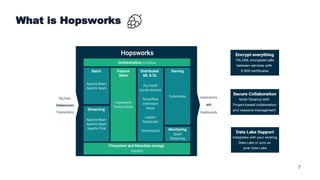
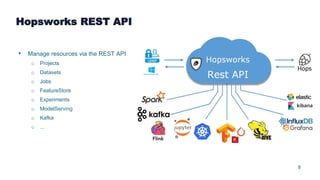
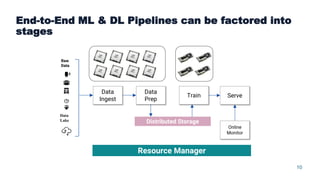
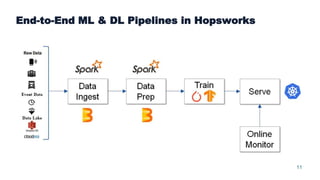
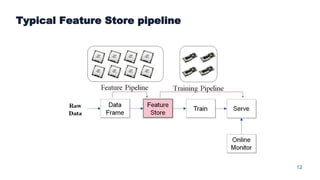
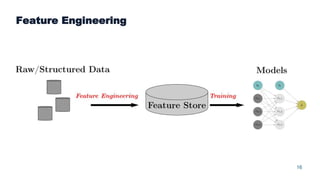
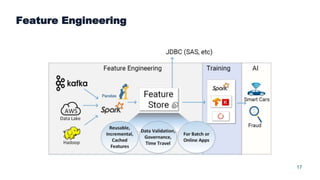
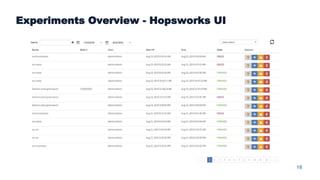
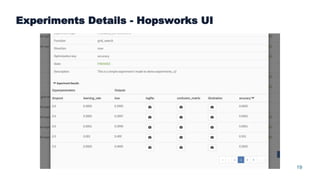
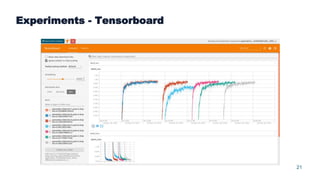
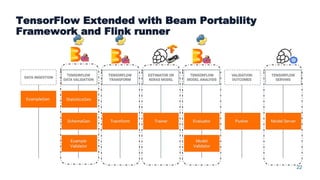
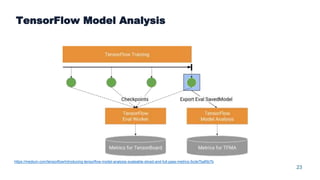
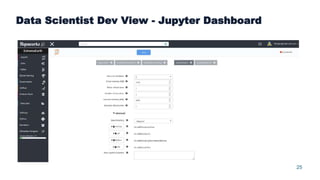
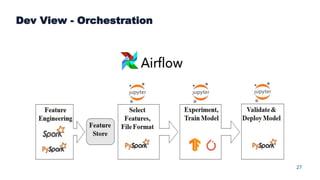
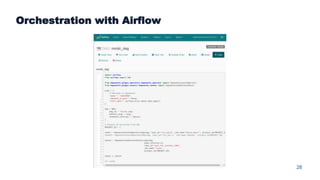
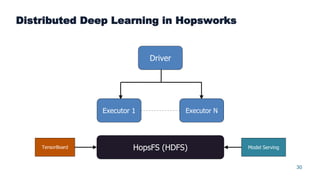
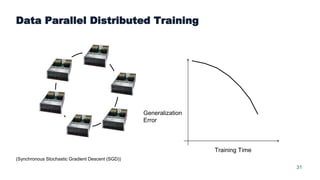
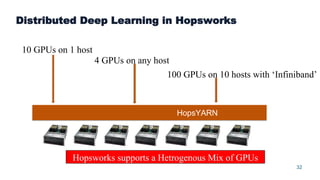
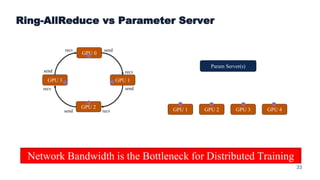
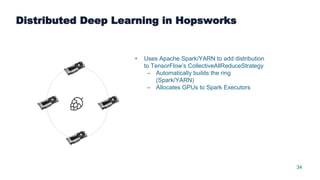
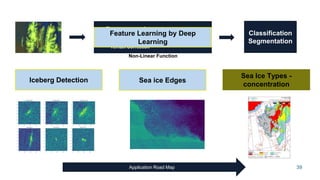
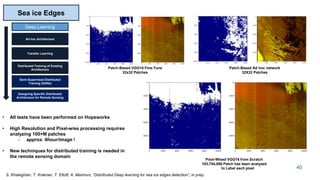
This document summarizes a presentation about scalable deep learning techniques for analyzing Copernicus Earth observation data using the Hopsworks platform. The presentation discusses Hopsworks' end-to-end machine learning pipelines, feature engineering capabilities, distributed deep learning techniques like data parallel training, and applications of these techniques to challenges in classifying satellite imagery like sea ice mapping. Deep learning architectures, preprocessing steps, and distributed training methods are highlighted as areas of ongoing work and improvement for analyzing large volumes of remote sensing data on Hopsworks.