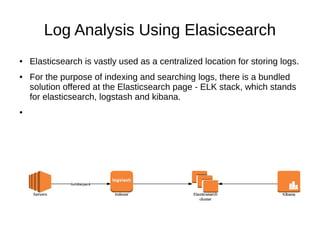
The document compares Elasticsearch, a NoSQL database, to relational databases highlighting their differences in structure, use cases, and relevance-based searching capabilities. It details Elasticsearch's various search functionalities, including full-text analysis, synonym and phonetic searches, as well as its role in log analysis through the ELK stack. Additionally, it explains core Elasticsearch terminology and demonstrates CRUD operations, covering index and document creation, reading, updating, and deleting documents.