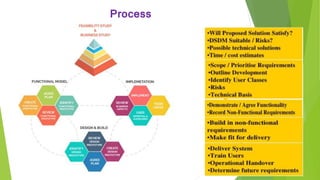
The Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) is a framework for developing computer-based systems, emphasizing iterative and incremental processes with active user involvement. It outlines principles for achieving business needs through frequent releases, while detailing roles, techniques, and the appropriate contexts for application. DSDM offers advantages like timely deliverables and user engagement but may be costly and less suitable for small or one-time projects.











![Referenc
es
[1] DSDM Public Version 4.2 Manual. (n.d.). DSDM
Consortium - Enabling Business Agility. Retrieved
March 24, 2010, from
http://www.dsdm.org/version4/2/public/default.asp
[2] What Is DSDM? - CodeProject. (n.d.). Your
Development Resource - CodeProject. Retrieved
March 24, 2010, from http://www.codeproject.com/KB/
[3] Davies, R. (2004, September 21). DSDN
Explained. Agile eXperience. Retrieved March 24,
2010, from
www.agilexp.com/presentations/DSDMexplained.pdf
[4] Dynamic Systems Development Method -
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. (n.d.). Wikipedia,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicsystemdevelopmentmethod-161227154229/85/Dynamic-system-development-method-14-320.jpg)
