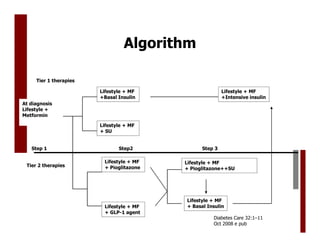
Saxagliptin is an oral DPP-4 inhibitor approved as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A clinical trial studied 768 adult patients with type 2 diabetes who had inadequate glycemic control on the sulfonylurea glibenclamide alone. Patients were randomized to add-on therapy with saxagliptin 2.5 mg or 5 mg daily or placebo, or to up-titrate glibenclamide from 7.5 mg to 10 mg daily. The primary endpoint was change in A1C from baseline after 24 weeks of treatment. Saxagliptin provided statistically significant reductions in A1C




















![HbA1c Mean Change From Baseline (LOCF) at
Week 102
SAXA 5mg + MET PBO + MET
Baseline HbA1c: 8.0 - 8.1%
0.4
Diabetes duration: 6.3 - 6.7 years
0.2
HbA1c (%) Mean ∆ From BL±SE
BL
0.0
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
BL 4 8 12 20 30 37 50 63 76 89 102
Weeks
Ravichandran S, et al. Diabetologia 2009; 52(Suppl. 1):S60 [Abstract] & Oral Presentation at EASD 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saxaslideshare-100827112720-phpapp01/85/Saxaslideshare-22-320.jpg)
![HbA1c Mean Change From Baseline (LOCF) at
Week 102
SAXA 5mg + MET PBO + MET
FPG 120-min PPG HbA1c <7%
SAXA (mg) SAXA (mg) SAXA (mg)
Dose 5+MET PBO+MET Dose 5+MET PBO+MET Dose 5+MET PBO+MET
n observed= 31 15 n observed= 46 24 n observed= 13 15
BL mean 179 175
12.0 10 50
9.0
-min
Percentage of patients Achieving
0.0
6.0 40 30
Adjusted Mean Change in 120-
Adjusted Mean Change in
HbA1c <7% (95% CI)
FPG (mg/dL) SE
PPG (mg/dL) SE
3.0 3.0
±
±
±
± ± -4 30
0.0
-20
-3.0
20 12
-6.0 -30
-9.0
10
-40
-12.0 -35
-15.0 -11 -50 0
SAXA: Saxagliptin; MET: Metformin; PBO: Placebo
Ravichandran S, et al. Diabetologia 2009; 52(Suppl. 1):S60 [Abstract] & Oral Presentation at EASD 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saxaslideshare-100827112720-phpapp01/85/Saxaslideshare-23-320.jpg)



















![45Version 1.3
Saxagliptin: Renal Impairment
• Mild Impairment, creatinine clearance [CrCl] ≤50
mL/min: No dosage adjustment
• Moderate or severe renal impairment, or with end-stage
renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis (creatinine
clearance [CrCl] ≤50 mL/min). Saxagliptin 2.5 mg is
recommended.
• Saxagliptin should be administered following hemodialysis.
Saxagliptin has not been studied in patients undergoing peritoneal
dialysis.
• Assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiation of
Saxagliptin and periodically thereafter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saxaslideshare-100827112720-phpapp01/85/Saxaslideshare-45-320.jpg)