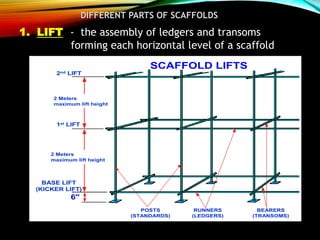
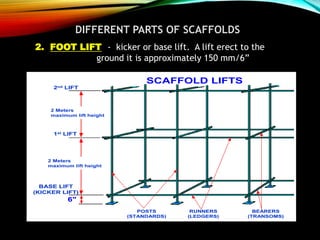
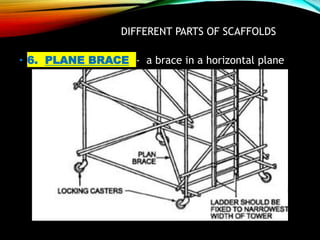
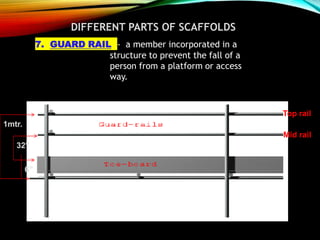
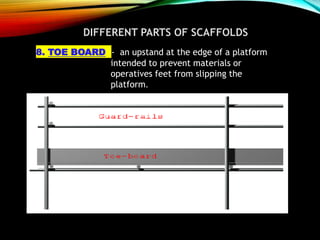
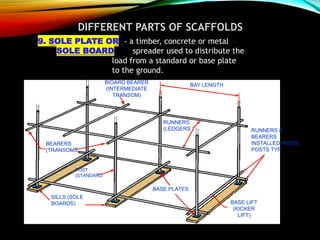
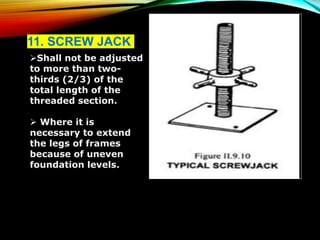
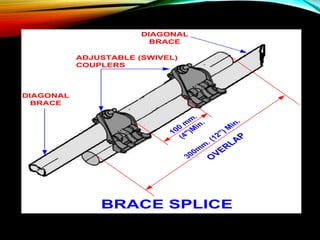
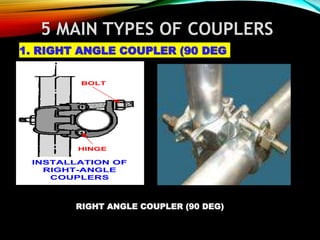
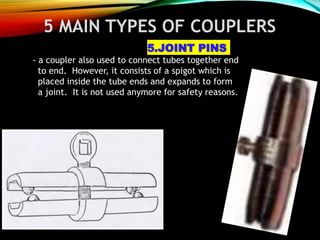
The document discusses different types of scaffolding components including locks, connectors, and their uses. It identifies 10 main parts of scaffolding structures: lifts, foot lifts, standards, ledgers, transoms, plane braces, guard rails, toe boards, sole plates/boards, and base plates. It also describes 5 main types of couplers used to connect scaffolding tubes: right angle couplers, putlog couplers, swivel couplers, sleeve couplers, and joint pins. The importance of scaffolding in the construction industry is explained in terms of efficiency, safety, easy access, and providing workers with a prime position for carrying out tasks.