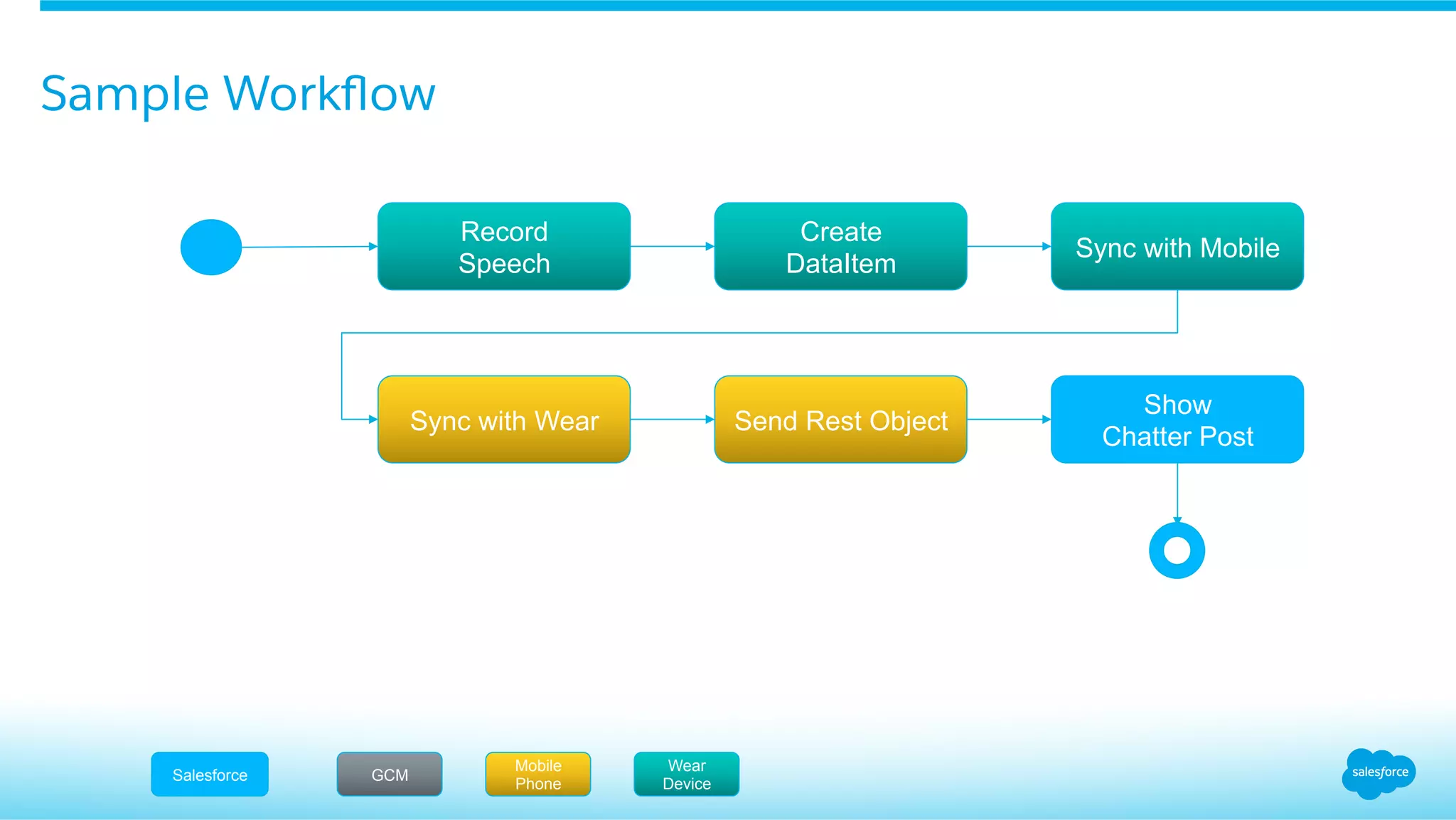
This document provides an overview of integrating Android Wear devices with Salesforce, detailing the architecture, requirements, and development process involved. It discusses key features such as notifications, data synchronization, and using the Salesforce Mobile SDK to create applications. Additionally, it highlights necessary setup steps and challenges developers might face while building their wearable applications for Salesforce.








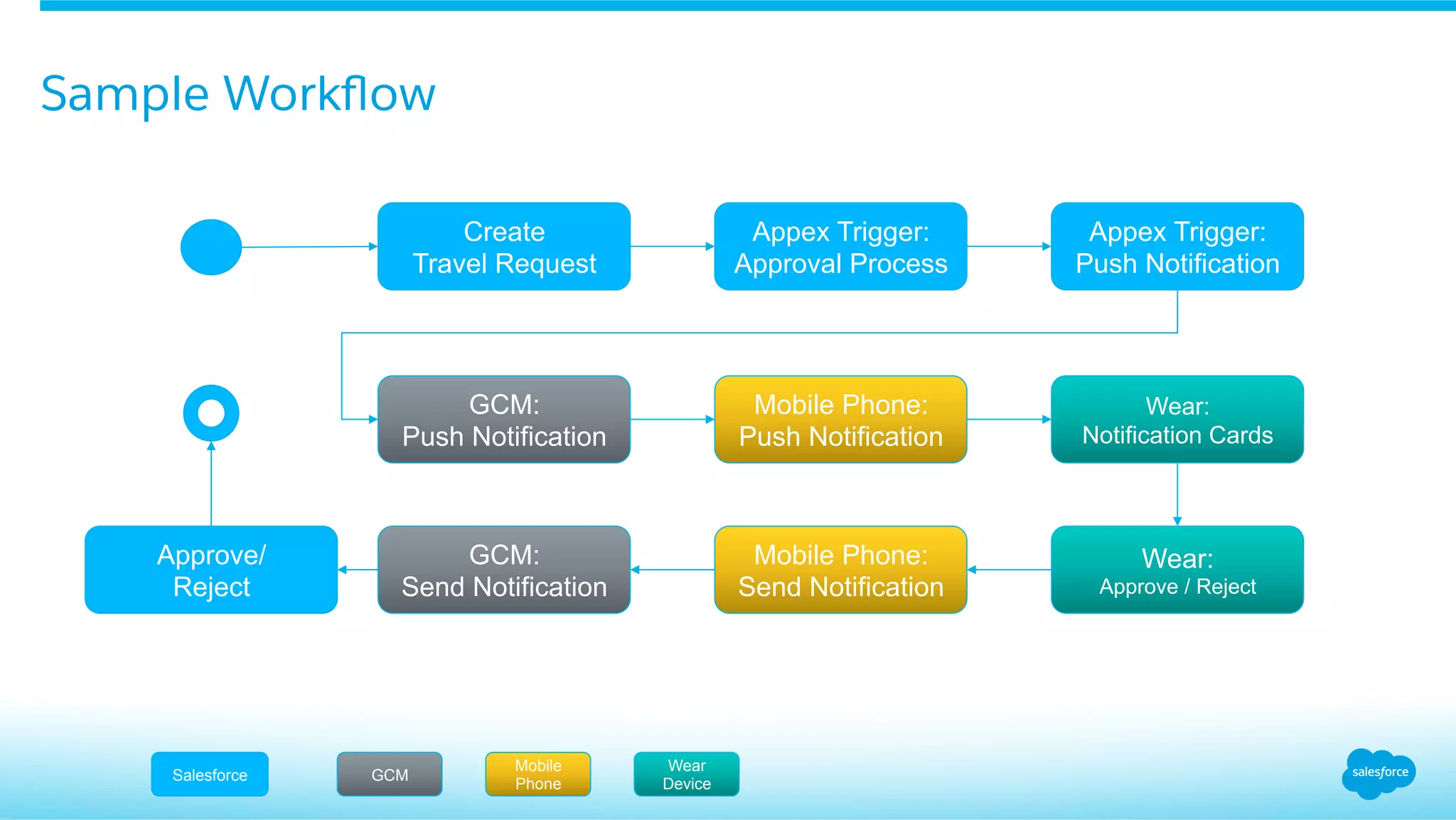
![Apex Code Snippet – Create & Send Notification/ Message
// send the notification
Messaging.PushNotification msg = new Messaging.PushNotification();
Map<String, Object> payload = new Map<String, Object>();
payload.put('ownerName', owner.Name);
payload.put('ownerFullPhotoUrl', owner.FullPhotoUrl);
...
msg.setPayload(payload);
// The approver's Id
String userId = result.actorIds[0];
Set<String> users = new Set<String>();
users.add(userId);
msg.send('Android_Wear', users);
Create Message Object
Create Payload
Add Payload to Message
Add target Users
Send Message to target
Users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uj32vpvqsmesl0beu9ex-signature-7873c75031ac31677418d06ca1135ba58cf1db5a062456d83a04778887726afe-poli-151012220143-lva1-app6892/75/See-Androids-Fighting-Connect-Salesforce-with-Your-Android-Wear-Watch-19-2048.jpg)
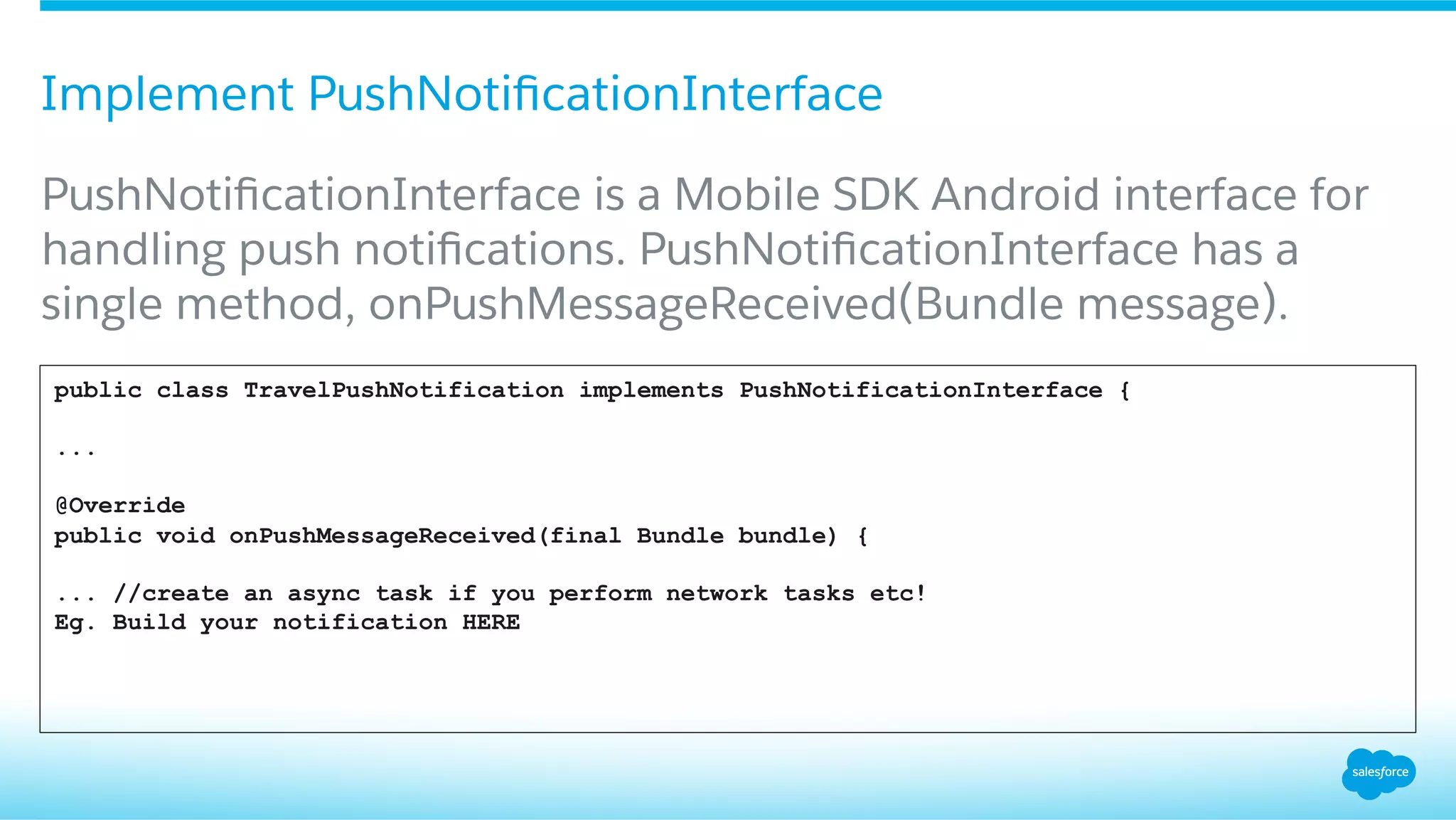





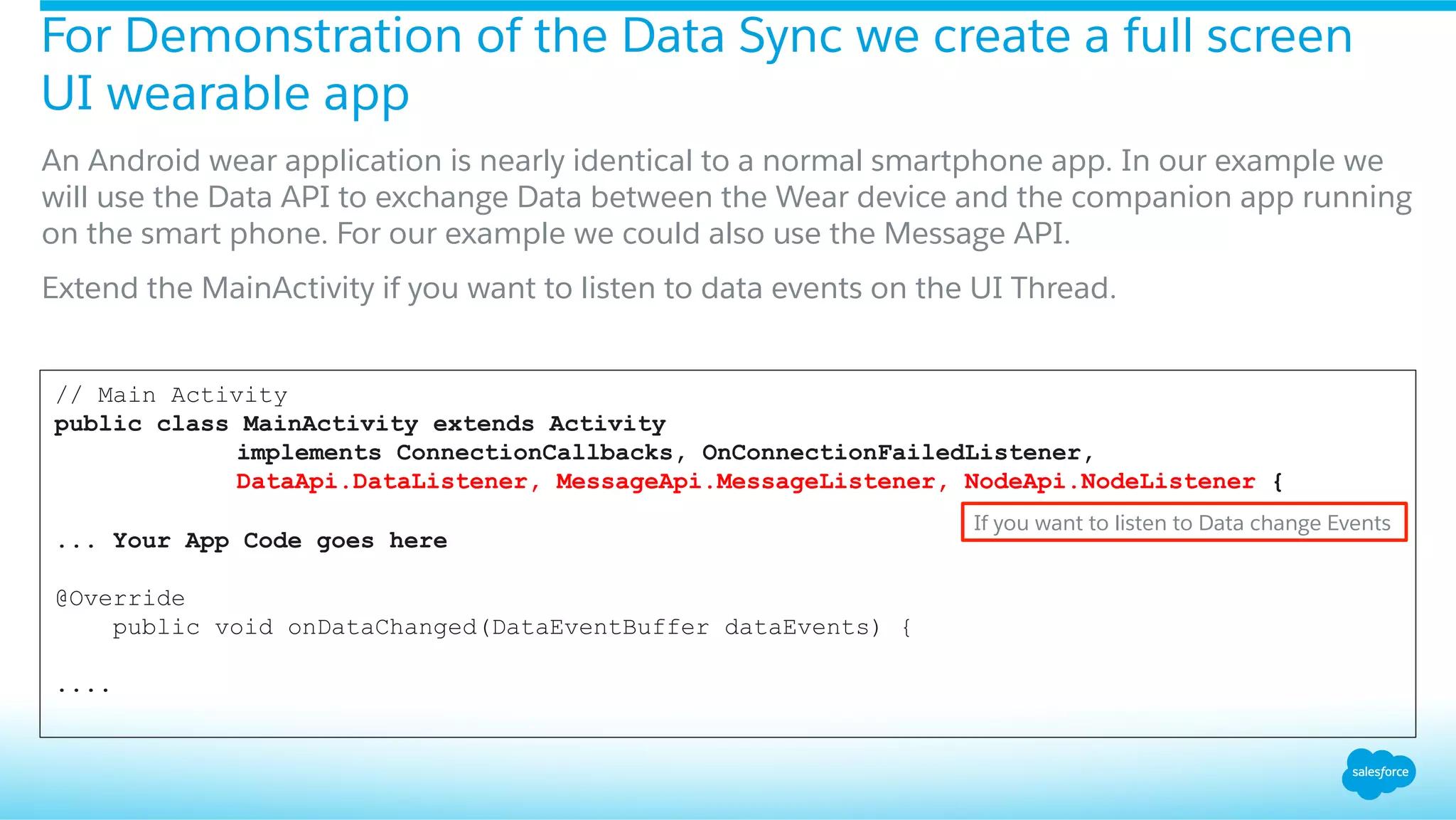

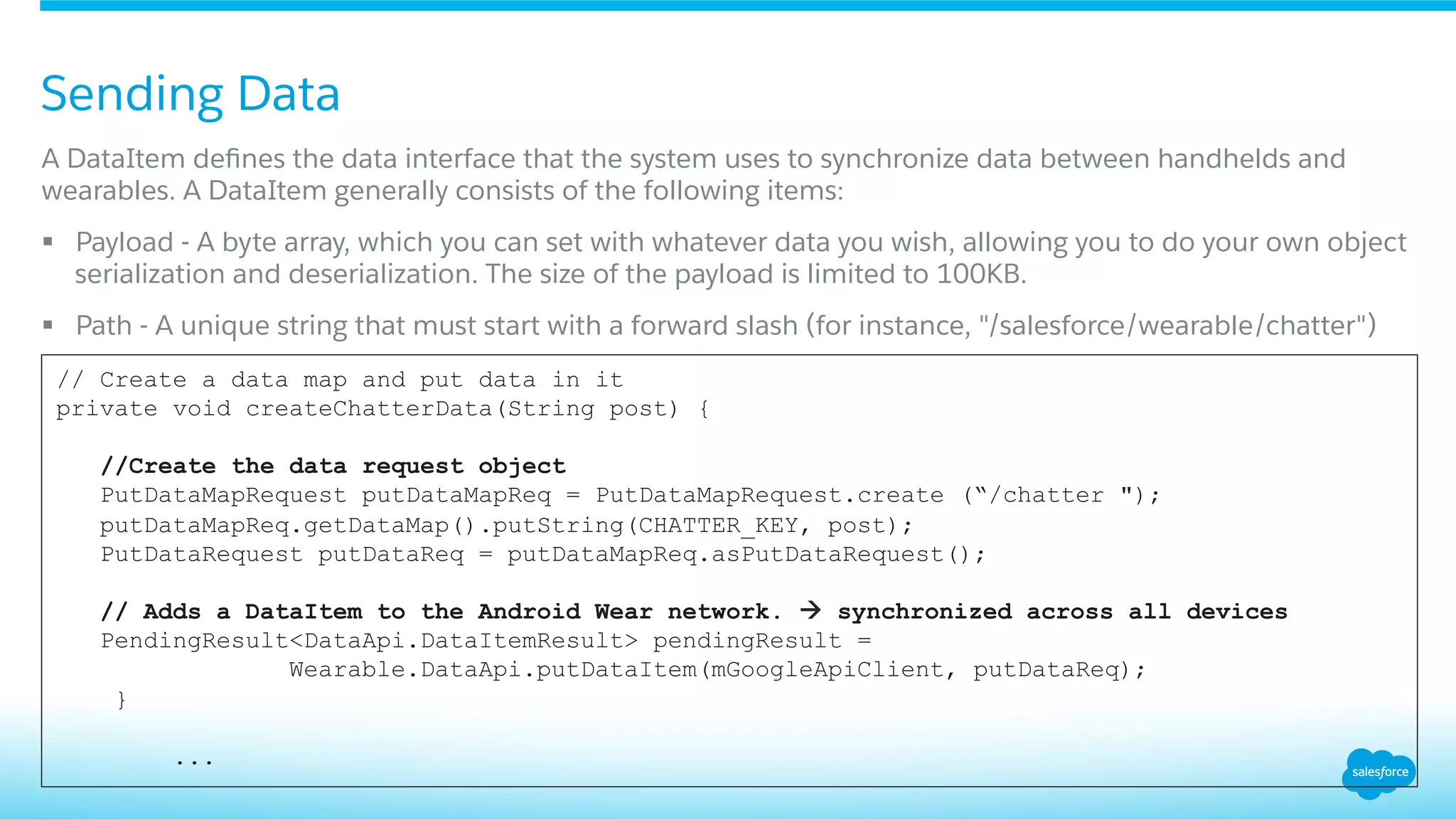
![A DataLayerService will listen on all data events
The data layer synchronizes and sends data across the handheld and wearable, you normally want to listen
for important events, such as when data items are created, are received, etc. Options:
§ Create a service that extends WearableListenerService.
§ Create an activity that implements DataApi.DataListener.
public class DataLayerListenerService extends WearableListenerService {
/.../
@Override
public void onDataChanged(DataEventBuffer dataEvents) {
if (!mGoogleApiClient.isConnected()... //check for connectivity!!!
// Loop through the events for (DataEvent event : dataEvents) {
Uri uri = event.getDataItem().getUri();
String path = uri.getPath();
if (COUNT_PATH.equals(path)) {
// get the payload
byte[] payload = uri.toString().getBytes();
// *Chatter something J
postChatterMessage(payload);
...
Leveraging the
MobileSDK
(Authentication, Rest
Calls etc…)
* See https://github.com/forcedotcom/JavaChatterRESTApi by Jasper Roel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uj32vpvqsmesl0beu9ex-signature-7873c75031ac31677418d06ca1135ba58cf1db5a062456d83a04778887726afe-poli-151012220143-lva1-app6892/75/See-Androids-Fighting-Connect-Salesforce-with-Your-Android-Wear-Watch-30-2048.jpg)