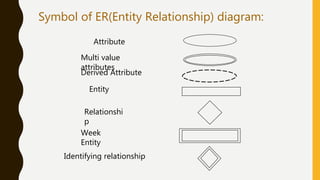
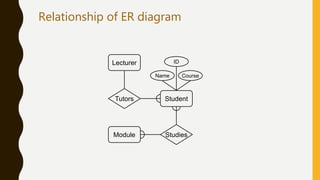
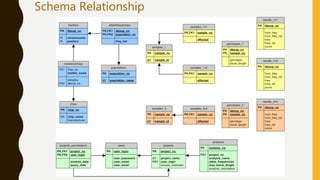
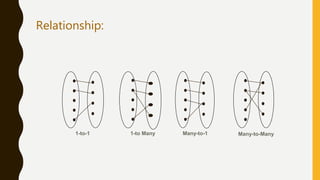
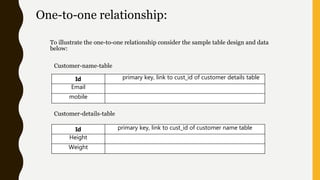
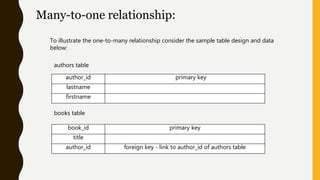
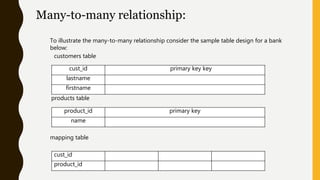
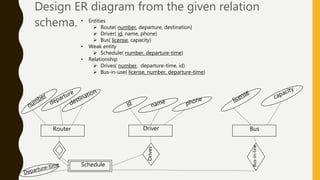
This presentation discusses the relationship between schema and entity-relationship (E-R) diagrams. It defines key E-R diagram symbols like entities, attributes, and relationships. It then provides examples of how to represent one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many relationships between tables in a relational database through E-R diagrams. Finally, it shows how to design an E-R diagram from a given schema involving bus routes, drivers, schedules, and their relationships.