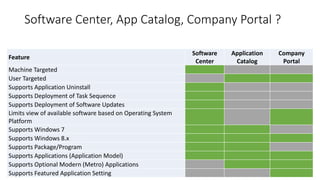
This document summarizes planning considerations for deploying Windows 10 in an enterprise environment. It discusses enabling Enterprise Mode IE 11 compatibility, Group Policy settings to manage OneDrive sync and Windows customization, ensuring UEFI Secure Boot is enabled, challenges with Secure Boot for operating system deployment, and options for deploying modern applications including the Software Center, Application Catalog, and Company Portal. The document provides an overview of key upgrade and deployment topics to facilitate a smooth transition to Windows 10.