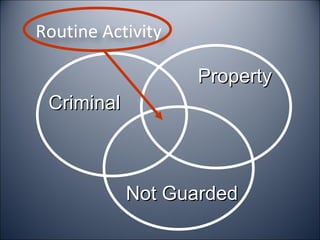
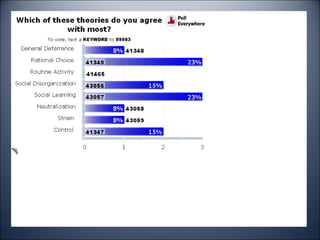
The document discusses several criminological theories: general deterrence, rational choice, routine activity, social disorganization, social learning, neutralization, strain, and control theories. It also mentions other approaches like critical theory and life course theories. The document asks which theory is agreed with most and provides a poll to vote on general deterrence, rational choice, routine activity, social disorganization, social learning, neutralization, or strain theory.