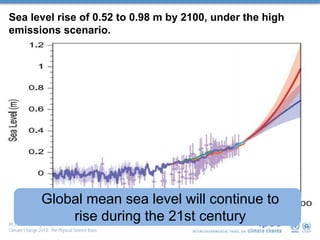
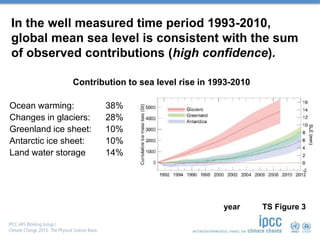
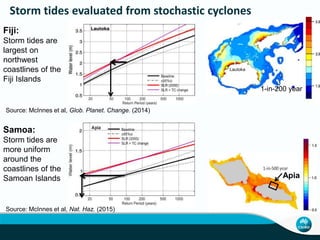
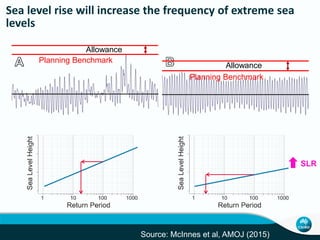
Global mean sea levels have risen significantly since 1901 according to multiple lines of evidence. From 1901-2010, sea levels rose by 0.19 meters and from 1993-2010 the rate of rise increased to 3.2 mm per year. Under a high emissions scenario, sea levels could rise between 0.52 to 0.98 meters by 2100. Contributions to the observed rise in sea levels from 1993-2010 include ocean warming (38%), changes to glaciers (28%), the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets (10% each), and land water storage (14%). Storm surges will also increase in frequency and severity due to sea level rise.

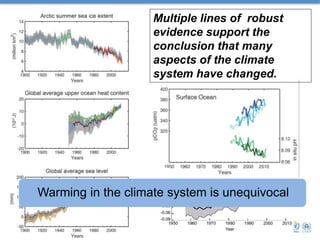
![Global mean sea level increased by 0.19 [0.17 to
0.21] m between 1901 and 2010
1901-2010: 1.7 mm/yr
1993-2010: 3.2 mm/yr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bindoffsealevelrise-171006015803/85/Sea-level-rise-3-320.jpg)