This document summarizes key topics related to networking in Java, including:
1) Stream sockets provide connection-oriented communication while datagram sockets provide connectionless communication using UDP.
2) URLs can be manipulated in Java by converting them to URLs and using showDocument() to display webpages.
3) Files on a web server can be read using JEditorPane and handling hyperlink clicks, displaying the contents.
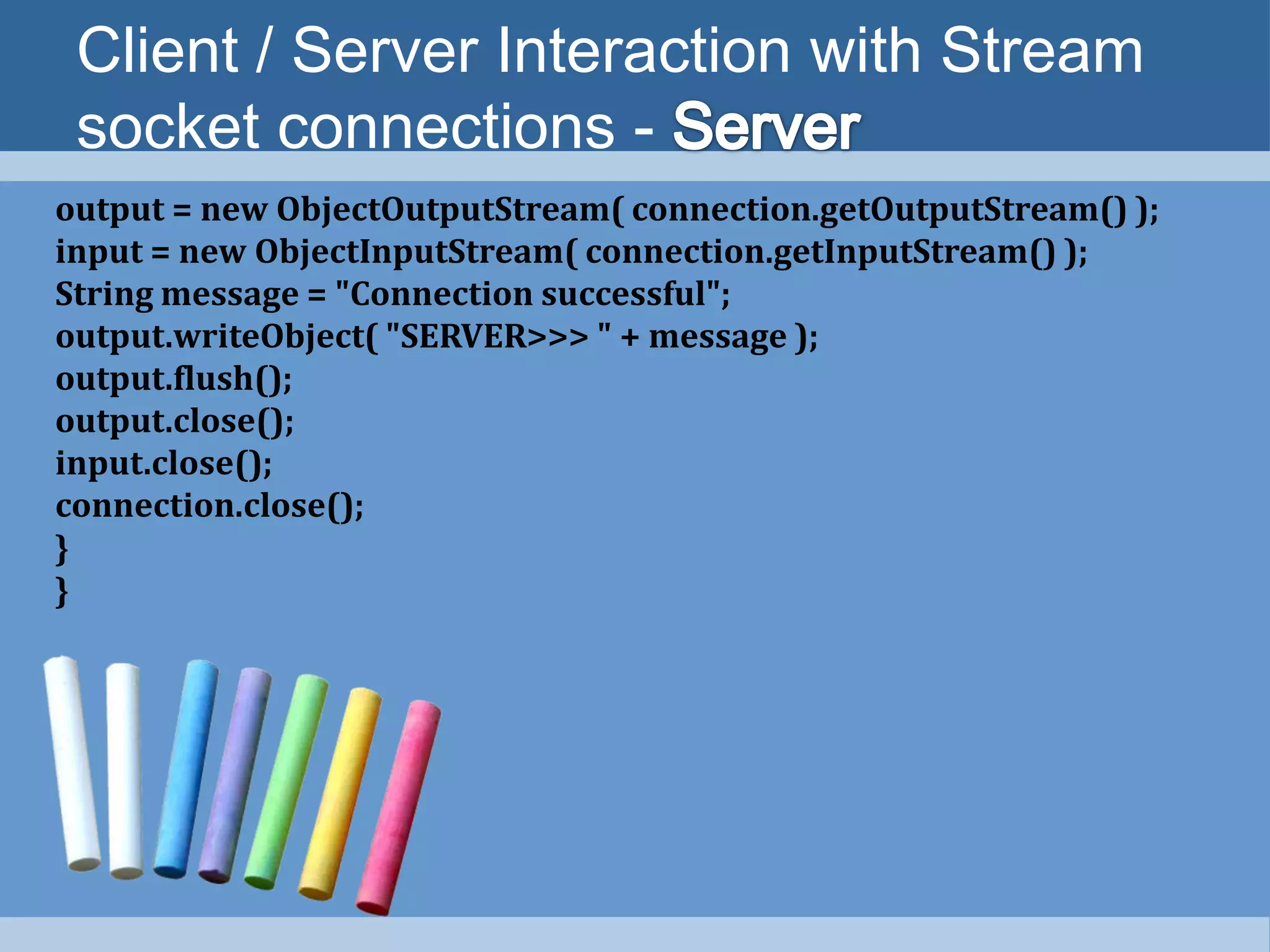
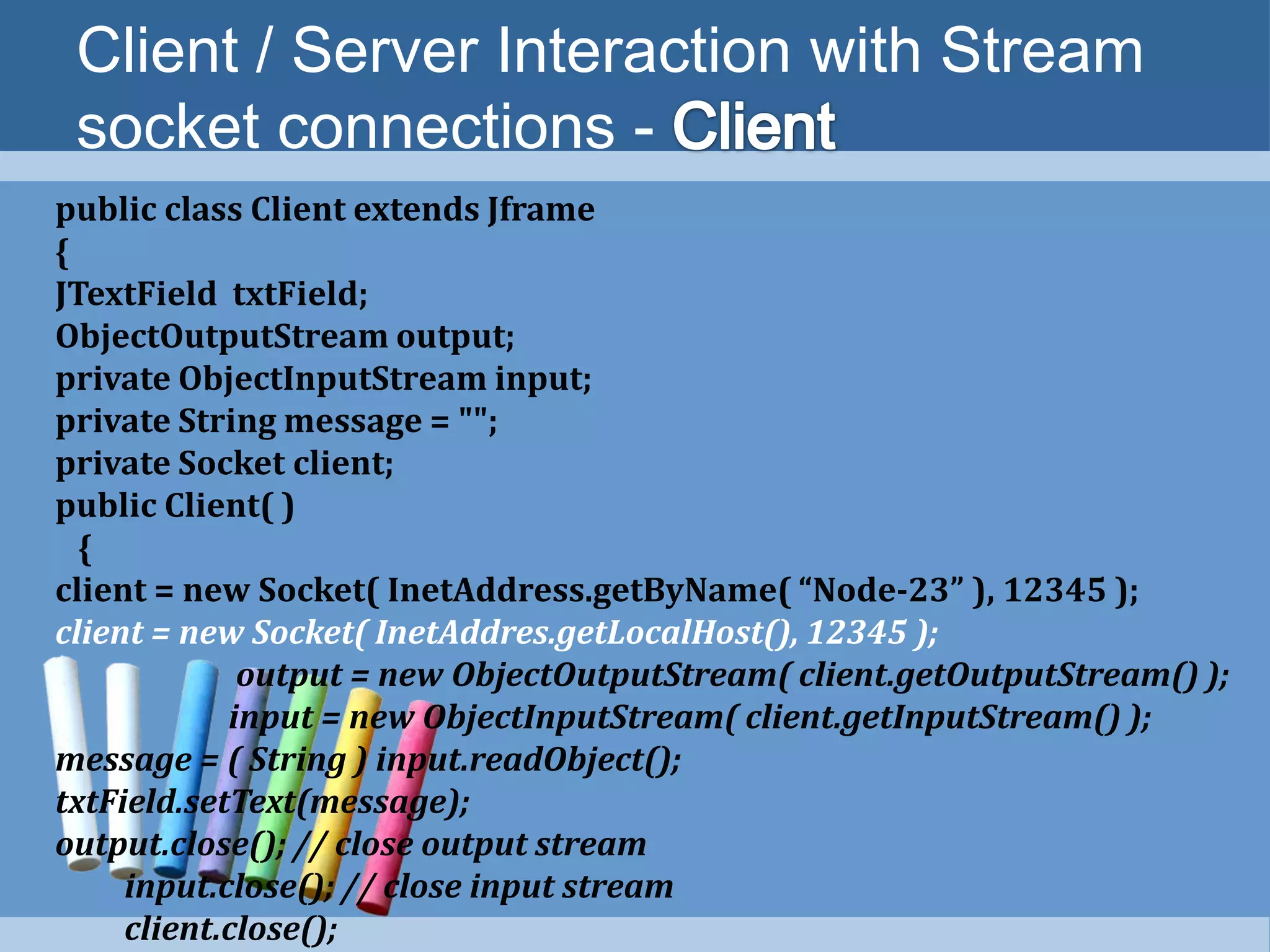
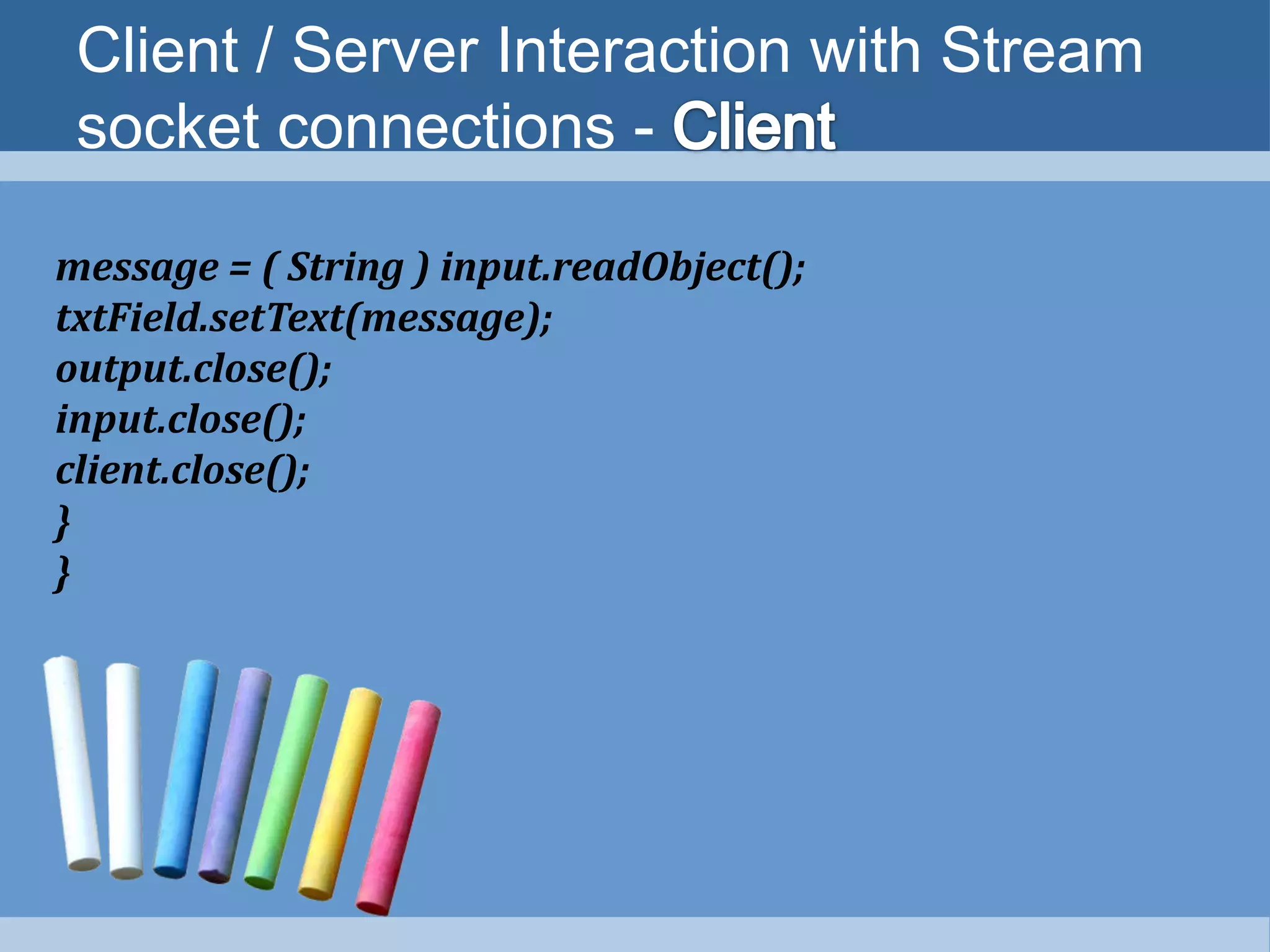
4) Simple client-server applications can be created using stream sockets by establishing connections, getting input/output streams, processing data, and closing connections.





























![Datagrams : Connectionless Client/Server
Interaction – SERVER class
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Server extends JFrame
{ JTextArea txtarea;
public Server()
{
Txtarea = new JTextArea(10,40);
socket = new DatagramSocket( 5000 );
byte[] data = new byte[ 100 ]; // set up packet
DatagramPacket receivePacket =
new DatagramPacket( data, data.length );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter27networking-190222114050/75/Chapter-27-Networking-Deitel-Deitel-36-2048.jpg)

![Datagrams : Connectionless Client/Server
Interaction – CLIENT class
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Client extends JFrame
{
public Server()
{
String msg = “Welcome to Datagram”;
byte[] data = msg.getBytes();
DatagramPacket sendPacket = new DatagramPacket( data,
data.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 5000 );
socket.send( sendPacket );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter27networking-190222114050/75/Chapter-27-Networking-Deitel-Deitel-38-2048.jpg)