SCRUM is an agile framework for managing projects, originally developed in the 1980s. It is intended to be a flexible, lightweight process that helps teams deliver value to customers more quickly through short cycles of work called sprints.
The core roles in SCRUM include the Product Owner, who represents stakeholders and prioritizes features; the ScrumMaster, who helps remove impediments and guide the team; and the cross-functional team.
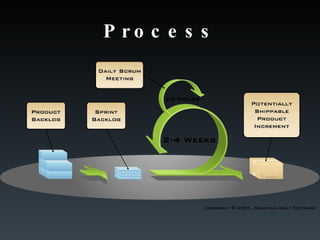
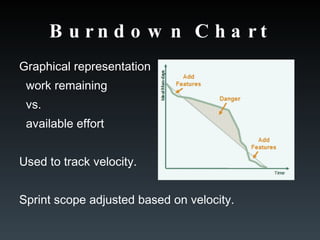
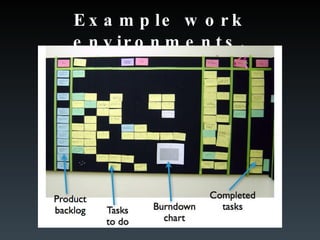
The team works in sprints, usually 2-4 weeks, to deliver a working product increment. They use a product backlog, sprint backlog, daily scrums, and burndown charts to stay aligned and track progress towards sprint goals.