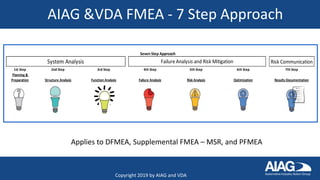
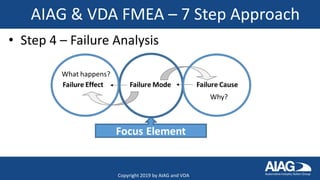
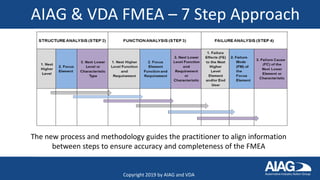
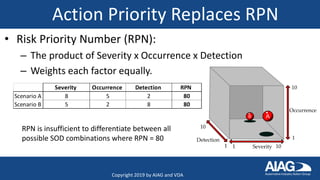
The document summarizes the new AIAG & VDA FMEA Handbook. It highlights that the handbook provides a consistent approach for automotive suppliers to conduct failure mode and effects analyses. It outlines the 7-step approach, new severity and occurrence tables, and action priority tables to evaluate risk. It also discusses the supplemental FMEA for monitoring and system response, new training options, and the timeline for adoption by automakers over the next few months.