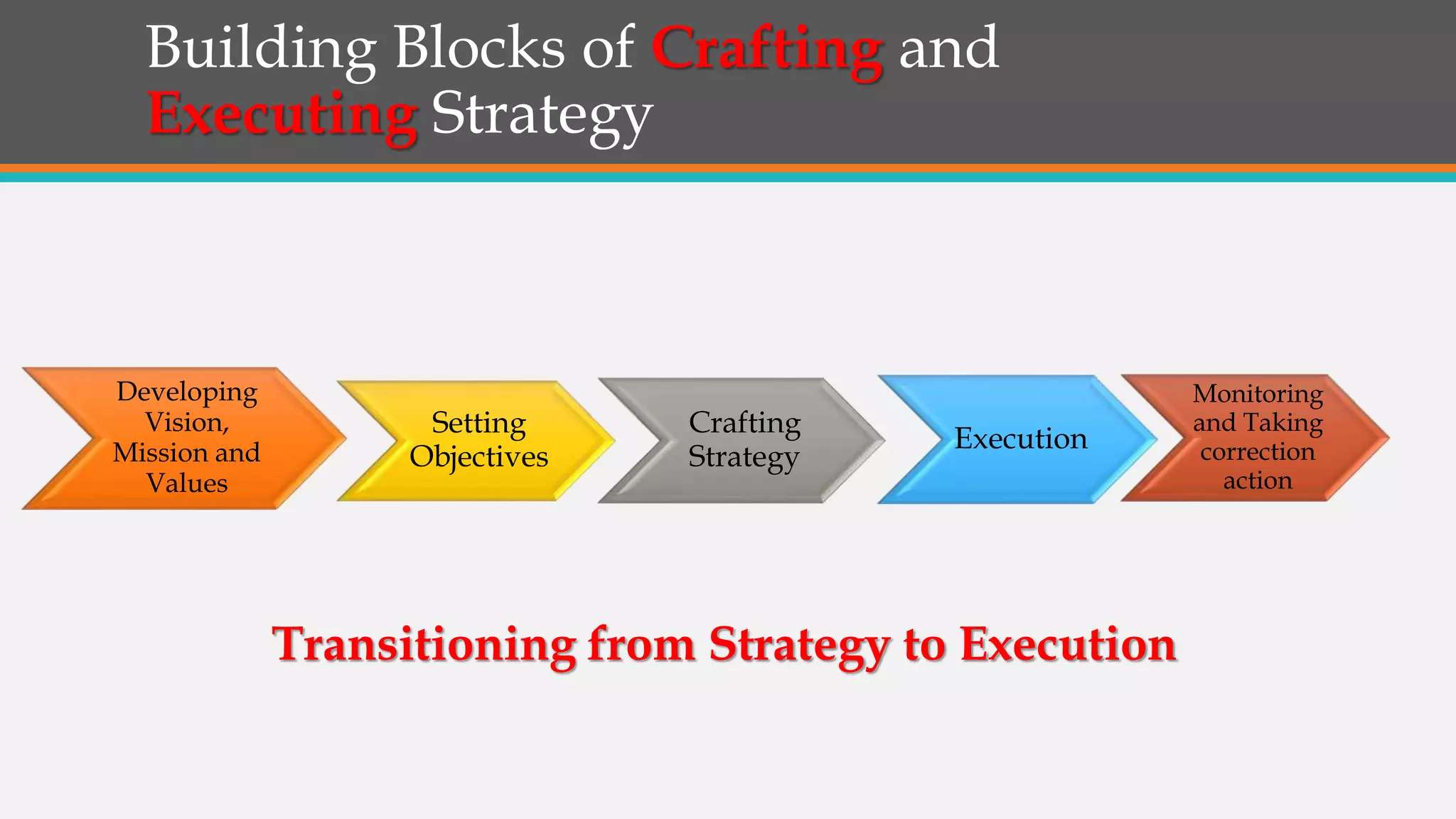
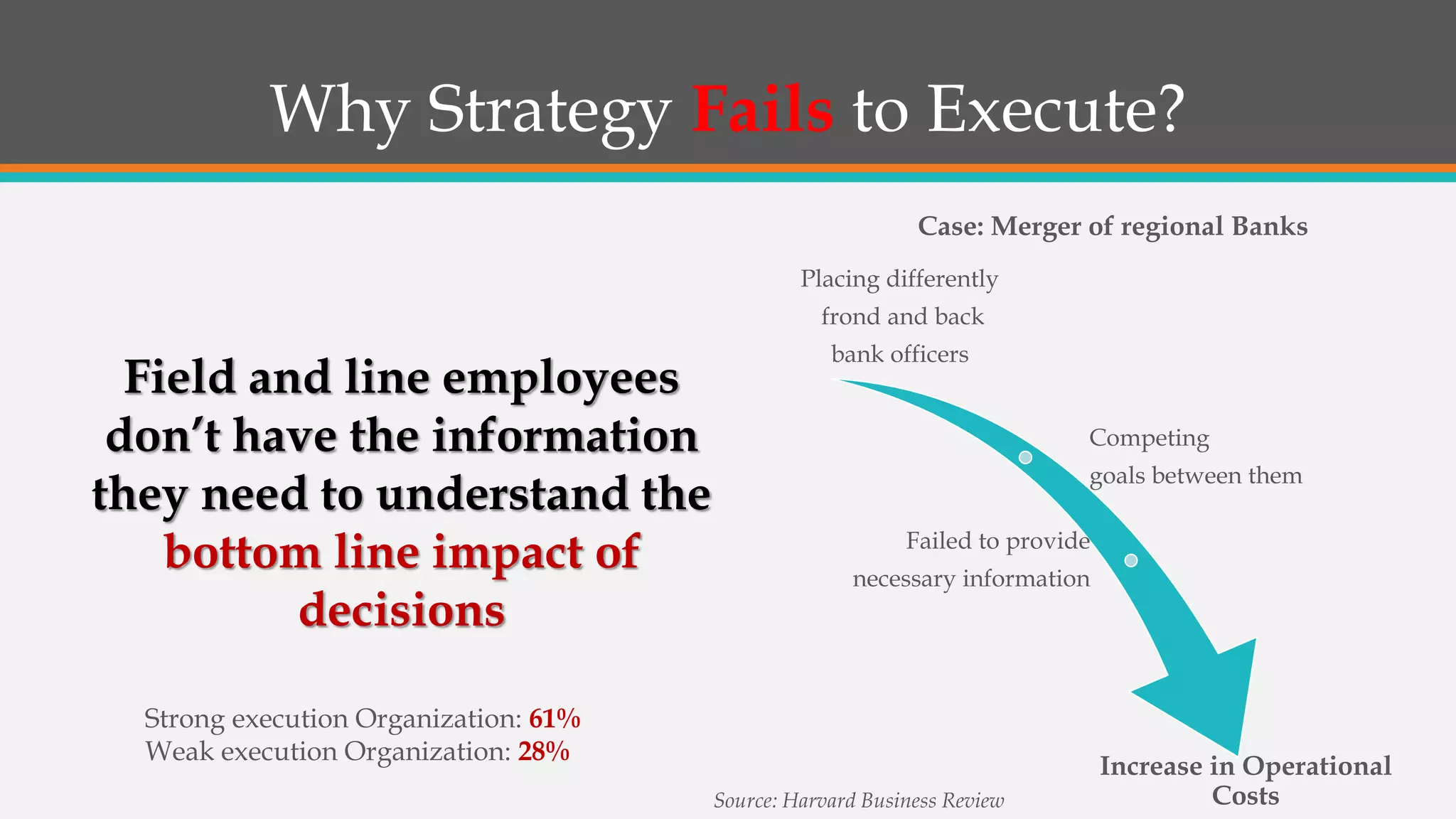
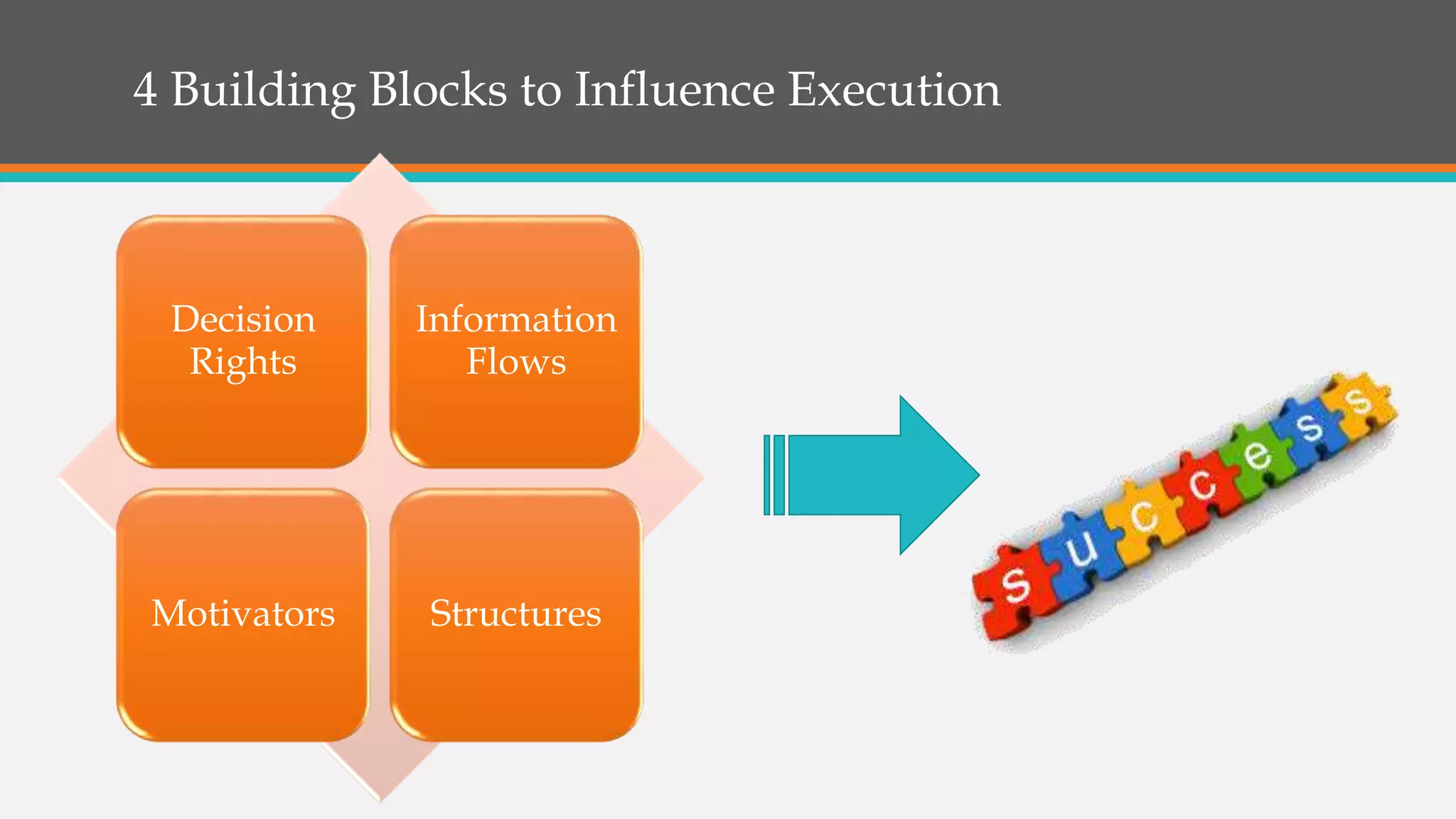
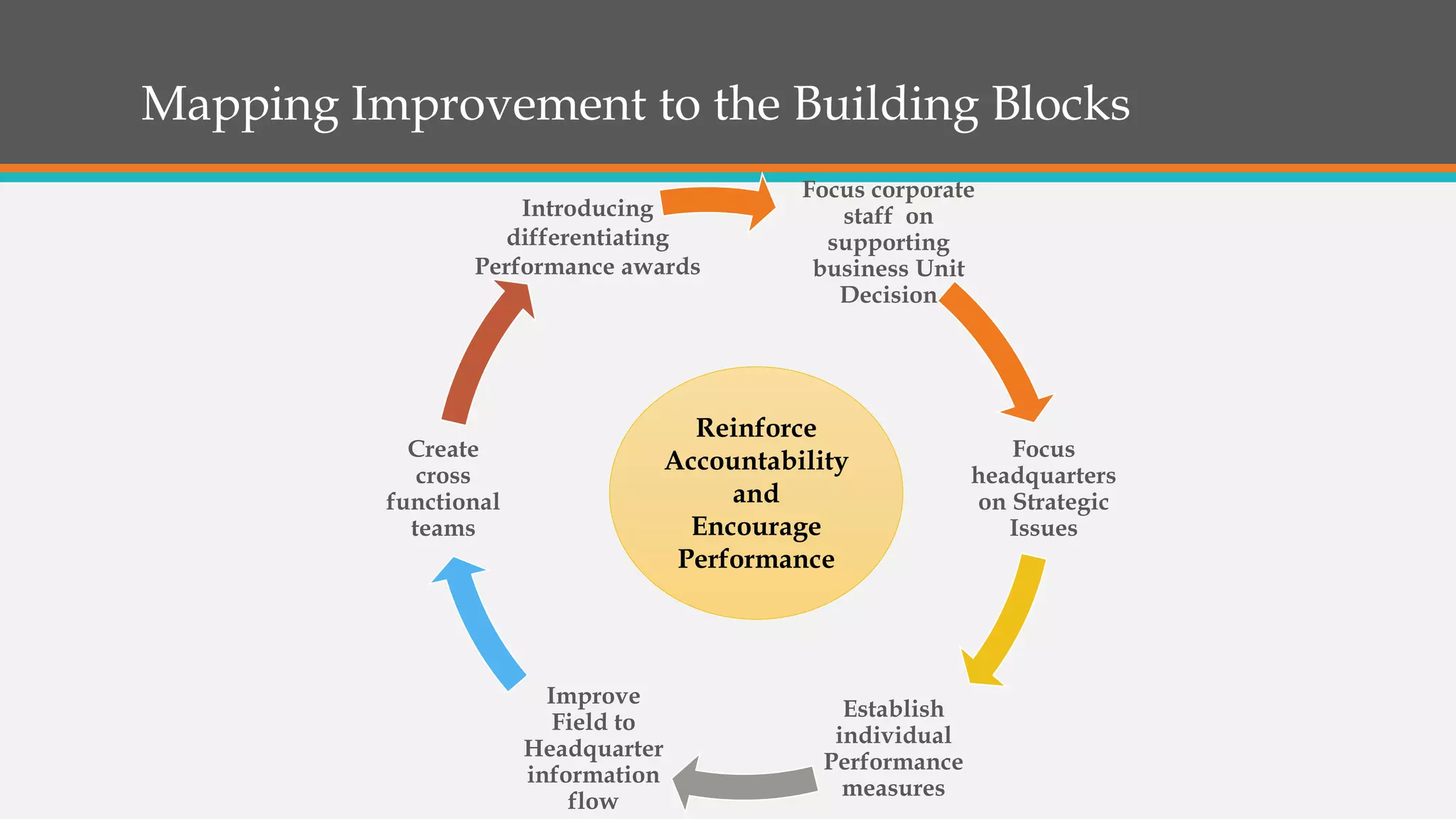
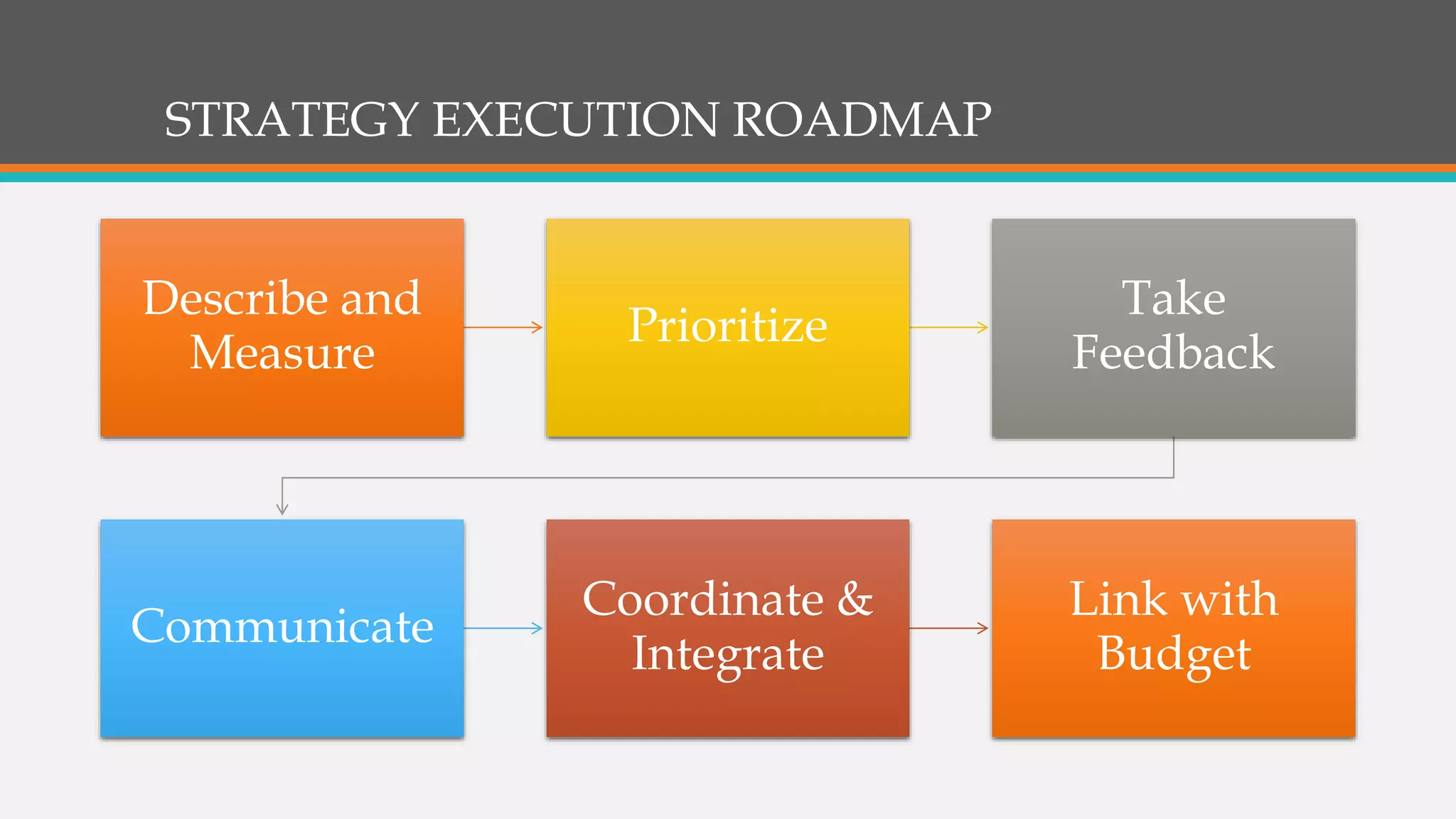
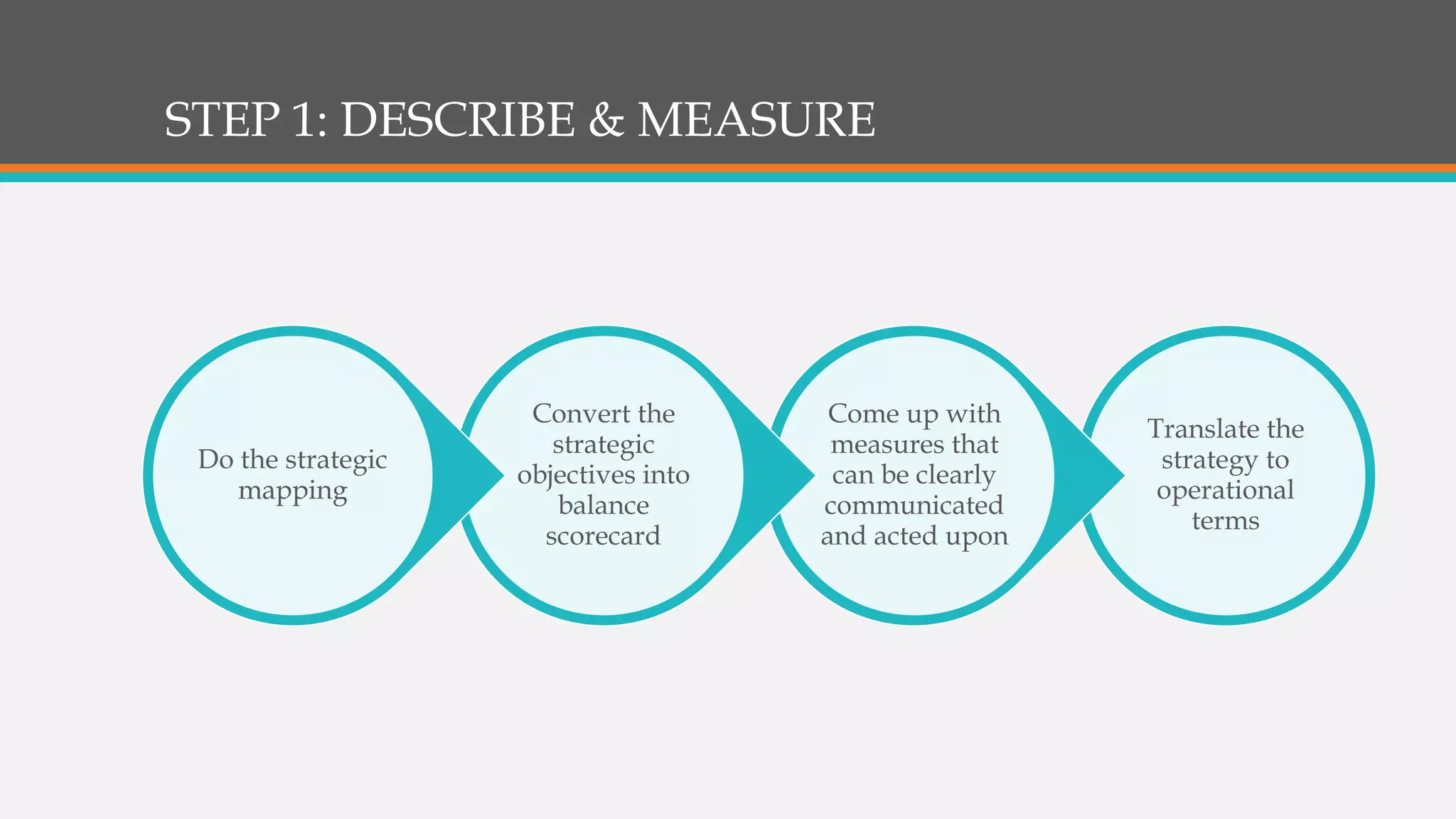
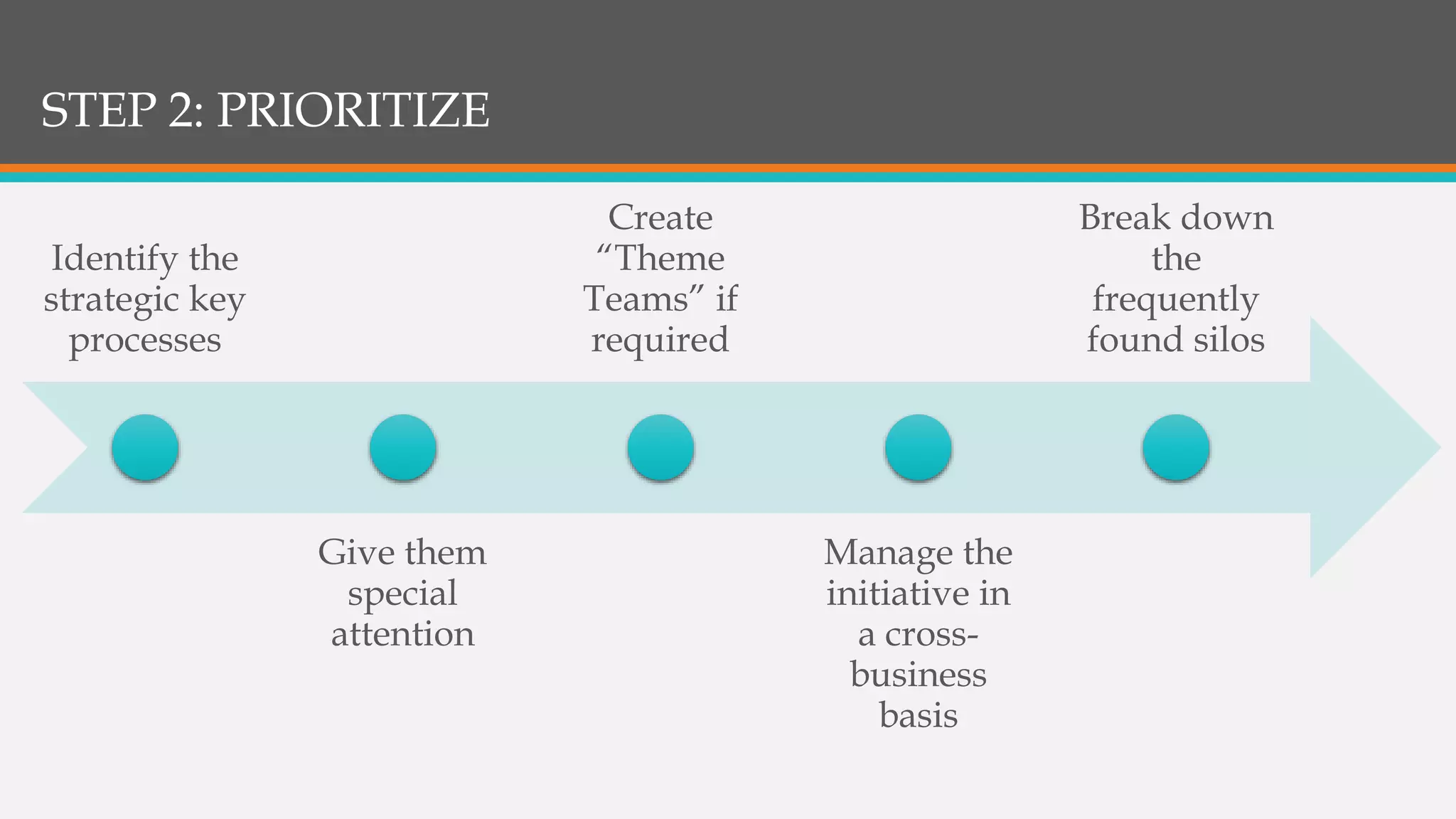
This document discusses strategies for successful strategy execution. It begins by outlining the building blocks of crafting and executing strategy, including developing vision/mission/values, setting objectives, crafting strategy, execution, and monitoring. It then discusses why strategy often fails, such as lack of communication, accountability, or necessary information. The document presents Harvard Business Review research finding most companies are weak in execution. It provides examples of companies where strategy failed due to these issues. Finally, it outlines a six-step roadmap for strategic execution: describe and measure objectives, prioritize initiatives, take feedback, communicate the strategy, coordinate/integrate efforts across the organization, and link the strategy to budgeting. The overall message is that good strategy plus