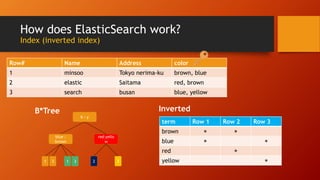
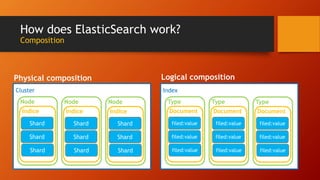
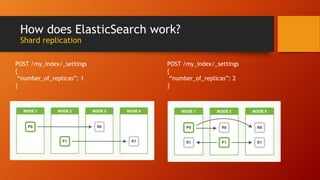
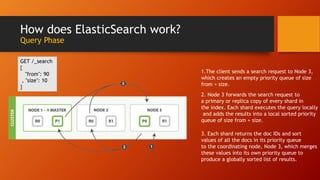
Elasticsearch is an open source search engine based on Lucene. It allows for distributed, highly available, and real-time search and analytics of documents. Documents are indexed and stored across multiple nodes in a cluster, with the ability to scale horizontally by adding more nodes. Elasticsearch uses an inverted index to allow fast full-text searches of documents.














![Analysis
Analysis & Analyzer
"The QUICK brown foxes jumped over the lazy dog!"
Analysis
[ quick, brown, fox, jump, over, lazy, dog]
Tokenizer (n-gram)
[ qu, ui, ic, ck]
Token filter
[ QU, ui, ic]
Character filters
[٠١٢٣٤٥٦٧٨٩] [0123456789]
Analyzer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aboutelasticsearchforgong-181111124114/85/About-elasticsearch-20-320.jpg)

![END
{
“name” : “minsoo.jun”,
“email” : “minsoo.jun@rakuten.com”
“department” : “TRVDD”,
“group” : “Search Platform”
“language” : [“java”,”ansible”,”SQL”,”korean”],
“database”: [”oracle”,”elasticsearch”,”mongodb”]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aboutelasticsearchforgong-181111124114/85/About-elasticsearch-22-320.jpg)