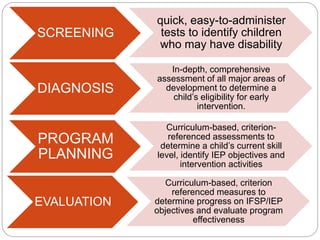
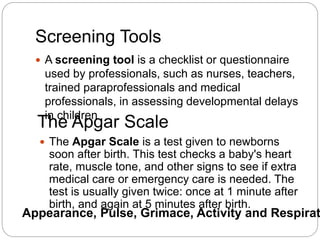
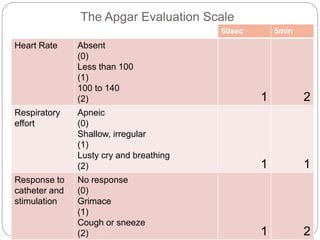
This document discusses screening, identification, and assessment of children for developmental delays or disabilities. It provides information on four main purposes of assessment: screening, diagnosis, program planning, and evaluation. Screening uses quick tests to identify children who may need further evaluation. Diagnosis involves comprehensive assessment to determine eligibility for early intervention. Program planning uses curriculum-based tests to identify skills and create education plans. Evaluation assesses progress on education plans and program effectiveness. The Apgar scale is described as a common screening tool used to quickly assess a newborn's health at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. Scores of 7-10 are typically normal while scores below 4 require immediate medical attention.