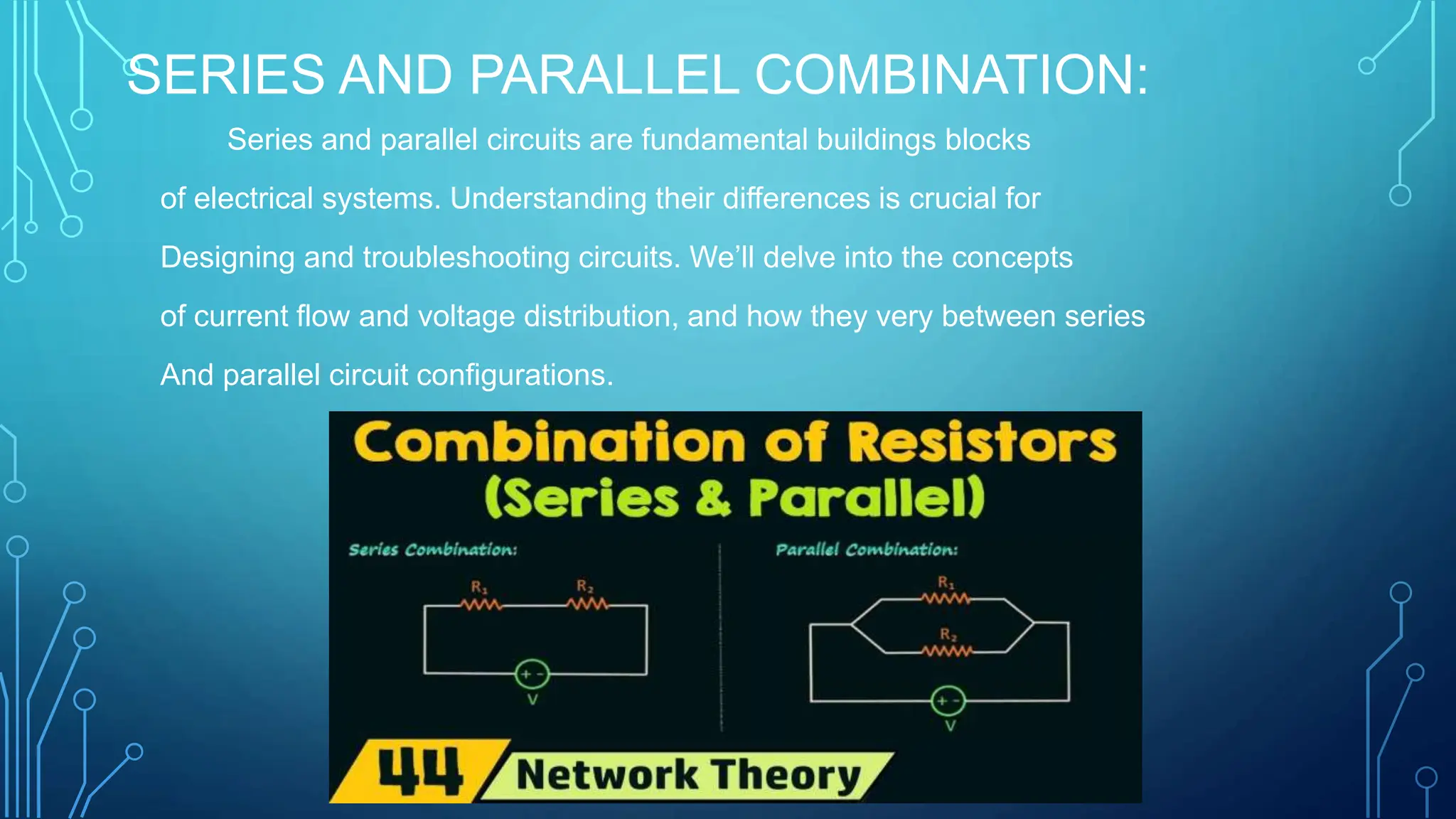
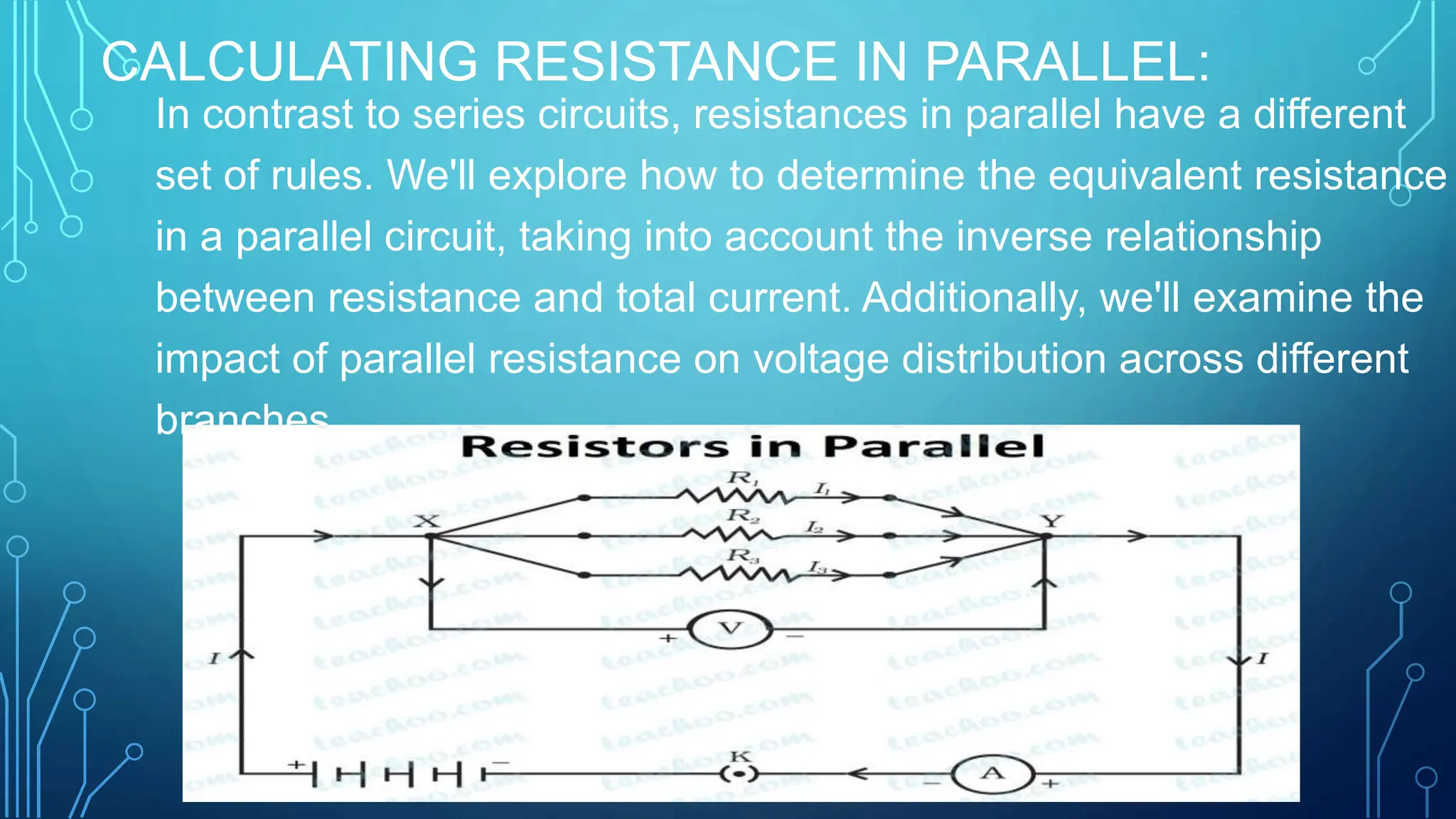
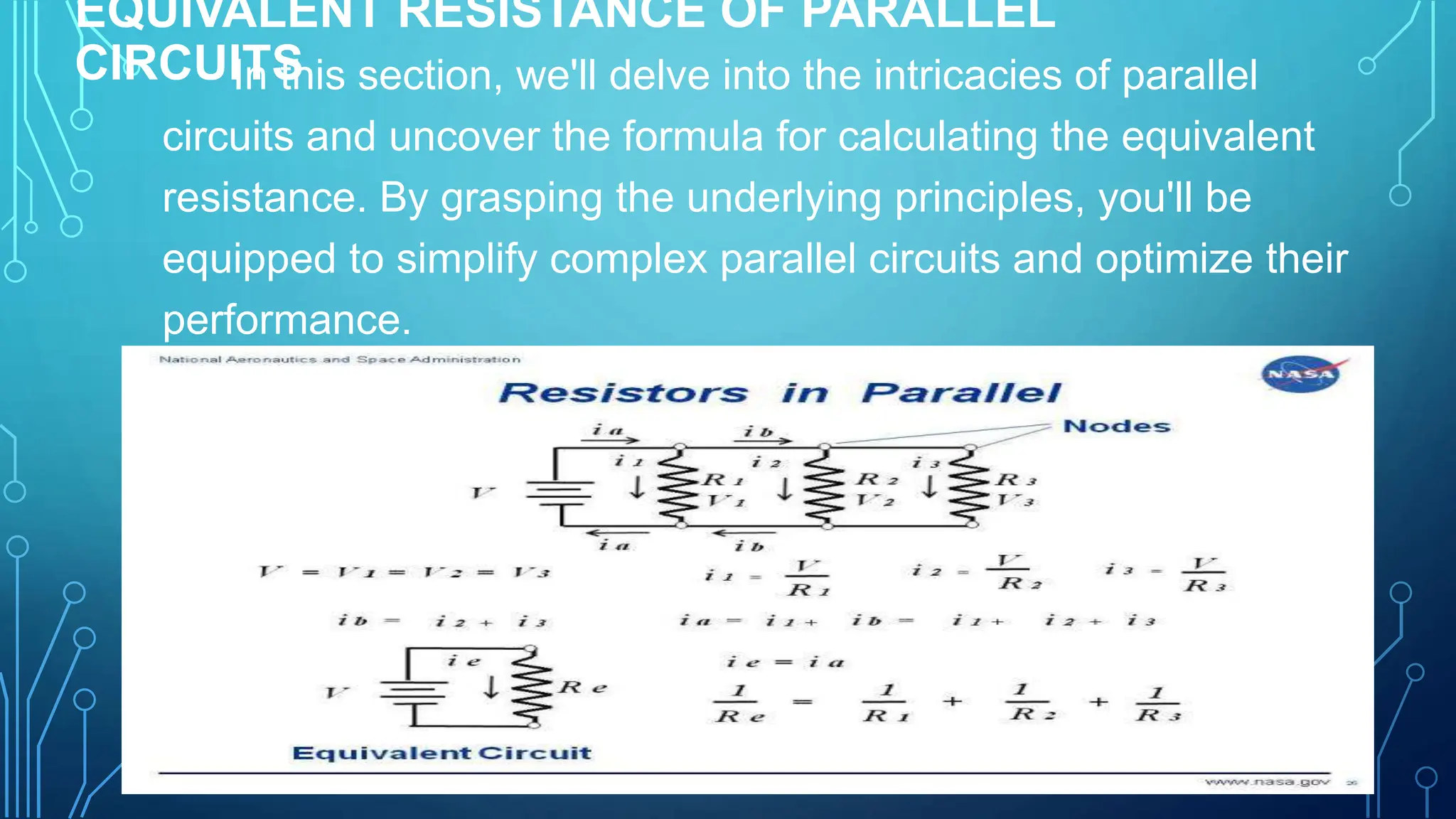
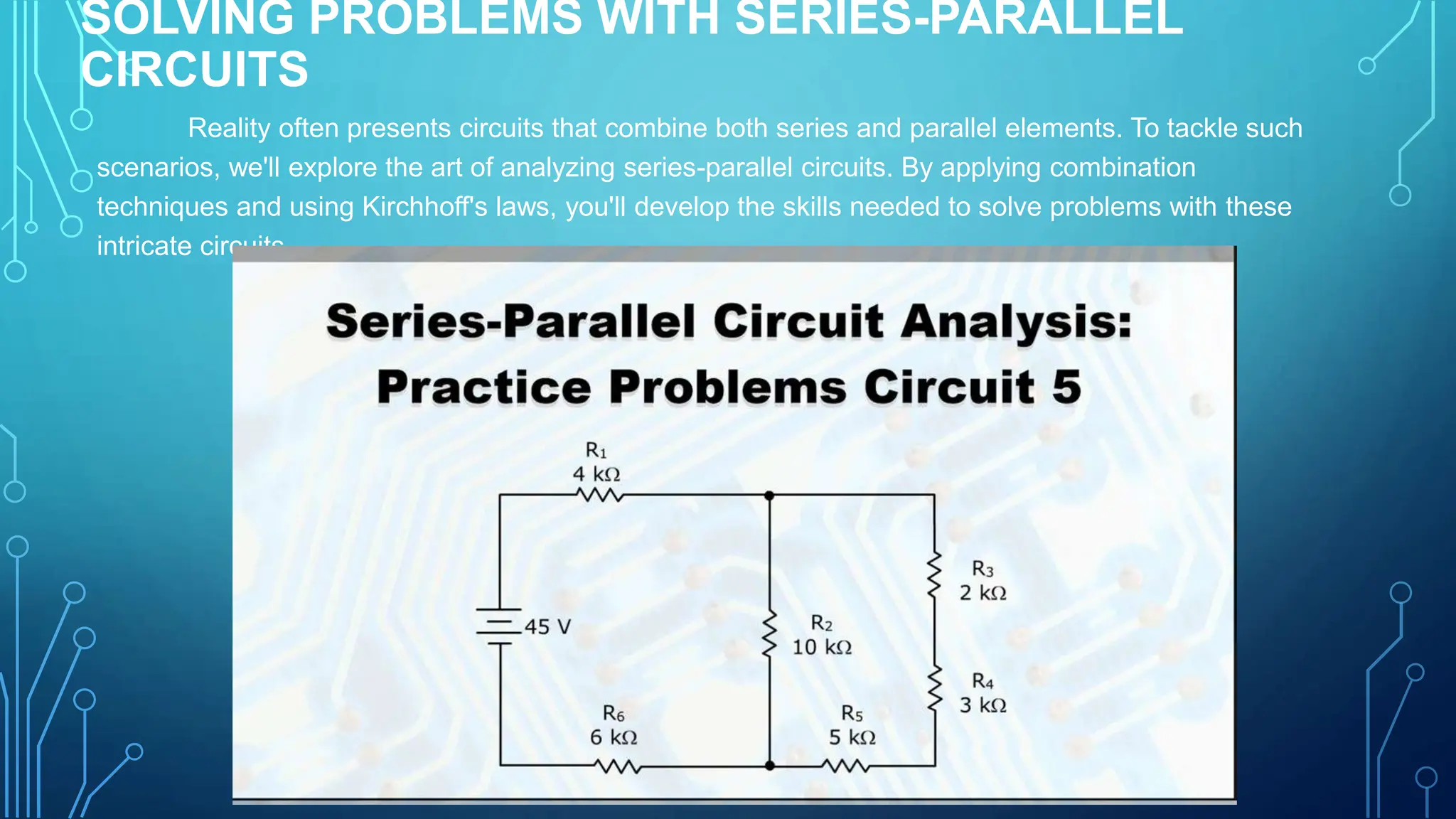
The document provides a comprehensive overview of series and parallel circuits, highlighting their importance in electrical systems and differences in current flow and voltage distribution. It offers guidelines for calculating total resistance in both configurations, along with implications for real-world applications such as power distribution and electronic devices. Additionally, it addresses how to approach problems involving circuits that combine series and parallel elements.