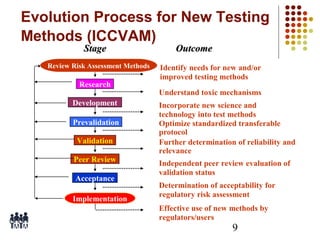
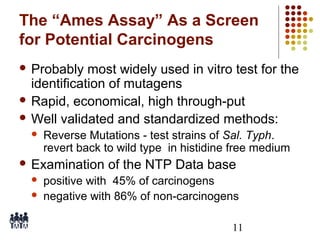
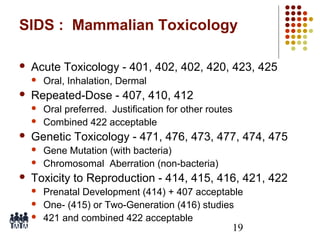
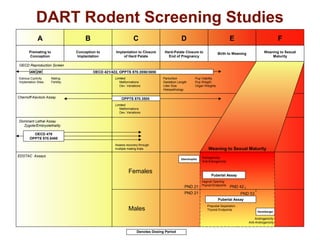
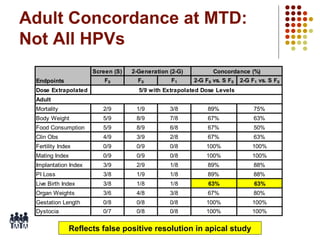
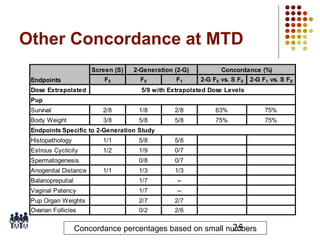
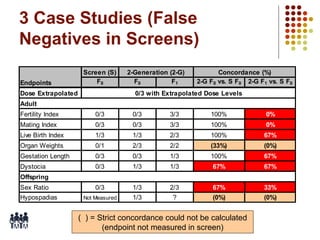
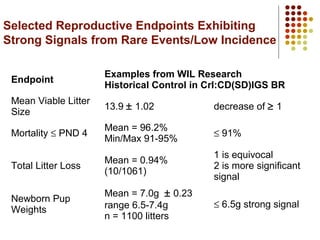
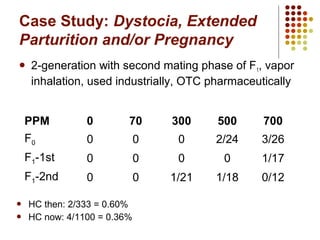
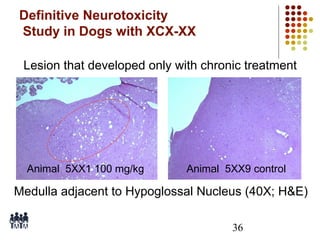
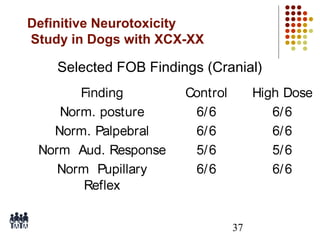
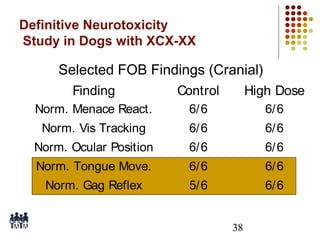
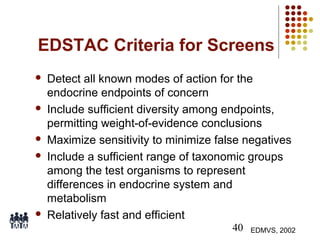
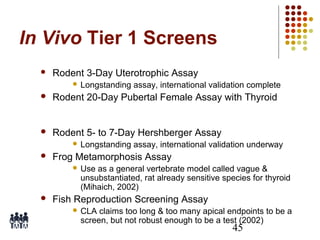
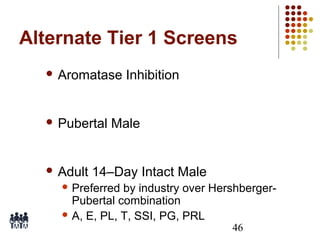
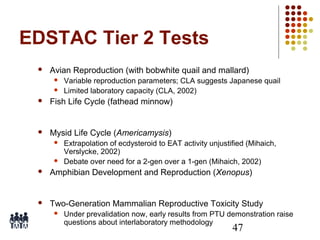
This document provides an overview of screening tests for toxic chemicals. It defines screens as simplified tests designed to identify agents requiring further evaluation or exclude them from further testing. Key purposes of screens include economic savings, increased speed and number of chemicals evaluated while decreasing animal use. Screens must be valid, sensitive, reproducible and practical. The document discusses criteria for validation and acceptance of new testing methods and provides examples of in vitro and in vivo screens used in toxicology. It also discusses how screens fit within the regulatory testing structure and notes some limitations of screens in fully characterizing toxicity.