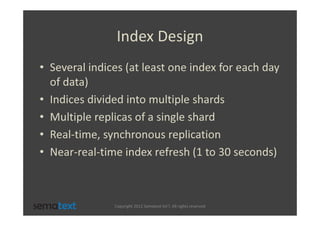
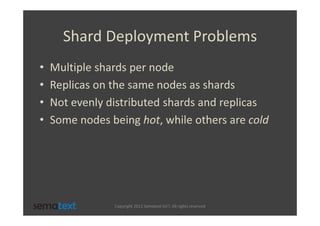
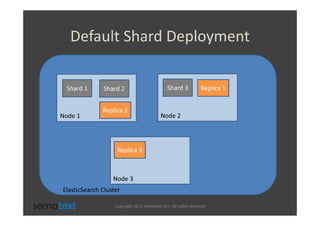
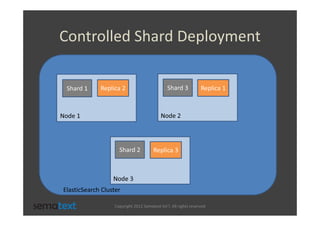
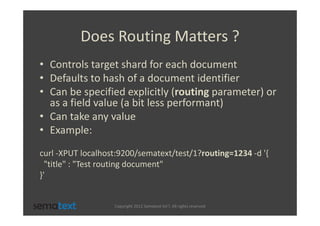
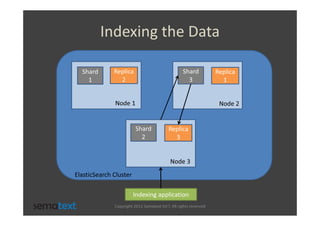
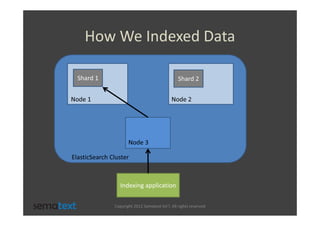
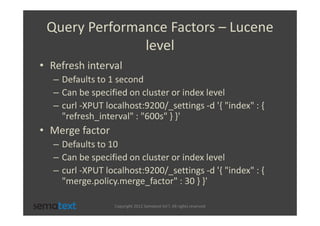
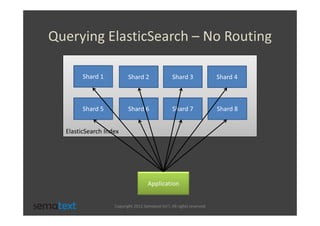
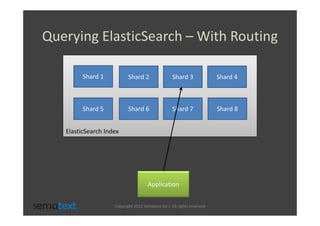
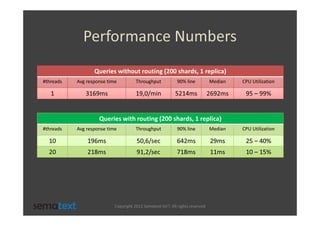
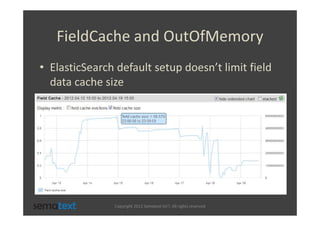
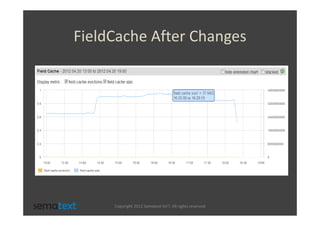
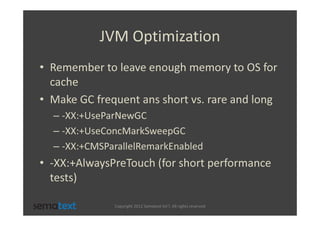
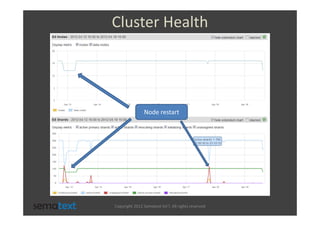
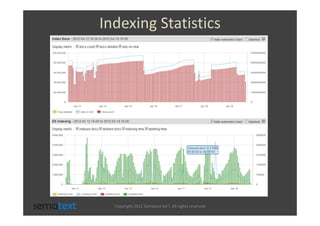
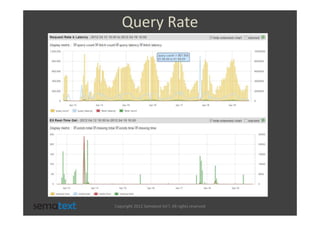
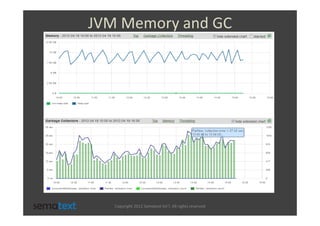
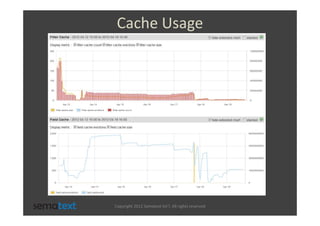
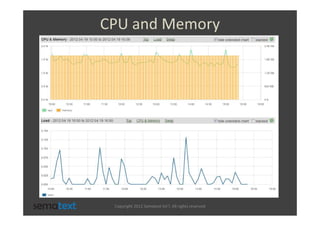
The document discusses strategies for scaling and optimizing Elasticsearch clusters, focusing on challenges such as handling large volumes of multilingual data with fast indexing and query responses. Key topics include shard and replica placement, routing, performance testing, and cluster monitoring. It emphasizes practical solutions for managing large datasets and monitoring cluster health while offering job opportunities at Sematext.