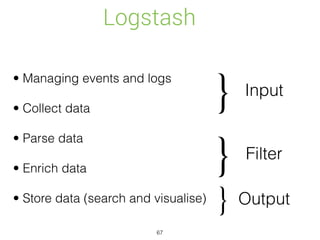
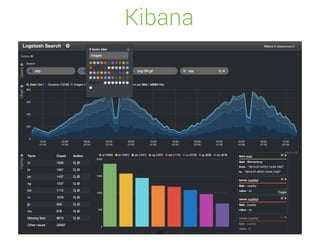
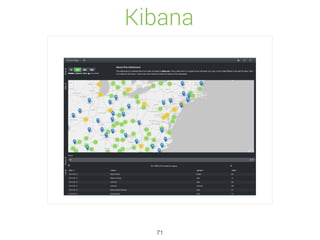
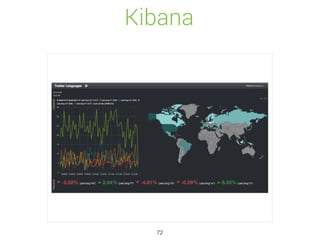
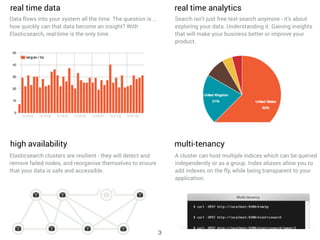
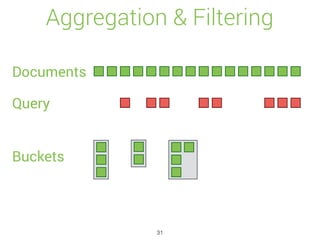
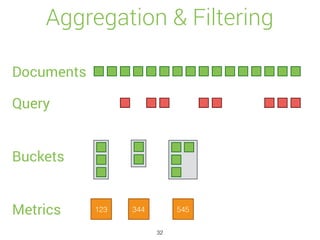
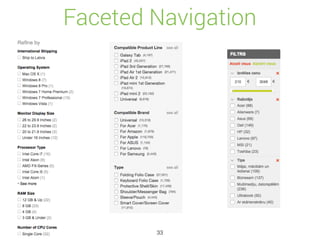
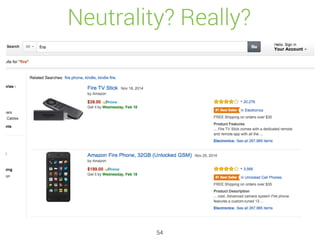
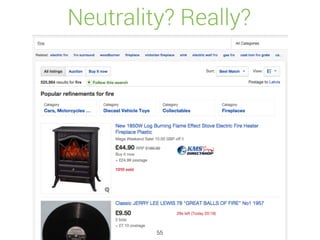
Elasticsearch is a distributed, schema-free document store designed for real-time data indexing and analytics, built on Apache Lucene. It provides full-text search capabilities, supports JSON documents, and features a RESTful API for operations, ensuring data safety and quick access. The platform is open-source under the Apache 2.0 license, making it highly extensible and accessible for various applications.






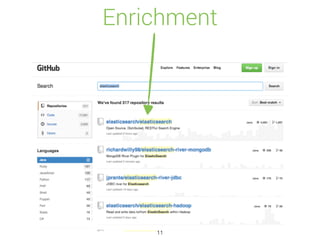
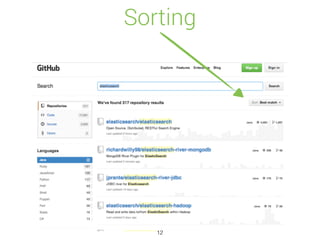
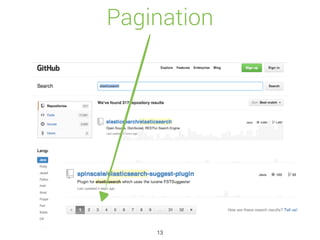
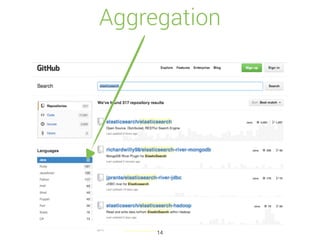
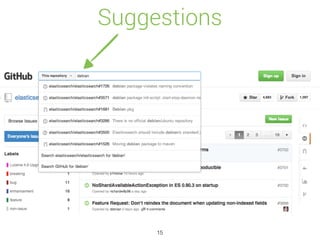








![Auto Completion
curl -X PUT localhost:9200/hotels/hotel/2 -d '
{
"name" : "Hotel Monaco",
"city" : "Munich",
"name_suggest" : {
"input" : [
"Monaco Munich",
"Hotel Monaco"
],
"output": "Hotel Monaco",
"weight": 10
}
}'
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearch-150225053202-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-26-320.jpg)






![Percolate API
38
{
"took" : 19,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"failed" : 0
},
"total" : 1,
"matches" : [
{
"_index" : "my-index",
"_id" : "1"
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearch-150225053202-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-38-320.jpg)


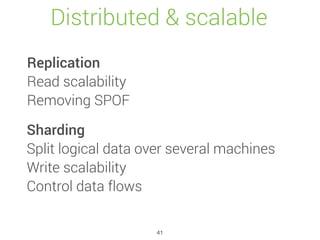
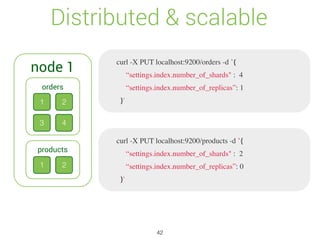
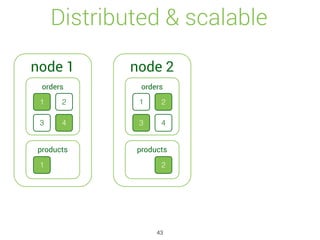
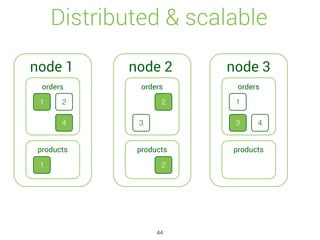


![Update
» curl -X PUT localhost:9200/books/book/1 -d '
{
"title" : "Elasticsearch - The definitive guide",
"authors" : [ "Clinton Gormley", "Zachary Tong"],
"started" : "2013-02-04",
"pages" : 230
}'
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearch-150225053202-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-47-320.jpg)

![Search
» curl -X GET localhost:9200/books/_search?q=elasticsearch
{
"took" : 2, "timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : { "total" : 5, "successful" : 5, "failed" : 0 },
"hits" : {
"total" : 1, "max_score" : 0.076713204,
"hits" : [ {
"_index" : “books", "_type" : “book", "_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.076713204, "_source" : {
"title" : "Elasticsearch - The definitive guide",
"authors" : [ "Clinton Gormley", "Zachary Tong" ],
"started" : “2013-02-04", "pages" : 230
}
}]
}
}
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearch-150225053202-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-49-320.jpg)







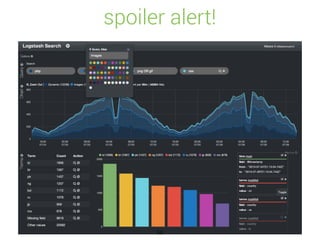






![Unify dates
• apache
• unix timestamp
• log4j
• postfix.log
• ISO 8601
[19/Feb/2015:19:00:00 +0000]
1424372400
[2015-02-19 19:00:00,000]
Feb 19 19:00:00
2015-02-19T19:00:00+02:00
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearch-150225053202-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-Elasticsearch-66-320.jpg)