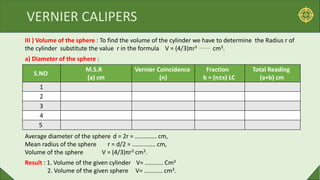
The document describes how to use vernier calipers to measure the volume of a cylinder and sphere. It explains that vernier calipers have a main scale and sliding vernier scale, allowing measurement to the nearest division which is the least count. To find a cylinder's volume, its length and diameter are measured multiple times and averaged. The sphere's diameter is similarly measured, then both objects' volumes are calculated using the appropriate formulas. Proper technique and correcting for zero error are emphasized.