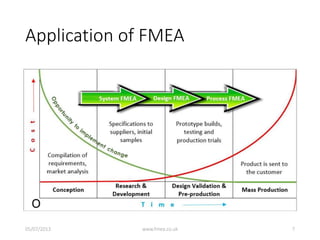
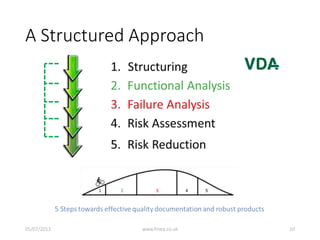
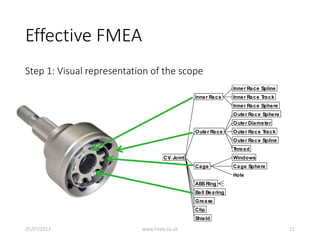
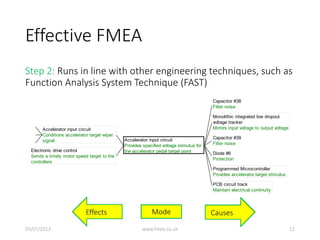
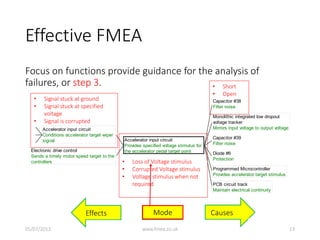
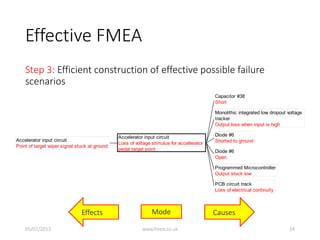
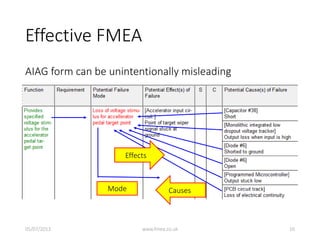
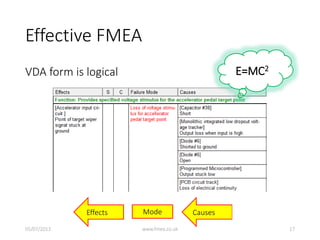
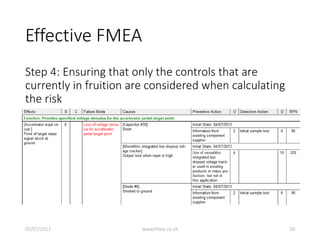
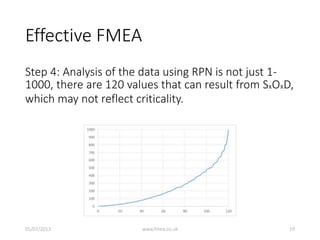
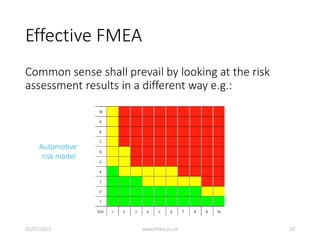
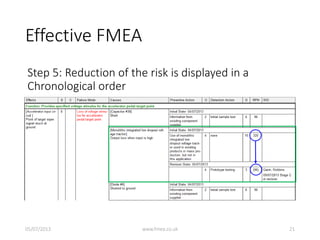
This document discusses Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). It begins by welcoming the audience in multiple languages and introducing the Advanced Powertrain Control Symposium topic of effectively applying FMEA. The document then defines FMEA, explains its origins and purpose, and discusses how to structure an effective FMEA process through cross-functional teams, facilitation, documentation, and risk analysis. It emphasizes using a logical structured approach and dedicated software to efficiently construct failure scenarios and analyze their risks and potential solutions.