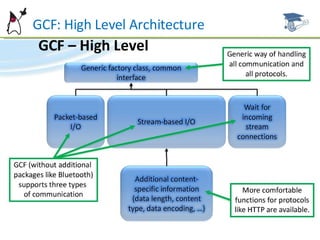
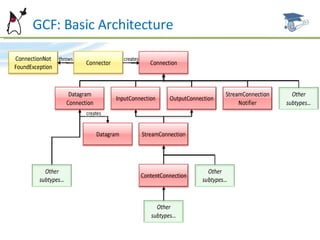
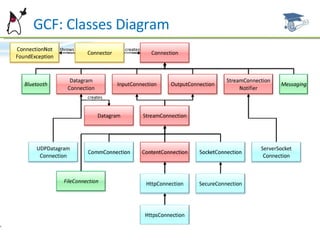
The document discusses the Generic Connection Framework (GCF) in Java ME, which defines interfaces for network connections on CLDC platforms. GCF includes interfaces for stream-based, datagram-based, and content-based connections. Example implementations are provided for HTTP, TCP sockets, UDP datagrams, serial communications, and more.






![DatagramConnection getMaximumLength(): Maximum size a datagram may have, in bytes newDatagram(size): Creates a new datagram with the specified size newDatagram (size,address): Creates a datagram addressed to the specified destination newDatagram( buffer[],size): Creates a datagram with the specified payload newDatagram( buffer[], size, address ): Creates a datagram with specified address and payload](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter09-1219802209972327-8/85/Scmad-Chapter09-10-320.jpg)


![Datagram: methods getAddress(): Destination or origin address getData(): Payload setData( buffer[],offset,length ): Sets the payload getLength(): Payload size setLength( length ): Changes the payload size setAddress( address): Sets the address setAddress( datagram): Copies the address from the parameter reset(): Resets DataInput and DataOutput pointers, returning the message to its original state](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter09-1219802209972327-8/85/Scmad-Chapter09-13-320.jpg)













![References ALVES F. Eduardo. SCMAD Study Guide, 27/04/2008. JAKL Andreas, Java Platform, Micro Edition Part 01 slides, 12/2007. Sun Certification Mobile Application Developer Website: [http://www.sun.com/training/certification/java/scmad.xml].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scmadchapter09-1219802209972327-8/85/Scmad-Chapter09-33-320.jpg)