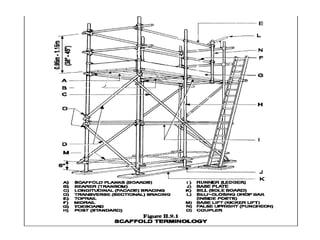
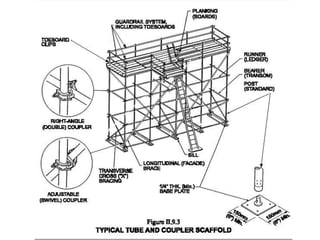
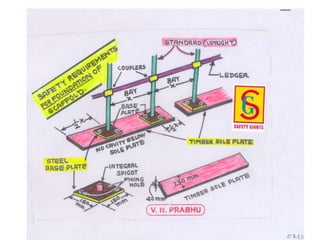
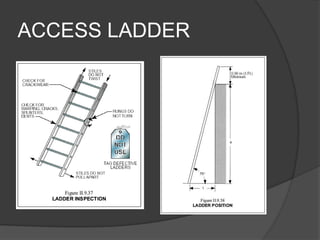
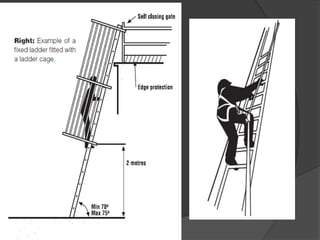
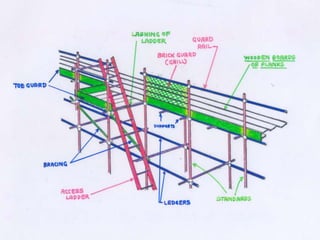
The document provides information on scaffolding safety training conducted by Mr. V N Parbhu at EERC Theramx Ltd. on September 24-25, 2012. It defines scaffolding and describes the main types of tubular scaffolding. It outlines the various parts of tubular scaffolding such as standards, ledgers, transoms, and couplers. The document discusses requirements for guardrails, toeboards, and access ladders on scaffolds. It also covers inspection procedures and checklists for competent persons, as well as applicable regulations from the Building and Other Construction Workers Act and Factories Act.