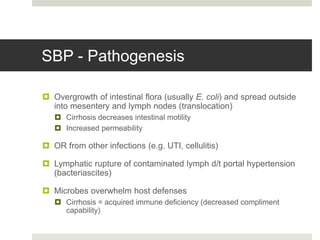
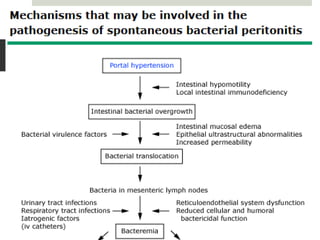
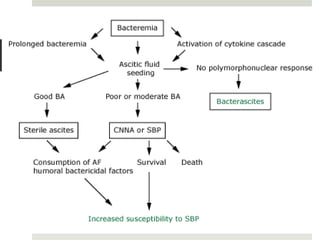
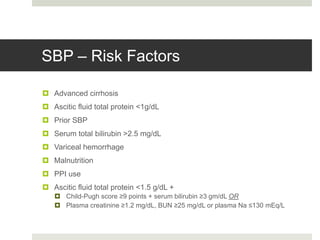
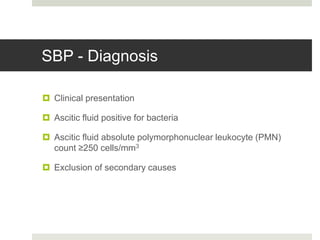
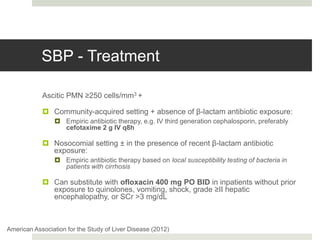
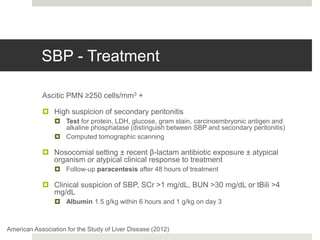
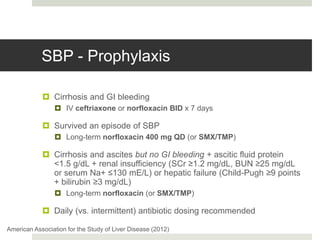
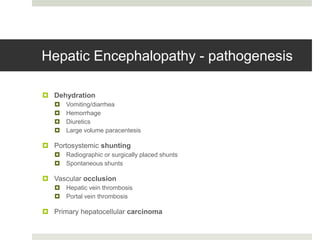
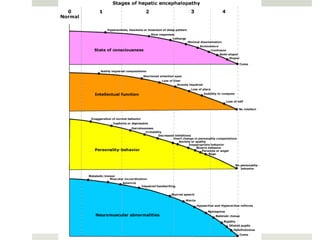
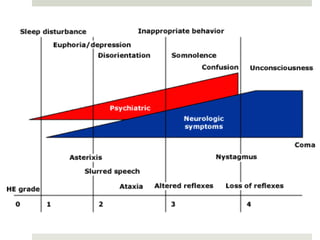
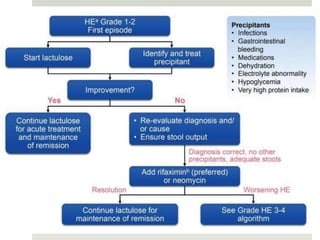
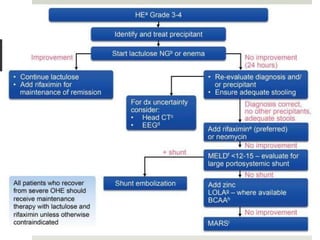
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is an infection of the ascitic fluid in cirrhotic patients without an evident surgical source. It occurs due to bacterial translocation from the intestines into the ascitic fluid due to decreased intestinal motility and immune defenses in cirrhosis. SBP is diagnosed when ascitic fluid has a polymorphonuclear leukocyte count over 250 cells/mm3. Treatment involves antibiotics like cefotaxime. Prophylaxis includes antibiotics for those with prior SBP or low ascitic fluid protein. Hepatic encephalopathy results from increased ammonia and other toxins reaching the brain in liver disease. It ranges from mild confusion to coma and is diagnosed clinically with lab