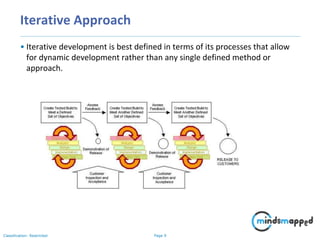
The document provides an overview of software development methodologies, focusing on incremental, iterative, and agile approaches. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each methodology, including when to use them, with a particular emphasis on agile practices like the Scrum framework. The document highlights the necessity of planning, flexibility, and customer collaboration in effective software development.