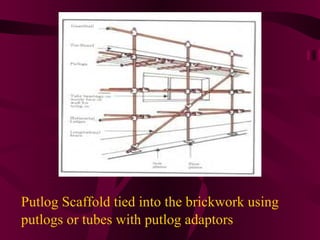
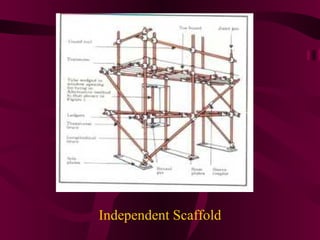
Scaffolding is a temporary structure used to provide access and a safe working platform for construction workers. The main types are putlog scaffolds, which use horizontal members called putlogs attached to a single row of uprights, and independent scaffolds, which have two rows of uprights connected by cross members. Scaffolding materials include tubular steel, tubular aluminum alloy, and timber. Safety precautions include inspecting scaffolds regularly and ensuring all components like handrails, boards, and braces are securely in place before use.